J Korean Acad Nurs.
2012 Apr;42(2):258-268. 10.4040/jkan.2012.42.2.258.
Development and Evaluation of a Program to Promote Self Management in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Inje University, Busan, Korea. jhyang@inje.ac.kr
- KMID: 1376067
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.2.258
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to identify the effects of the program to promote self management for patients with chronic hepatitis B.
METHODS
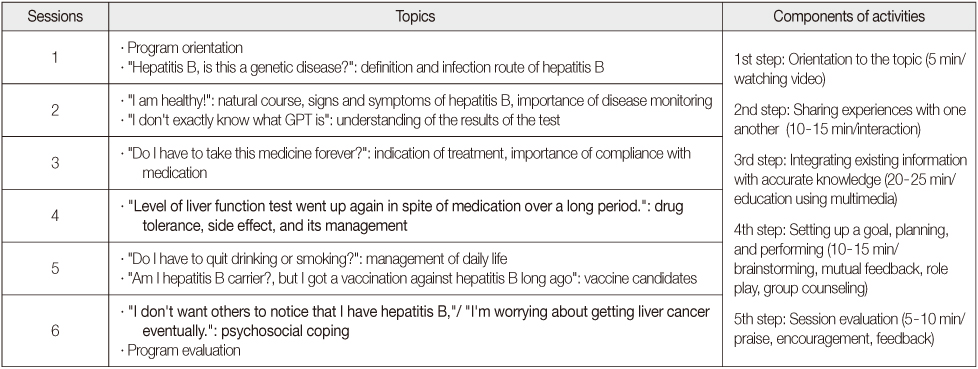
The research was a quasi-experimental design using a non-equivalent control group pre-post test. The participants were 61 patients, 29 in the experimental group and 32 in the control group. A pretest and 2 posttests were conducted to measure main variables. For the experimental group, the self-management program, consisting of counseling-centered activities in small groups, was given for 6 weeks. Data were analyzed using chi2, t-test, and repeated measures ANOVA with PASW statistics program.
RESULTS
There were statistically significant increases in knowledge, self-efficacy, active ways of coping, and self-management compliance but not in passive ways of coping in the experimental group compared to the control group over two different times.
CONCLUSION
The results of this study indicate that the self-management program is effective in increasing knowledge, self-efficacy, active ways of coping, and self-management compliance among patients with chronic hepatitis B. Therefore, it can be usefully utilized in the field of nursing for patients with chronic disease as a nursing intervention for people with chronic hepatitis B.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alizadeh A.H., Ranjbar M., Yadollahzadeh M. Patient concerns regarding chronic hepatitis B and C infection. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal. 2008. 14:1142–1147.2. Bandura A. Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. 1986. 1st ed. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.3. Chao S.D., Chang E.T., Le P.V., Prapong W., Kiernan M., So S.K.S. The Jade Ribbon Campaign: A model program for community outreach and education to prevent liver cancer in Asian Americans. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health. 2009. 11:281–290. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10903-007-9094-2.4. Choe J.H., Chan N., Do H.H., Woodall E., Lim E., Taylor V.M. Hepatitis B and liver cancer beliefs among Korean immigrants in Western Washington. Cancer. 2005. 104:2955–2958.5. Eum S.J. Effect of the structured education for knowledge of hepatitis B type and self-care behavior in chronic hepatitis B patients. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 1998. 5:65–79.6. Gifford A.L., Groessl E.J. Chronic disease self-management and adherence to HIV medications. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes. 2002. 31:S163–S166.7. What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B Foundation. 2009. Retrieved September 18, 2010. from http://www.hepb.org/hepb.8. Hill-Briggs F. Problem solving in diabetes self-management: A model of chronic illness self-management behavior. Annals of Behavioral Medicine. 2003. 25:182–193.9. Holman H.R., Lorig K. Schwarzer R, editor. Perceived self-efficacy in self-management of chronic disease. Self-efficacy: Thought control of action. 1992. Washington DC: Hemisphere;305–324.10. Hsu C.E., Zhang G., Yan F.A., Shang N., Le T. What made a successful hepatitis B program for reducing liver cancer disparities: An examination of baseline characteristics and educational intervention, infection status, and missing responses of at-risk Asian Americans. Journal of Community Health. 2010. 35:325–335. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10900-010-9238-5.11. Kang S.J. The relationships among self-efficacy, practice of self-care and quality of life in patients with liver cirrhosis. 2003. Jinju: Gyeongsang National University;Unpublished master's thesis.12. Kim J.H. Relations of perceived stress, cognitive set and coping behaviors to depression. 1987. Seoul: Seoul National University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.13. Kim K.S., Yi M., Choi E.O., Paik S.W., Kwak S., Kwon S. Quality of life and related factors in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2007. 