Korean J Urol.
2008 Nov;49(11):1051-1054. 10.4111/kju.2008.49.11.1051.
Myxofibrosarcoma of Bladder
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Maryknoll Hospital, Busan, Korea. LJOURO@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 1328181
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2008.49.11.1051
Abstract
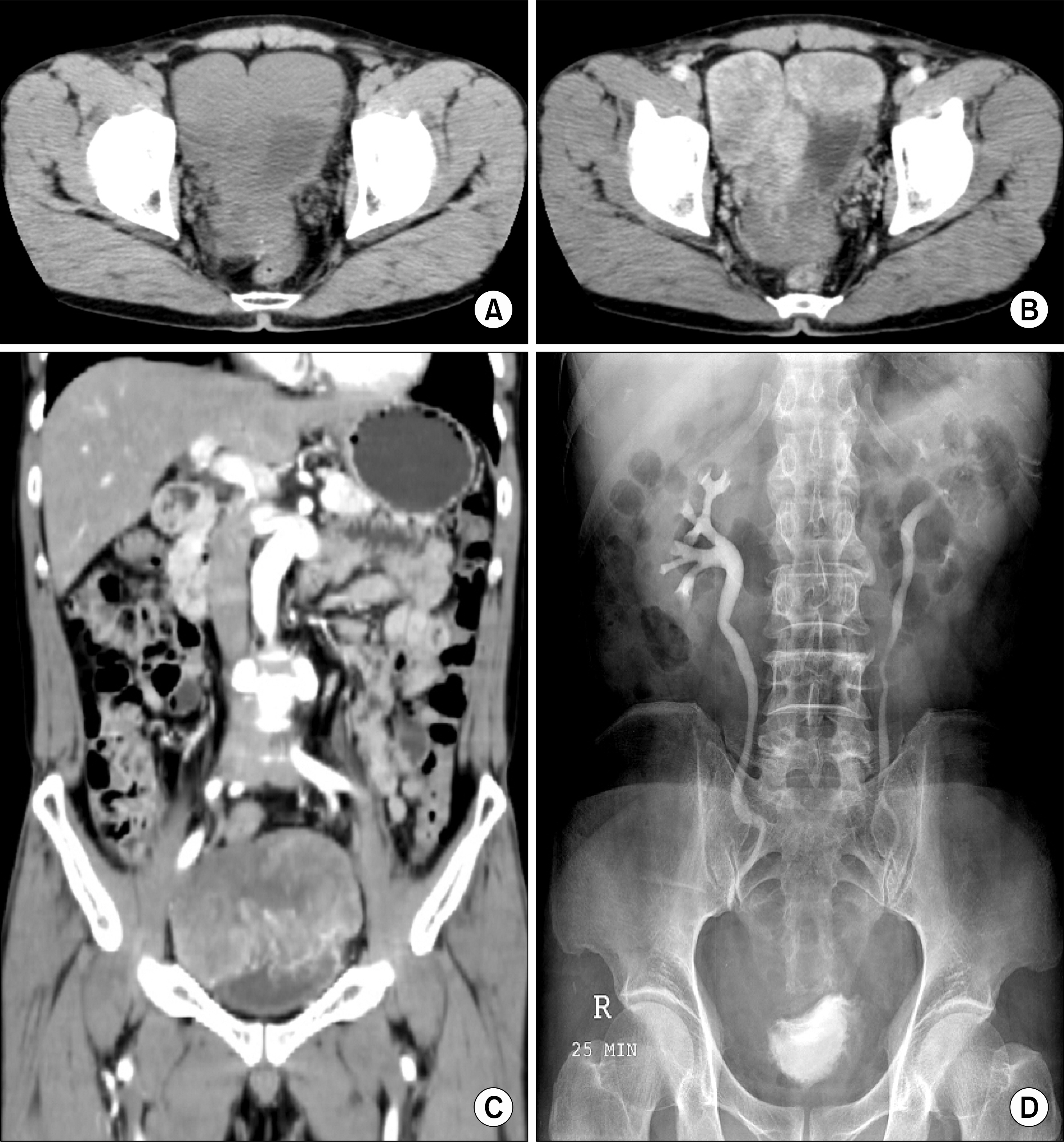
- Myxofibrosarcoma is also known as a myxoid variant of malignant fibrous histiocytoma, and this is one of the most common sarcomas in the extremities of elderly people; it is characterized by a high frequency of local recurrence. We herein report on a case of myxofibrosarcoma of the bladder. A 58-year-old man was referred to our hospital because of microscopic hematuria. Computed tomography(CT) and intravenous pyelography(IVP) showed a 12x7cm sized bladder mass in the pelvic cavity. The cystoscopic finding shows a protruding mass at the dome and posterior wall of the bladder. After exploratory laparotomy and tissue frozen biopsy were done, radical cystectomy and uretero-ileo-cutaneous anastomosis were then carried out. The diagnosis of the tumor was confirmed by histopathological examination. The myxofibrosarcoma of the bladder was completely excised, and there was no evidence of recurrence after 10 months of follow-up.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Angervall L, Kindblom LG, Merck C. Myxofibrosarcoma. A study of 30 cases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1977; 85A:127–40.2. Kindblom LG, Merck C, Svendsen P. Myxofibrosarcoma: a pathologico-anatomical, microangiographic and angiographic correlative study of eight cases. Br J Radiol. 1977; 50:876–87.
Article3. Weiss WS, Goldblum JR. Enzinger and Weiss's soft tissue tumors. 4th ed.St. Louis: Mosby;2001. p. 422–5.4. Fletcher CD, Unni KK, Mertens F. Pathology and genetics of tumors of soft tissue and bone. Kleihues P, Sobin LH, editors. editors.World health organization classification of tumors. Lyon: IARC Press;2002. p. 102–3.5. Mentzel T, Calonje E, Wadden C, Camplejohn RS, Beham A, Smith MA, et al. Myxofibrosarcoma. Clinicopathologic analysis of 75 cases with emphasis on the low-grade varient. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996; 20:391–405.6. Lee SK, Moon KH, Ji YH, Hwang HH, Choo HS, Kim YM, et al. Solitary fibrous tumor as misdiagnosed as bladder cancer. Korean J Urol. 2007; 48:1319–21.
Article7. Wang M, Khurana RN, Parikh JG, Hidayat AA, Rao NA. Myxofibrosarcoma of the orbit: an underrecognized entity? Case report and review of the literature. Ophthalmology. 2007; 115:1237–40.8. Lazaros GA, Matsakas EP, Madas JS, Toli DI, Nikas DJ, Kershaw MA, et al. Primary myxofibrosarcoma of the left atrium: case report and review of the literature. Angiology. 2008; 2:[Epub ahead of print].
Article9. Wada T, Hasegawa T, Nagoya S, Kawaguchi S, Kaya M, Ishii S. Myxofibrosarcoma with an infiltrative growth pattern: a case report. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2000; 30:458–62.
Article10. Fujimura T, Okuyama R, Terui T, Okuno K, Masu A, Masu T, et al. Myxofibrosarcoma (myxoid malignant fibrous histiocytoma) showing cutaneous presentation: report of two cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2005; 32:512–5.
Article