J Korean Med Sci.
2012 May;27(5):484-488. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.5.484.
Serum Elastin-Derived Peptides and Anti-Elastin Antibody in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ysong@snu.ac.kr
- 2Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Department of Molecular Medicine and Biopharmaceutical Sciences, Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology and College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1372788
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.5.484
Abstract
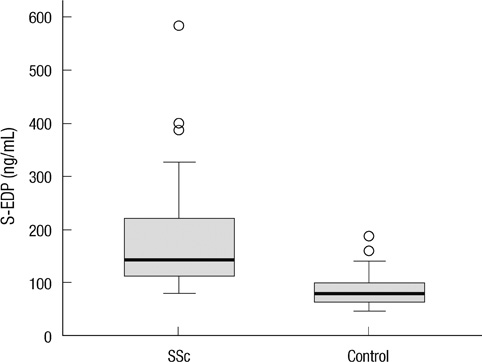
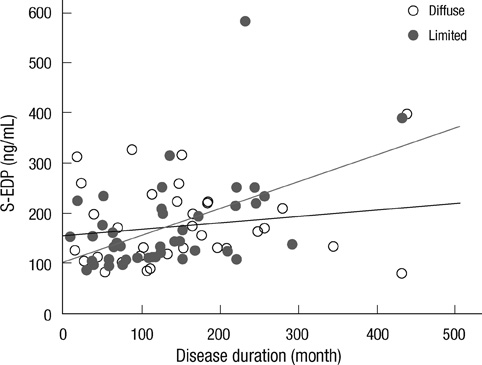
- The elastin metabolism in systemic sclerosis (SSc) has been known to be abnormal. The authors investigated relationship between the clinical manifestations of systemic sclerosis (SSc) and serum levels of soluble elastin-derived peptide (S-EDP) and anti-elastin antibodies. Serum samples were obtained from 79 patients with SSc and 79 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. Concentrations of serum S-EDP and anti-elastin antibodies were measured by ELISA. The serum concentrations of S-EDP in SSc patients were significantly higher than in healthy controls (median, 144.44 ng/mL vs 79.59 ng/mL, P < 0.001). Serum EDP concentrations were found to be correlated with disease duration in SSc (P = 0.002) and particularly in diffuse cutaneous SSc (P = 0.005). Levels of anti-elastin antibodies were found to be more elevated in SSc patients than in healthy controls (median, 0.222 U vs 0.191 U, P = 0.049), more increased in diffuse cutaneous SSc than limited cutaneous SSc (median, 0.368 U vs 0.204 U, P = 0.031). In addition, levels of anti-elastin antibodies were also found to be negatively associated with presence of anti-centromere antibody (P = 0.023). The S-EDP levels were not found to be correlated with levels of anti-elastin antibodies. The increased S-EDP and anti-elastin antibody levels and association with clinical and laboratory characteristics may reflect the abnormal metabolism in SSc.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Circulating Anti-Elastin Antibody Levels and Arterial Disease Characteristics: Associations with Arterial Stiffness and Atherosclerosis
Seung-Hyun Lee, Kihyuk Shin, Sungha Park, Seok-Min Kang, Donghoon Choi, Seung-Hyo Lee, Sang-Hak Lee
Yonsei Med J. 2015;56(6):1545-1551. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1545.
Reference
-
1. Gabrielli A, Avvedimento EV, Krieg T. Scleroderma. N Engl J Med. 2009. 360:1989–2003.2. Debelle L, Tamburro AM. Elastin: molecular description and function. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999. 31:261–272.3. Bizbiz L, Alpérovitch A, Robert L. Aging of the vascular wall: serum concentration of elastin peptides and elastase inhibitors in relation to cardiovascular risk factors. The EVA study. Atherosclerosis. 1997. 131:73–78.4. Fülöp T Jr, Wei SM, Robert L, Jacob MP. Determination of elastin peptides in normal and arteriosclerotic human sera by ELISA. Clin Physiol Biochem. 1990. 8:273–282.5. Pardo A, Selman M. Proteinase-antiproteinase imbalance in the pathogenesis of emphysema: the role of metalloproteinases in lung damage. Histol Histopathol. 1999. 14:227–233.6. Lindholt JS, Heickendorff L, Henneberg EW, Fasting H. Serum-elastin-peptides as a predictor of expansion of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 1997. 14:12–16.7. Petersen E, Wågberg F, Anquist KA. Serum concentrations of elastin-derived peptides in patients with specific manifestations of atherosclerotic disease. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2002. 24:440–444.8. Quaglino D Jr, Bergamini G, Boraldi E, Manzini E, Davidson J, Pasquali Ronchetti I. Connective tissue in skin biopsies from patients suffering systemic sclerosis. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol. 1996. 28:287–296.9. Pasquali Ronchetti I, Guerra D, Quaglino D Jr, Vincenzi D, Manzini E, Canossi B, Manzini CU. Dermal elastin and collagen in systemic sclerosis. Effect of D-penicillamine treatment. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1989. 7:373–383.10. Stone PJ, Korn JH, North H, Lally EV, Miller LC, Tucker LB, Strongwater S, Snider GL, Franzblau C. Cross-linked elastin and collagen degradation products in the urine of patients with scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1995. 38:517–524.11. Daskalova M, Taskov H, Dimitrova E, Baydanoff S. Humoral and cellular immune response to elastin in patients with systemic sclerosis. Autoimmunity. 1997. 25:233–241.12. Colburn KK, Langga-Shariffi E, Kelly GT, Malto MC, Sandberg LB, Baydanoff S, Green LM. Abnormalities of serum antielastin antibodies in connective tissue diseases. J Investig Med. 2003. 51:104–109.13. LeRoy EC, Black C, Fleischmajer R, Jablonska S, Krieg T, Medsger TA Jr, Rowell N, Wollheim F. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol. 1988. 15:202–205.14. Sivaprasad S, Chong NV, Bailey TA. Serum elastin-derived peptides in age-related macular degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. 46:3046–3051.15. Lee SH, Goswani S, Grudo A, Song LZ, Bandi V, Goodnight-White S, Green L, Hacken-Bitar J, Huh J, et al. Antielastin autoimmunity in tobacco smoking-induced emphysema. Nat Med. 2007. 13:567–569.16. Pasquali-Ronchetti I, Baccarani-Contri M. Elastic fiber during development and aging. Microsc Res Tech. 1997. 38:428–435.17. Rustin MH, Papadaki L, Rode J, Dowd PM. Elastic fibers in patients with systemic sclerosis. A morphological study. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1989. 416:115–120.18. Davis EC, Blattel SA, Mecham RP. Remodeling of elastic fiber components in scleroderma skin. Connect Tissue Res. 1999. 40:113–121.19. Crestani B, Seta N, Palazzo E, Rolland C, Venembre P, Dehoux M, Boutten A, Soler P, Dombret MC, Kahn MF, et al. Interleukin-8 and neutrophils in systemic sclerosis with lung involvement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994. 150:1363–1367.20. Hara T, Ogawa F, Yanaba K, Iwata Y, Muroi E, Komura K, Takenaka M, Shimizu K, Hasegawa M, Fujimoto M, et al. Elevated serum concentration is of polymorphonuclear neutrophilic leukocyte elastase in systemic sclerosis: association with pulmonary fibrosis. J Rheumatol. 2009. 36:99–105.21. Rabinovitch M. Elastase, remodeling of extracellular matrix, and pulmonary hypertension. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 1994. 15:199–206.22. Humbert M, Morrell NW, Archer SL, Stenmark KR, MacLean MR, Lang IM, Christman BW, Weir EK, Eickelberg O, Voelkel NF, et al. Cellular and molecular pathobiology of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004. 43:13S–24S.23. Senior RM, Griffin GL, Mecham RP. Chemotactic responses of fibroblasts to tropoelastin and elastin-derived peptides. J Clin Invest. 1982. 70:614–618.24. Hance KA, Tataria M, Ziporin SJ, Lee JK, Thompson RW. Monocytic chemotactic activity in human abdominal aortic aneurysms: role of elastin degradation peptides and the 67-kD cell surface elastin receptor. J Vasc Surg. 2002. 35:254–261.25. Robinet A, Fahem A, Cauchard JH, Huet E, Vincent L, Lorimier S, Antonicelli F, Soria C, Crepin M, Hornebeck W, et al. Elastin-derived peptides enhance angiogenesis by promoting endothelial cell migration and tubulogenesis through upregulation of MT1-MMP. J Cell Sci. 2005. 118:343–356.26. Mochizuki S, Brassart B, Hinek A. Signaling pathways transduced through the elastin receptor facilitate proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:44854–44863.27. Debret R, Antonicelli F, Theill A, Hornebeck W, Bernard P, Guenounou M, Le Naour R. Elastin-derived peptides induced a T-helper type 1 polarization of human blood lymphocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005. 25:1353–1358.28. Colburn KK, Kelly GT, Malto MC, Sandberg LB, Boucek RJ. Serum anti-tropo: anti-alpha-elastin antibody ratio assessing elastin turnover in scleroderma. Clin Rheumatol. 1992. 11:206–210.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Circulating Anti-Elastin Antibody Levels and Arterial Disease Characteristics: Associations with Arterial Stiffness and Atherosclerosis
- Three dimensional structures of pulmonary elastin; airway vs vascular elastin
- Development of elastin layers in the aortic wall of human fetuses
- The Effect of Nicotine on Elastin Gene Expression in Cultured Skin Fibroblasts
- Detection of microdeletion of elastin gene in patients with Williams syndrome and their family by fluorescent in situ hybridization and evaluation of clinical manifestations