14:331–339.14. 2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. 2010. Retrieved July 25, 2011. from http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr.15. Lazarus R.S., Folkman S. Stress appraisal and coping. 1984. New York, NY: Springer.16. Lee H., Baik S.Y. Health disparities or data disparities: Sampling issues in hepatitis B Virus infection among Asian American Pacific Islander studies. Applied Nursing Research. 2011. 24:e9–e15. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apnr.2009.12.005.17. Lee J.E., Kim S.S., Kim S., Han K.H., Kim S.H., Ji E.J., et al. Factors influencing health behavior of patients with chronic hepatitis B. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing. 2011. 23:20–30.18. Lee M.K., Han O.S., Lee Y.S. The study on psychological characteristics of chronic viral B hepatitis patients. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 1996. 35:320–328.19. Levy A.R., Kowdley K.V., Iloeje U., Tafesse E., Mukherjee J., Gish R., et al. The impact of chronic hepatitis B on quality of life: A multinational study of utilities from infected and uninfected persons. Value in Health. 2008. 11:527–538.20. Cancer mortality rate. National Cancer Information Center. 2011. Retrieved May 25, 2011. from http://www.cancer.go.kr/cms/statics/mortality/index.html.21. Nyamathi A., Liu Y., Marfisee M., Shoptaw S., Gregerson P., Saab S., et al. Effects of a nurse-managed program on hepatitis A and B vaccine completion among homeless adults. Nursing Research. 2009. 58:13–22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/NNR.0b013e3181902b93.22. Park M.J. Knowledge, health belief and preventive health behavior on hepatitis in hepatitis B carriers. 2002. Seoul: Yonsei University;Unpublished master's thesis.23. Perrillo R. Management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: Current perspectives for the nurse practitioner. Journal of the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners. 2006. 18:203–215.24. Sorrell M.F., Belongia E.A., Costa J., Gareen I.F., Grem J.L., Inadomi J.M., et al. National institutes of health consensus development conference statement: Management of hepatitis B. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2009. 150:104–110. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/hep.22946.25. Suh D.J. Current treatment in chronic hepatitis B. The Korean Journal of Hepatology. 2008. 14:S39–S43.26. Tan N.C., Cheah S.L., Teo E.K. A qualitative study of health-seeking behavior of hepatitis B carriers. Singapore Medical Journal. 2005. 46:6–10.27. Wallace J., McNally S., Richmond J., Hajarizadeh B., Pitts M. Managing chronic hepatitis B: A qualitative study exploring the perspectives of people living with chronic hepatitis B in Australia. Biomed Central Research Notes. 2011. 4:1–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1756 -0500-4-45.28. Wang W.L., Wang C.J., Tseng H.F. Comparing knowledge, health beliefs, and self-efficacy toward hepatitis B prevention among university students with different hepatitis B virus infectious statuses. The Journal of Nursing Research. 2009. 17:10–19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/JNR.0b013e3181999ca3.29. Yang J.H., Cho M.O., Lee H.O. Qualitative research investigating patterns of health care behavior among Korean patients with chronic hepatitis B. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2009. 39:805–817. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.6.805.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development and Evaluation of Health Care Providers' Counseling Manual in Mobile Application for Lifelong Health Care among Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- Factors Influencing Self-Management Compliance of Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- 2017 KASL clinical practice guidelines management of hepatitis C: Treatment of chronic hepatitis C
- KASL clinical practice guidelines for management of chronic hepatitis B
- Quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen predicts the antiviral response and hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis B