Recent Update of Embolization of Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Bleeding
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul 138-736, Korea. jhshin@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 1372865
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.S1.S31
Abstract
- Nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal (UGI) bleeding is a frequent complication with significant morbidity and mortality. Although endoscopic hemostasis remains the initial treatment modality, severe bleeding despite endoscopic management occurs in 5-10% of patients, necessitating surgery or interventional embolotherapy. Endovascular embolotherapy is now considered the first-line therapy for massive UGI bleeding that is refractory to endoscopic management. Interventional radiologists need to be familiar with the choice of embolic materials, technical aspects of embolotherapy, and the factors affecting the favorable or unfavorable outcomes after embolotherapy for UGI bleeding.
MeSH Terms
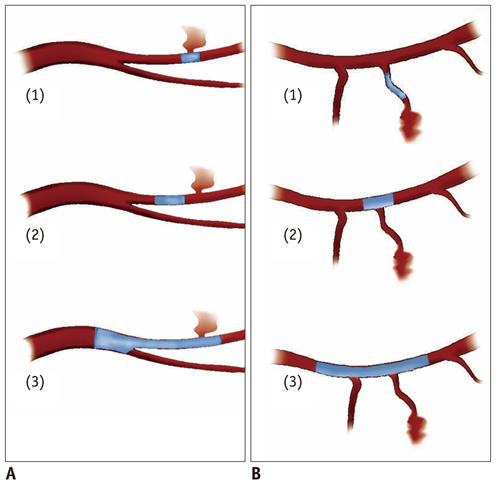
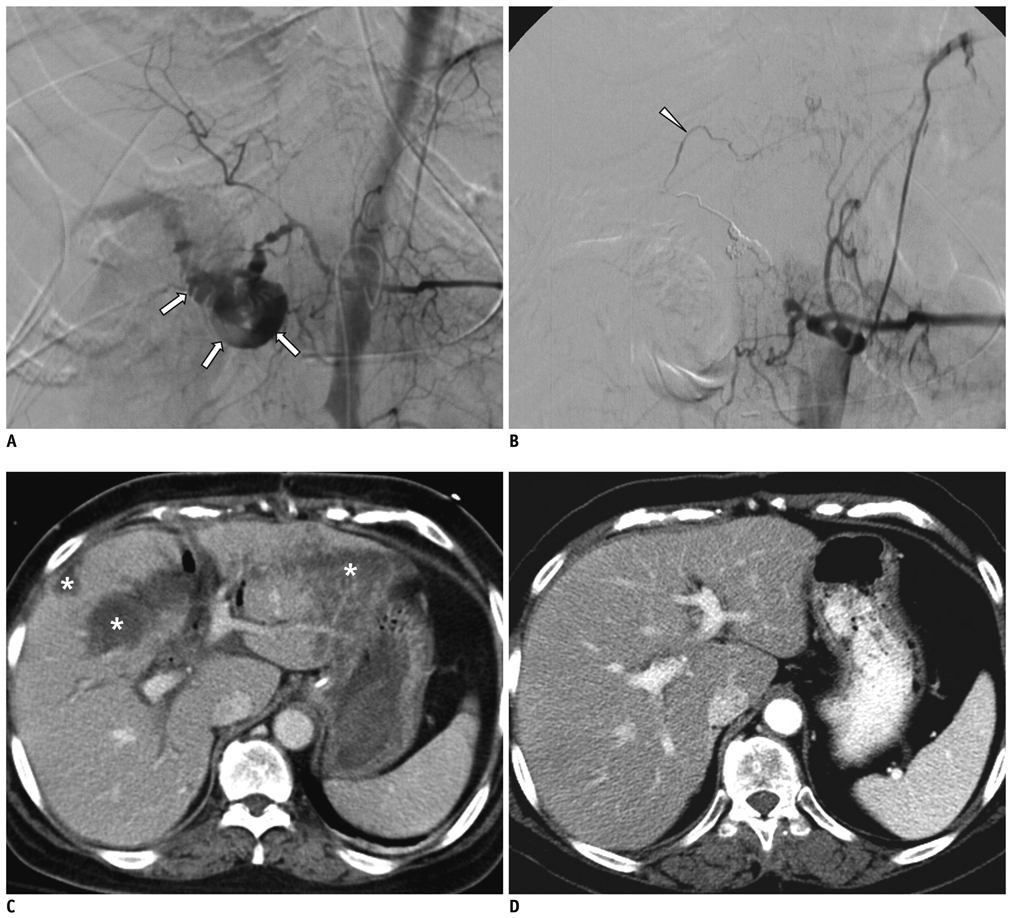
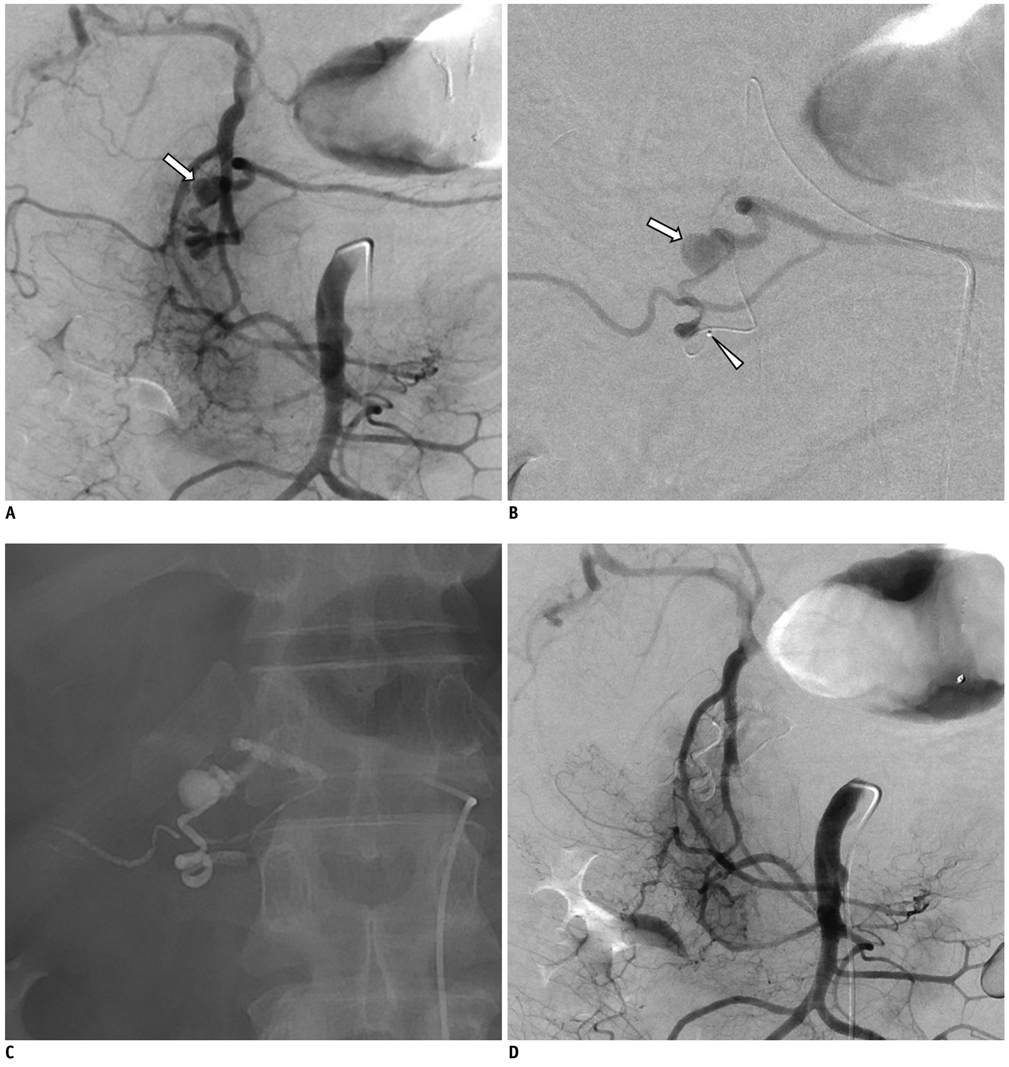
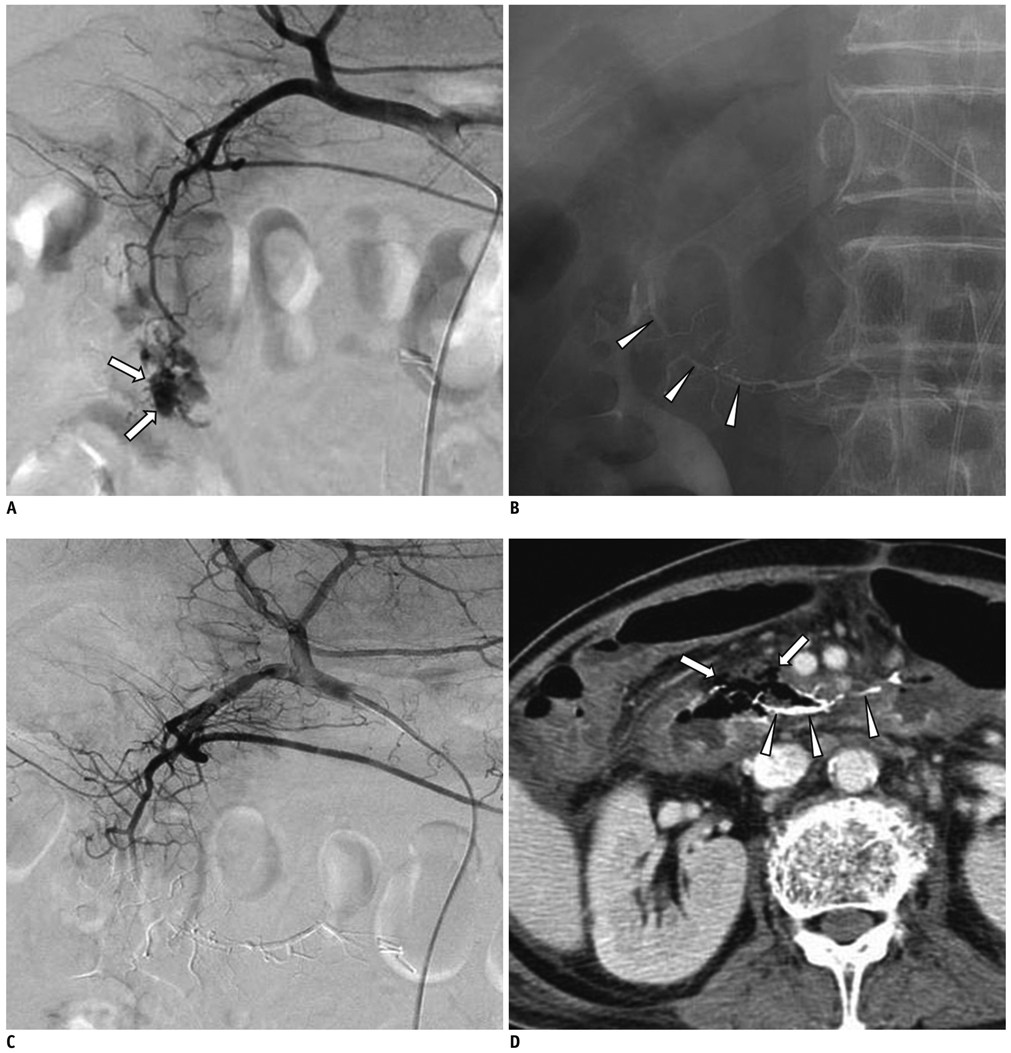
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Clinical Outcomes of Angiography and Transcatheter Arterial Embolization for Acute Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Analyses according to Bleeding Sites and Embolization Types
Soo Min Noh, Ji Hoon Shin, Ha Il Kim, Sun-Ho Lee, Kiju Chang, Eun Mi Song, Sung Wook Hwang, Dong-Hoon Yang, Byong Duk Ye, Seung-Jae Myung, Suk-Kyun Yang, Jeong-Sik Byeon
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2018;71(4):219-228. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2018.71.4.219.Massive Duodenal Bleeding after the Migration of Endovascular Coils into the Small Bowel
Chung-Jo Choi, Hyun Lim, Dong-Suk Kim, Yong-Seol Jeong, Sang-Young Park, Jeong-Eun Kim
Clin Endosc. 2019;52(6):612-615. doi: 10.5946/ce.2019.020.Highlights of International Digestive Endoscopy Network 2013
Kwang An Kwon, Il Ju Choi, Eun Young Kim, Seok Ho Dong, Ki Baik Hahm
Clin Endosc. 2013;46(5):425-435. doi: 10.5946/ce.2013.46.5.425.Refractory Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Role of Angiographic Intervention
Ji Hoon Shin
Clin Endosc. 2013;46(5):486-491. doi: 10.5946/ce.2013.46.5.486.
