J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Aug;22(4):687-692. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.4.687.
Survival Rate Changes in Neonates with Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia and its Contributing Factors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimhans@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1127088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.4.687
Abstract
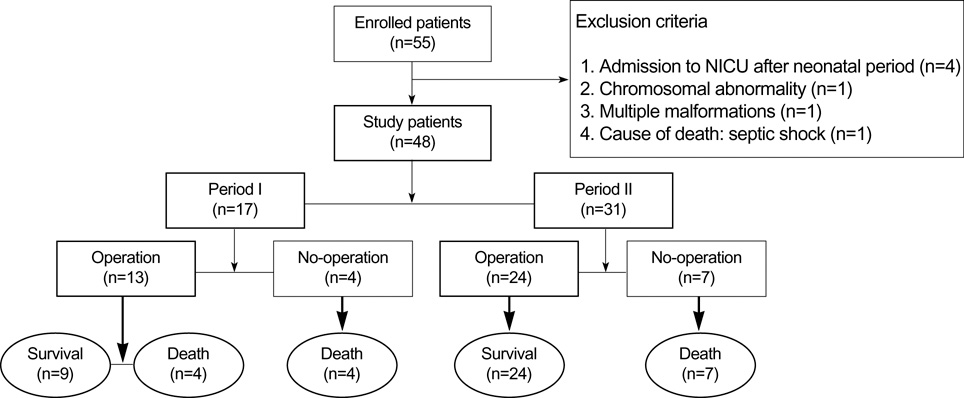
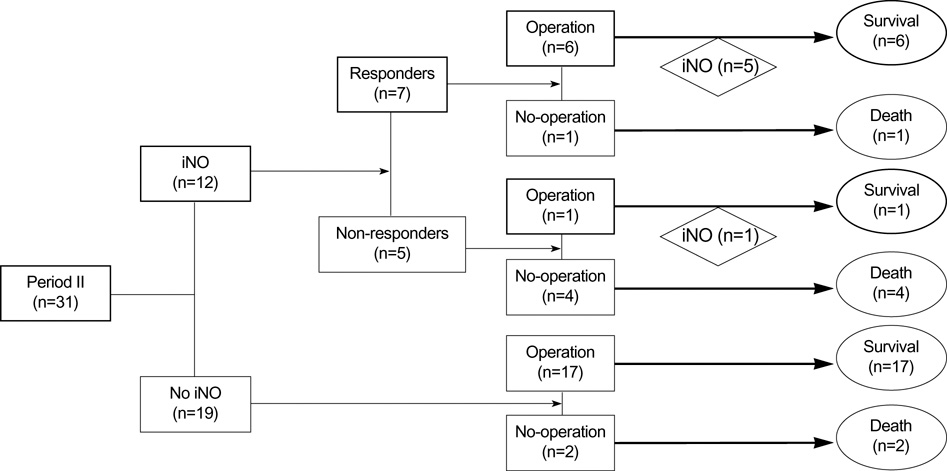
- The purpose of this study was to demonstrate survival rate changes after the introduction of inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) therapy, and to identify the factors that influence these changes in neonates with a congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) at a single center. A total of 48 neonates were divided into two groups based on the time of admission, i.e., into period I (P1; n=17; before the introduction of iNO therapy) and period II (P2; n=31; after the introduction of iNO therapy). Survival rates of the 48 neonates showed a tendency to increase from 53% during P1 to 77% during P2, but without a statistical significance, but a significant difference was found between survival rates during the two periods after adjusting for initial clinical characteristics, when the postoperative survival rate increased significantly from 69% for P1 to 100% for P2. The mean duration of preoperative respiratory management was significantly longer for P2 than for P1. Seven of 12 patients who received preoperative iNO therapy due to persistent pulmonary hypertension or refractory preductal hypoxemia in P2 survived after operation. We speculate that a management strategy based on iNO therapy and delayed operation, rather than differences between the initial clinical characteristics of the two study groups, might partially contribute to the observed improvements in postoperative and overall survival rates in neonates with CDH.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Weinstein S, Stolar CJ. Newborn surgical emergency, congenital diaphragmatic hernia and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1993. 40:1315–1333.2. Clark RH, Hardin WD Jr, Hirschl RB, Jaksic T, Lally KP, Langham MR Jr, Wilson JM. Current surgical management of congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a report from the congenital diaphragmatic hernia study group. J Pediatr Surg. 1998. 33:1004–1009.
Article3. Beresford MW, Shaw NJ. Outcome of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2000. 30:249–256.
Article4. The Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Study Group. Estimating disease severity of congenital diaphragmatic hernia in the first 5 minutes of life. J Pediatr Surg. 2001. 36:141–145.5. The Neonatal Inhaled Nitric Oxide Study Group (NINOSG). NINOSG). Inhaled nitric oxide and hypoxic respiratory failure in infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatrics. 1997. 99:838–845.6. Lally KP. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2002. 14:486–490.
Article7. Downard CD, Wilson JM. Current therapy of infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Semin Neonatol. 2003. 8:215–221.
Article8. Dimitriou G, Greenough A, Kavvadia V, Devane SP, Rennie JM. Outcome predictors in nitric oxide treated preterm infants. Eur J Pediatr. 1999. 158:589–591.
