J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med.
2013 Mar;17(1):47-49. 10.13104/jksmrm.2013.17.1.47.
MRI Imaging of Simultaneously Developed Endogenous Endophthalmitis and Brain Abscesses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea. hyukwonchang@korea.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea.
- 3Department of General Surgery, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 1426751
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/jksmrm.2013.17.1.47
Abstract
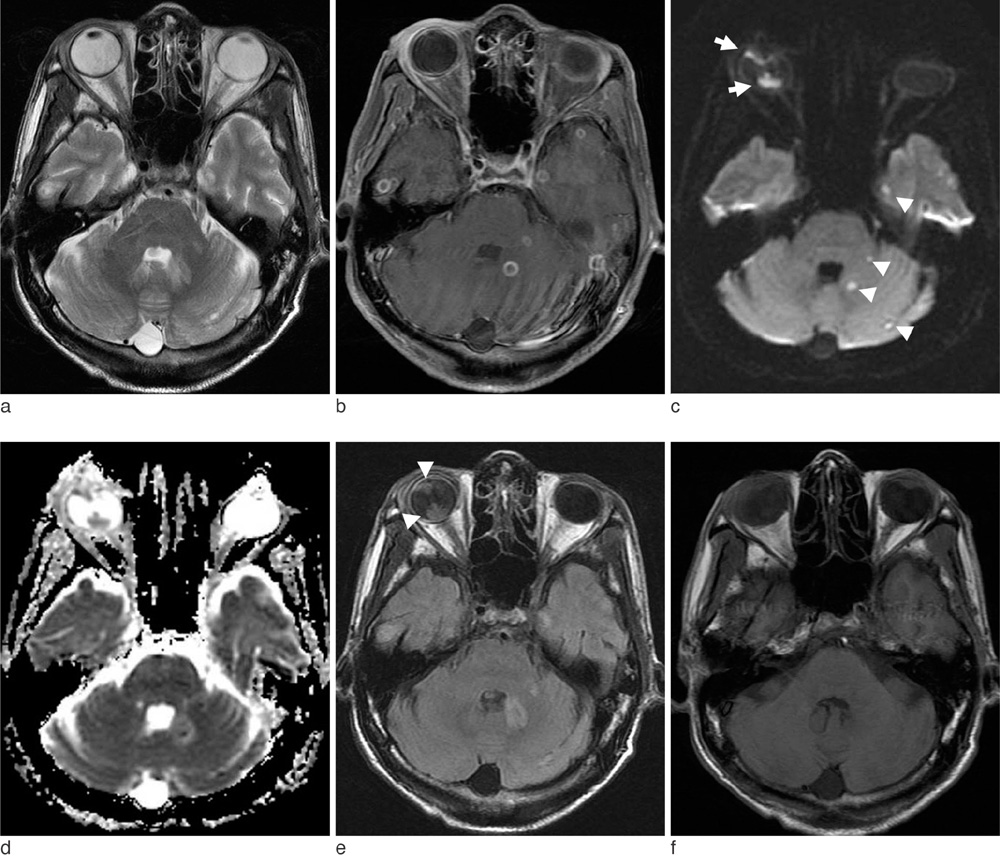
- Endogenous endophthalmitis is rare and refers to an intraocular inflammatory process that may result from exogenous or endogenous causes. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is useful for diagnosing endophthalmitis, and valuable to reach the diagnosis of brain abscess. We report here the MR findings of simultaneously developed endogenous endophthalmitis and brain abscesses.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Okada AA, Johnson RP, Liles Wc, D'Amico DJ, Baker AS. Endogenous bacterial endophthalmitis: report of a ten-year retrospective study. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:832–838.2. Wong JS, Chan TK, Lee HM, Chee SP. Endogenous bacterial endophthalmitis: an east asia experience and a reappraisal of a severe ocular affliction. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:1483–1491.3. Greenwald MJ, Wohl LG, Sell CH. Metastatic bacterial endophthalmitis: a contemporary reappraisal. Surv Ophthalmol. 1986; 31:81–101.4. Seale M, Lee WK, Daffy J, Tan Y, Trost N. Fulminant endogenous Klebsiella pneumoniae endophthalmitis: imaging findings. Emerg Radiol. 2007; 13:209–212.5. Osborn AG. Diagnostic imaging brain. Amirsys. 2004; I-8:24–27.6. Rumboldt Z, Moses C, Wieczerzynski U, Saini R. Diffusion-weighted imaging, apparent diffusion coefficients, and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging in endophthalmitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:1869–1872.7. Matsushita M, Hajiro K, Okazaki K, Takakuwa M, Nishio A. Endophthalmitis with brain, lung, and liver abscesses associated with an occult colon cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95:3664–3665.8. Yang CS, Tsai HY, Sung CS, Lin KH, Lee FL, Hsu WM. Endogenous Klebsiella endophthalmitis associated with pyogenic liver abscess. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:876–880.9. Lee CC, Chen CY, Chen FH, Zimmerman RA, Hsiao HS. Septic metastatic endophthalmitis from Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: CT and MR imaging characteristics-report of three cases. Radiology. 1998; 207:411–416.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endogenous Klebsiella Endophthalmitis Concurrent with Prostate and Perianal Abscesses
- Endogenous Candida Endophthalmitis with Bilateral Massive Submacular Abscess
- A Case of Renal Abscess associated with endogeneous endophthalmitis and septic pulmonary embolism by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Klebsiella pneumoniae Brain Abscess and Endophthalmitis after Acute Epiglottitis
- Endophthalmitis