Reference
-
1. Mirsadraee S, Tirukonda P, Nicholson A, Everett SM, McPherson SJ. Embolization for non-variceal upper gastrointestinal tract haemorrhage: a systematic review. Clin Radiol. 2011. 66:500–509.2. Loffroy R, Rao P, Ota S, De Lin M, Kwak BK, Geschwind JF. Embolization of acute nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage resistant to endoscopic treatment: results and predictors of recurrent bleeding. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010. 33:1088–1100.3. Rösch J, Dotter CT, Brown MJ. Selective arterial embolization. A new method for control of acute gastrointestinal bleeding. Radiology. 1972. 102:303–330.4. Darcy M. Kandarpa K, Machan L, editors. Acute Gastrointestinal Arterial Bleeding. 2011. PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;233–239.5. Nusbaum M, Baum S. Raduographic demonstration of unknown sites of gastrointestinal bleeding. Surg Forum. 1963. 14:374–375.6. Krüger K, Heindel W, Dölken W, Landwehr P, Lackner K. Angiographic detection of gastrointestinal bleeding. An experimental comparison of conventional screen-film angiography and digital subtraction angiography. Invest Radiol. 1996. 31:451–457.7. Hastings GS. Angiographic localization and transcatheter treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding. Radiographics. 2000. 20:1160–1168.8. Burke SJ, Golzarian J, Weldon D, Sun S. Nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Eur Radiol. 2007. 17:1714–1726.9. Ryan JM, Key SM, Dumbleton SA, Smith TP. Nonlocalized lower gastrointestinal bleeding: provocative bleeding studies with intraarterial tPA, heparin, and tolazoline. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001. 12:1273–1277.10. Aina R, Oliva VL, Therasse E, Perreault P, Bui BT, Dufresne MP, et al. Arterial embolotherapy for upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage: outcome assessment. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001. 12:195–200.11. Loffroy R, Guiu B, D'Athis P, Mezzetta L, Gagnaire A, Jouve JL, et al. Arterial embolotherapy for endoscopically unmanageable acute gastroduodenal hemorrhage: predictors of early rebleeding. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. 7:515–523.12. Toyoda H, Nakano S, Kumada T, Takeda I, Sugiyama K, Osada T, et al. Estimation of usefulness of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate-lipiodol mixture in transcatheter arterial embolization for urgent control of life-threatening massive bleeding from gastric or duodenal ulcer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996. 11:252–258.13. Eriksson LG, Sundbom M, Gustavsson S, Nyman R. Endoscopic marking with a metallic clip facilitates transcatheter arterial embolization in upper peptic ulcer bleeding. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006. 17:959–964.14. Song JS, Kwak HS, Chung GH. Nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding: the usefulness of rotational angiography after endoscopic marking with a metallic clip. Korean J Radiol. 2011. 12:473–480.15. Gomes AS, Lois JF, McCoy RD. Angiographic treatment of gastrointestinal hemorrhage: comparison of vasopressin infusion and embolization. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986. 146:1031–1037.16. Gwon DI, Ko GY, Sung KB, Shin JH, Kim JH, Yoon HK. Endovascular management of extrahepatic artery hemorrhage after pancreatobiliary surgery: clinical features and outcomes of transcatheter arterial embolization and stent-graft placement. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011. 196:W627–W634.17. Song HH, Won YD, Kim YJ. Transcatheter N-butyl cyanoacrylate embolization of pseudoaneurysms. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010. 21:1508–1511.18. Holme JB, Nielsen DT, Funch-Jensen P, Mortensen FV. Transcatheter arterial embolization in patients with bleeding duodenal ulcer: an alternative to surgery. Acta Radiol. 2006. 47:244–247.19. Loffroy R, Guiu B, Cercueil JP, Lepage C, Latournerie M, Hillon P, et al. Refractory bleeding from gastroduodenal ulcers: arterial embolization in high-operative-risk patients. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008. 42:361–367.20. Larssen L, Moger T, Bjørnbeth BA, Lygren I, Kløw NE. Transcatheter arterial embolization in the management of bleeding duodenal ulcers: a 5.5-year retrospective study of treatment and outcome. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2008. 43:217–222.21. Poultsides GA, Kim CJ, Orlando R 3rd, Peros G, Hallisey MJ, Vignati PV. Angiographic embolization for gastroduodenal hemorrhage: safety, efficacy, and predictors of outcome. Arch Surg. 2008. 143:457–461.22. Koo HJ, Shin JH, Yoon HK, Ko GY, Gwon DI. Transcatheter arterial embolization of gastrointestinal tract bleeding with N-Bytyl-2-Cyanoacrylate in 71 patients at a single institution. Abstract of oral presentation of The 5th Meeting of Society of Gastrointestinal Intervention.23. Walsh RM, Anain P, Geisinger M, Vogt D, Mayes J, Grundfest-Broniatowski S, et al. Role of angiography and embolization for massive gastroduodenal hemorrhage. J Gastrointest Surg. 1999. 3:61–65. discussion 66.24. Schenker MP, Duszak R Jr, Soulen MC, Smith KP, Baum RA, Cope C, et al. Upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage and transcatheter embolotherapy: clinical and technical factors impacting success and survival. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001. 12:1263–1271.25. Jae HJ, Chung JW, Jung AY, Lee W, Park JH. Transcatheter arterial embolization of nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding with N-butyl cyanoacrylate. Korean J Radiol. 2007. 8:48–56.26. Kim JH, Shin JH, Yoon HK, Chae EY, Myung SJ, Ko GY, et al. Angiographically negative acute arterial upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding: incidence, predictive factors, and clinical outcomes. Korean J Radiol. 2009. 10:384–390.27. Morris DC, Nichols DM, Connell DG, Burhenne HJ. Embolization of the left gastric artery in the absence of angiographic extravasation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1986. 9:195–198.28. Lee HJ, Shin JH, Yoon HK, Ko GY, Gwon DI, Song HY, et al. Transcatheter arterial embolization in gastric cancer patients with acute bleeding. Eur Radiol. 2009. 19:960–965.29. Dempsey DT, Burke DR, Reilly RS, McLean GK, Rosato EF. Angiography in poor-risk patients with massive nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Surg. 1990. 159:282–286.30. Loffroy R, Guiu B, Cercueil JP, Krausé D. Endovascular therapeutic embolisation: an overview of occluding agents and their effects on embolised tissues. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2009. 7:250–263.31. Lang EK. Transcatheter embolization in management of hemorrhage from duodenal ulcer: long-term results and complications. Radiology. 1992. 182:703–707.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Embolization of procedure-related upper gastrointestinal bleeding
- Outcomes and complications of embolization for gastrointestinal bleeding
- Refractory Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Role of Angiographic Intervention
- A case of cytomegalovirus esophagitis associated with upper gastrointestinal bleeding
- Recurrent Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding from Gastro-Cystic Fistula and Pancreatic Pseudocyst Bleeding