Article9. Dillon E, Renwick M, Wright C. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: antenatal detection and outcome. Br J Radiol. 2000. 73:360–365.10. Dubois A, Storme L, Jaillard S, Truffert P, Riou Y, Rakza T, Pierrat V, Gottrand F, Pruvot FR, Leclerc F, Lequien P. Congenital hernia of the diaphragm. A retrospective study of 123 cases recorded in the Neonatal Medicine Department, URHC in Lille between 1985 and 1996. Arch Pediatr. 2000. 7:132–142.11. Reickert CA, Hirschl RB, Atkinson JB, Dudell G, Georgeson K, Glick P, Greenspan J, Kays D, Klein M, Lally KP, Mahaffey S, Ryckman F, Sawin R, Short BL, Stolar CJ, Thompson A, Wilson JM. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia survival and use of extracorporeal life support at selected level III nurseries with multimodality support. Surgery. 1998. 123:305–310.
Article12. Skari H, Bjornland K, Haugen G, Egeland T, Emblem R. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a meta-analysis of mortality factors. J Pediatr Surg. 2000. 35:1187–1197.
Article13. Boloker J, Bateman DA, Wung JT, Stolar CJ. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia in 120 infants treated consecutively with permissive hypercapnea/spontaneous respiration/elective repair. J Pediatr Surg. 2002. 37:357–366.
Article14. Bedoyan JK, Blackwell SC, Treadwell MC, Johnson A, Klein MD. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: associated anomalies and antenatal diagnosis. Pediatr Surg Int. 2004. 20:170–176.
Article15. Bétrémieux P, Gaillot T, de la Pintiere A, Beuchee A, Pasquier L, Habonimana E, Le Bouar G, Branger B, Milon J, Fremond B, Wodey E, Odent S, Poulain P, Pladys P. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: prenatal diagnosis permits immediate intensive care with high survival rate in isolated cases. A population-based study. Prenat Diagn. 2004. 24:487–493.
Article16. Adzick NS, Vacanti JP, Lillehei CW, O'Rourke PP, Crone RK, Wilson JM. Fetal diaphragmatic hernia: ultrasound and clinical outcome in 38 cases. J Pediatr Surg. 1989. 24:654–658.17. Albanese CT, Lopoo J, Goldstein RB, Filly RA, Feldstein VA, Calen PW, Jennings RW, Farrell JA, Harrison MR. Fetal liver position and perinatal outcome for congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Prenat Diagn. 1998. 18:1138–1142.
Article18. Laudy JA, Van Gucht M, Van Dooren MF, Wladimiroff JW, Tibboel D. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: an evaluation of the prognostic value of the lung-to-head ratio and other prenatal parameters. Prenat Diagn. 2003. 23:634–639.
Article19. Kinsella JP, Truog WE, Walsh WF, Goldberg RN, Bancalari E, Mayock DE, Redding GJ, deLemos RA, Sardesai S, McCurnin DC, Moreland SG, Cutter GR, Abman SH. Randomized, multicenter trial of inhaled nitric oxide and high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in severe, persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. J Pediatr. 1997. 131:55–62.
Article20. Bohn DJ, Pearl R, Irish MS, Glick PL. Postnatal management of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Clin Perinatol. 1996. 23:843–872.
Article21. Henneberg SW, Jepsen S, Andersen PK, Pedersen SA. Inhalation of nitric oxide as a treatment of pulmonary hypertension in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg. 1995. 30:853–855.
Article22. Karamanoukian HL, Glick PL, Zayek M, Steinhorn RH, Zwass MS, Fineman JR, Morin FC 3rd. Inhaled nitric oxide in congenital hypoplasia of the lungs due to diaphragmatic hernia or oligohydramnios. Pediatrics. 1994. 94:715–718.23. Okuyama H, Kubota A, Oue T, Kuroda S, Ikegami R, Kamiyama M, Kitayama Y, Yagi M. Inhaled nitric oxide with early surgery improves the outcome of antenatally diagnosed congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg. 2002. 37:1188–1190.
Article24. Reyes C, Chang LK, Waffarn F, Mir H, Warden MJ, Sills J. Delayed repair of congenital diaphragmatic hernia with early high-frequency oscillatory ventilation during preoperative stabilization. J Pediatr Surg. 1998. 33:1010–1014.25. Stege G, Fenton A, Jaffray B. Nihilism in the 1990s: the true mortality of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatrics. 2003. 112:532–535.
Article26. Okazaki T, Kohno S, Hasegawa S, Urushihara N, Yoshida A, Kawano S, Saito A, Tanaka Y. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: efficacy of ultrasound examination in its management. Pediatr Surg Int. 2003. 19:176–179.
Article27. Bagolan P, Casaccia G, Crescenzi F, Nahom A, Trucchi A, Giorlandino C. Impact of a current treatment protocol on outcome of high-risk congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg. 2004. 39:313–318.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Unilateral Congenital Diaphragmatic Eventration Mimicking Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
- A Case of Sliding Hiatal Hernia associated with Bochdalek Hernia Repair
- Cardiac Arrest Due to Unrecognized Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
- Congenital diaphragmatic Hernia Associated with Hypoplasia of the Lung
- Clinical Study of Congenital Diaphragmatic Diseases in Neonates and Infants