Korean J Radiol.
2012 Oct;13(5):643-647. 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.5.643.
Hemorrhagic Cardiac Tamponade: Rare Complication of Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Imaging, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur 50603, Malaysia. kokbeng.loh@gmail.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur 50603, Malaysia.
- 3Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur 50603, Malaysia.
- KMID: 1392945
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.5.643
Abstract
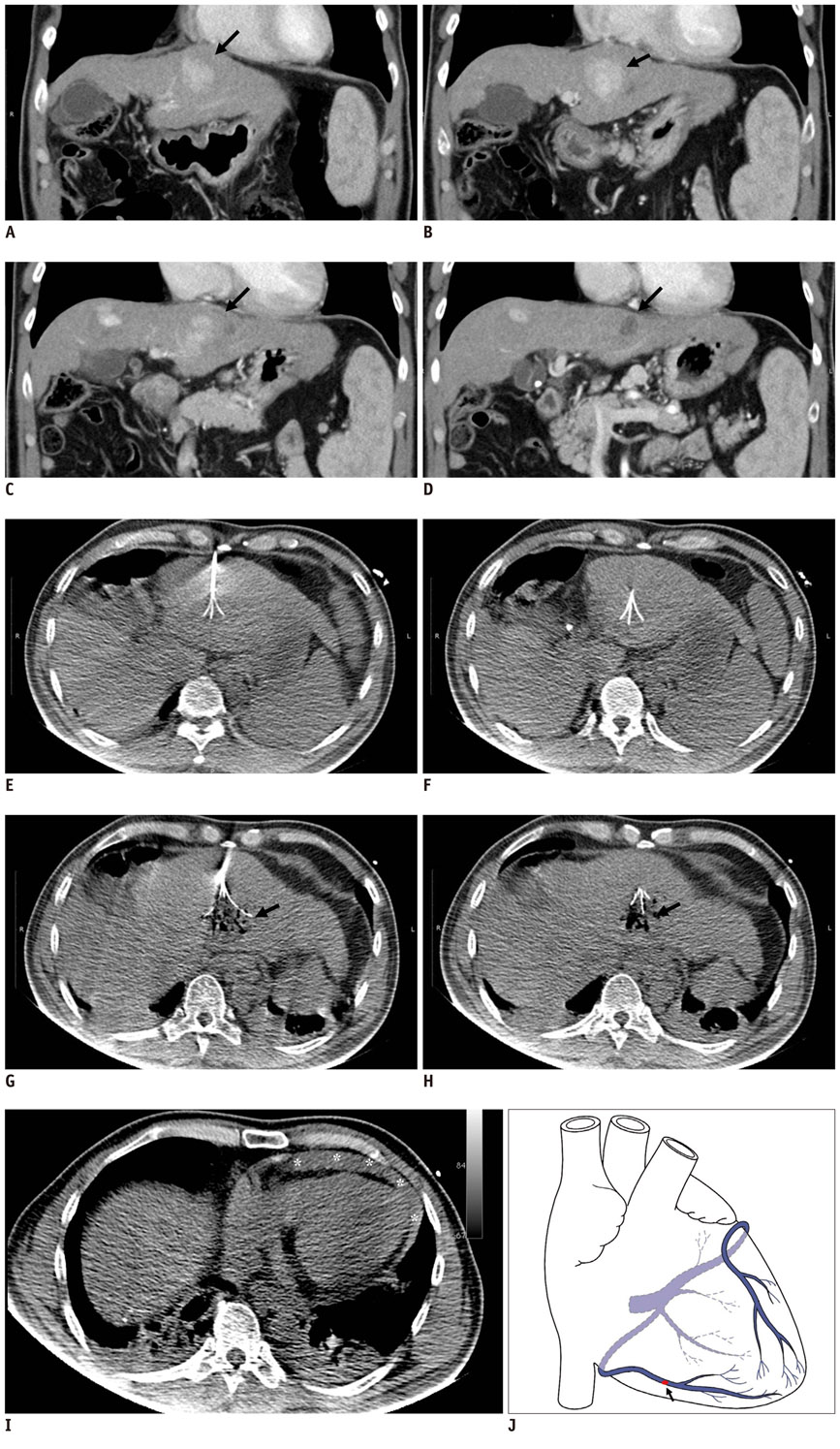
- Local treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been widely used in clinical practice due to its minimal invasiveness and high rate of cure. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is widely used because its treatment effectiveness. However, some serious complications can arise from percutaneous RFA. We present here a rare case of hemorrhagic cardiac tamponade secondary to an anterior cardiac vein (right marginal vein) injury during RFA for treatment of HCC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Omata M, Tateishi R, Yoshida H, Shiina S. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma by percutaneous tumor ablation methods: ethanol injection therapy and radiofrequency ablation. Gastroenterology. 2004. 127:S159–S166.2. Rhim H, Yoon KH, Lee JM, Cho Y, Cho JS, Kim SH, et al. Major complications after radio-frequency thermal ablation of hepatic tumors: spectrum of imaging findings. Radiographics. 2003. 23:123–134. discussion 134-136.3. Moumouh A, Hannequin J, Chagneau C, Rayeh F, Jeanny A, Weber-Holtzscherer A, et al. A tamponade leading to death after radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Radiol. 2005. 15:234–237.4. Gao J, Sun WB, Tong ZC, Ding XM, Ke S. Successful treatment of acute hemorrhagic cardiac temponade in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma during percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010. 123:1470–1472.5. Chen EA, Neeman Z, Lee FT, Kam A, Wood B. Thermal protection with 5% dextrose solution blanket during radiofrequency ablation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006. 29:1093–1096.6. Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Akeboshi M, Takeda K. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of liver neoplasms adjacent to the gastrointestinal tract after balloon catheter interposition. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003. 14:1183–1186.7. Buy X, Tok CH, Szwarc D, Bierry G, Gangi A. Thermal protection during percutaneous thermal ablation procedures: interest of carbon dioxide dissection and temperature monitoring. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009. 32:529–534.8. Steinke K, King J, Glenn D, Morris DL. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors: difficulty withdrawing the hooks resulting in a split needle. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2003. 26:583–585.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Microwave thermosphere versus radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Are we approaching the time to end the debate?
- A Case of Delayed Fatal Hemobilia after Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation is the best option for the local treatment of early hepatocellular carcinoma?
- Small Bowel Perforation after Percutaneous Ultrasound-guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Completely Ablated Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Percutaneous Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation