Korean J Ophthalmol.
2012 Oct;26(5):319-323. 10.3341/kjo.2012.26.5.319.
Outcomes of Various Surgical Procedures on Acquired Lower Eyelid Epiblepharon in Thyroid Associated Ophthalmopathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. resourceful@hanmail.net
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1397481
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.5.319
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report the outcomes of acquired lower eyelid epiblepharon after various surgeries in thyroid associated ophthalmopathy (TAO) patients.
METHODS
A retrospective review of the medical records of 53 TAO patients with acquired lower eyelid epiblepharon between October 1999 and June 2011 was performed. Data were collected on demographics, type of lower eyelid epiblepharon, the detailed surgical history such as orbital decompression, retraction repair, or epiblepharon repair and surgical outcomes including follow-up period, recurrence of epiblepharon, and post-operative complications.
RESULTS
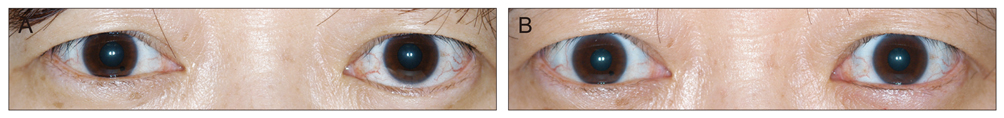
Among the 53 TAO patients with acquired lower eyelid epiblepharon, 25 eyes of 17 patients underwent surgical management; 6 eyes of orbital decompression, 1 eye of orbital decompression followed by retraction repair, 2 eyes of orbital decompression followed by epiblepharon repair, 6 eyes of lower eyelid retraction repair, and 10 eyes of epiblepharon repair. Twenty two lower eyelid epiblepharons (88%) were resolved after final surgical treatment without complication during mean 16.2 months (SD, +/-29.9 months) of follow up period; three of 6 epiblepharons that remained after orbital decompression underwent subsequent surgical management of retraction repair or epiblepharon repair, and epiblepharons were well-corrected. Mean amount of lower eyelid retraction was decreased from 1.68 mm (SD, +/-1.17 mm) to 0.29 mm (SD, +/-0.44 mm) after surgery, regardless of the type of surgery (n = 25, p < 0.000, Wilcoxon signed rank test).
CONCLUSIONS
Acquired lower eyelid epiblepharon of TAO should be managed sequentially according to the general serial order of surgical managements in TAO; orbital decompression, correction of lower eyelid retraction and epiblepharon repair. Acquired lower eyelid epiblepharon was well resolved after surgical management in consecutive order, especially after repair of the lower eyelid retraction with a graft, or lower eyelid epiblepharon repair. Decreased lower eyelid retraction with a resolution of epiblepharon after surgery implied that lower eyelid retraction was associated with lower eyelid epiblepharon.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Levitt JM. Epiblepharon and congenital entropion. Am J Ophthalmol. 1957. 44:112–113.2. Park RI, Meyer DR. Acquired lower eyelid epiblepharon. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996. 122:449–451.3. Jordan R. The lower-lid retractors in congenital entropion and epiblepharon. Ophthalmic Surg. 1993. 24:494–496.4. Park SW, Khwarg SI, Kim N, et al. Acquired lower eyelid epiblepharon in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy of Koreans. Ophthalmology. 2012. 119:390–395.5. Woo KI, Yi K, Kim YD. Surgical correction for lower lid epiblepharon in Asians. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000. 84:1407–1410.6. Sundar G, Young SM, Tara S, et al. Epiblepharon in East Asian patients: the Singapore experience. Ophthalmology. 2010. 117:184–189.7. Chang EL, Hayes J, Hatton M, Rubin PA. Acquired lower eyelid epiblepharon in patients with thyroid eye disease. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005. 21:192–196.8. Sung MS, Lee MJ, Choung HK, et al. Lower eyelid epiblepharon associated with lower eyelid retraction. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2010. 24:4–9.9. Moon JW, Choung HK, Khwarg SI. Correction of lower lid retraction combined with entropion using an ear cartilage graft in the anophthalmic socket. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005. 19:161–167.10. Khwarg SI, Choung HK. Epiblepharon of the lower eyelid: technique of surgical repair and quantification of excision according to the skin fold height. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 2002. 33:280–287.11. Almousa R, Sundar G. Acquired epiblepharon treated by lateral orbital and fat decompression. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2011. 18:80–81.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lower Eyelid Epiblepharon Associated with Lower Eyelid Retraction
- Clinical Outcomes of Lower Eyelid Epiblepharon Repair Combined with Minimal Incision of Medial Epicanthoplasty
- Etiology of Eyelid Retraction in Koreans
- The Effect of Levator Recession for Upper Eyelid Retraction in Patients with Thyroid-associated Ophthalmopathy
- Surgical Efficacyin the Upper and Lower Eyelid Retraction