J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Aug;22(4):629-632. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.4.629.
Cardiac Autonomic Function Evaluated by the Heart Rate Turbulence Method was not Changed in Obese Patients without Co-morbidities
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, School of Medicine, Afyon Kocatepe University, Afyonkarahisar, Turkey. alavsar@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Afyon Kocatepe University, Afyonkarahisar, Turkey.
- KMID: 1127077
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.4.629
Abstract
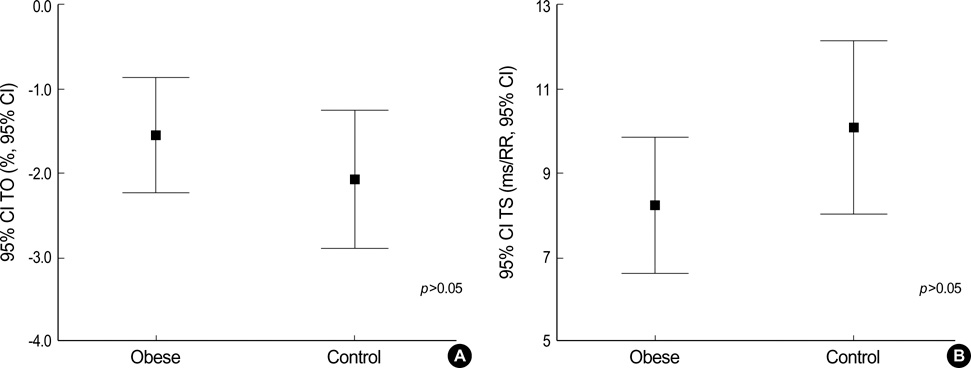
- Obese subjects are more prone to sudden deaths and arrhythmias than non-obese subjects. Heart rate turbulence (HRT) impairment reflects cardiac autonomic dysfunction, in particular impaired baroreflex sensitivity and reduced parasympathetic activity. Our aim was to evaluate the cardiac autonomic function in obesity by the HRT method. Ninety obese subjects and 112 healthy subjects were included in the study. Twenty-four hours ambulatory electrocardiograms were recorded and Holter recordings were analyzed. HRT parameters, turbulence onset (TO) and turbulence slope (TS), were calculated with HRT View Version 0.60-0.1 software program. HRT were calculated in 43 obese and 43 control subjects who had at least one ventricular premature beat in their Holter recordings. We excluded 47 obese patients and 69 control subjects who showed no ventricular premature beats in their Holter recordings from the statistical analysis. There were no significant differences in TO and TS between obese and control subjects (TO obese: -1.6+/-2.2%, TO control: -2.1+/-2.6%, p>0.05; TS obese: 8.2+/-5.2, TS control: 10.1+/-6.7, p>0.05, respectively). HRT parameters seem to be normal in obese patients without comorbidities.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Laederach-Hofmann K, Mussgay L, Ruddel H. Autonomic cardiovascular regulation in obesity. J Endocrinol. 2000. 164:59–66.
Article2. Ferrannini E, Camastra S, Gastaldelli A, Maria Sironi A, Natali A, Muscelli E, Mingrone G, Mari A. beta-cell function in obesity: effects of weight loss. Diabetes. 2004. 53:S26–S33.
Article3. Kannel WB, Plehn JF, Cupples LA. Cardiac failure and sudden death in the Framingham Study. Am Heart J. 1988. 115:869–875.
Article4. Gutin B, Howe C, Johnson MH, Humphries MC, Snieder H, Barbeau P. Heart rate variability in adolescents: relations to physical activity, fitness, and adiposity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005. 37:1856–1863.
Article5. Lee ZS, Critchley JA, Ko GT, Anderson PJ, Thomas GN, Young RP, Chan TY, Cockram CS, Tomlinson B, Chan JC. Urinary epinephrine and norepinephrine interrelations with obesity, insulin, and the metabolic syndrome in Hong Kong Chinese. Metabolism. 2001. 50:135–143.
Article6. Poehlman ET, Gardner AW, Goran MI, Arciero PJ, Toth MJ, Ades PA, Calles-Escandon J. Sympathetic nervous system activity, body fatness, and body fat distribution in younger and older males. J Appl Physiol. 1995. 78:802–806.
Article7. La Rovere MT. Baroreflex sensitivity as a new marker for risk stratification. Z Kardiol. 2000. 89:44–50.
Article8. Karason K, Molgaard H, Wikstrand J, Sjostrom L. Heart rate variability in obesity and the effect of weight loss. Am J Cardiol. 1999. 83:1242–1247.
Article9. Emdin M, Gastaldelli A, Muscelli E, Macerata A, Natali A, Camastra S, Ferrannini E. Hyperinsulinemia and autonomic nervous system dysfunction in obesity: effects of weight loss. Circulation. 2001. 103:513–519.10. Barthel P, Schneider R, Bauer A, Ulm K, Schmitt C, Schomig A, Schmidt G. Risk stratification after acute myocardial infarction by heart rate turbulence. Circulation. 2003. 108:1221–1226.
Article11. Mrowka R, Persson PB, Theres H, Patzak A. Blunted arterial baroreflex causes "pathological" heart rate turbulence. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2000. 279:R1171–R1175.
Article12. Guzik P, Schmidt G. A phenomenon of heart-rate turbulence, its evaluation, and prognostic value. Card Electrophysiol Rev. 2002. 6:256–261.13. Priori SG, Aliot E, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Bossaert L, Breithardt G, Brugada P, Camm AJ, Cappato R, Cobbe SM, Di Mario C, Maron BJ, McKenna WJ, Pedersen AK, Ravens U, Schwartz PJ, Trusz-Gluza M, Vardas P, Wellens HJ, Zipes DP. Task Force on Sudden Cardiac Death of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2001. 22:1374–1450.
Article14. World Health Organization. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2000. 894:1–253.15. Amador N, Guizar JM, Malacara JM, Perez-Luque E, Paniagua R. Sympathetic activity and response to ACE inhibitor (enalapril) in normotensive obese and non-obese subjects. Arch Med Res. 2004. 35:54–58.
Article16. Wang W, Ma R. Cardiac sympathetic afferent reflexes in heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2000. 5:57–71.17. Schwartz PJ, Zipes DP. Zipes DP, Jalife editors, editors. Autonomic modulation of Cardiac Arrhythmias. Cardiac electrophysiology: From Cell to Bedside. 1995. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;300–314.18. La Rovere MT, Pinna GD, Hohnloser SH, Marcus FI, Mortara A, Nohara R, Bigger JT Jr, Camm AJ, Schwartz PJ. ATRAMI Investigators. Autonomic Tone and Reflexes After Myocardial Infarcton. Baroreflex sensitivity and heart rate variability in the identification of patients at risk for life-threatening arrhythmias: implications for clinical trials. Circulation. 2001. 103:2072–2077.19. Hombach V, Osterhues HH, Hoher M, Scharf B, Kochs M. Risk stratification after myocardial infarct. Z Kardiol. 2000. 89:75–86.20. Hirsch J, Leibel RL, Mackintosh R, Aguirre A. Heart rate variability as a measure of autonomic function during weight change in humans. Am J Physiol. 1991. 261:R1418–R143.
Article21. Poirier P, Hernandez TL, Weil KM, Shepard TJ, Eckel RH. Impact of diet-induced weight loss on the cardiac autonomic nervous system in severe obesity. Obes Res. 2003. 11:1040–1047.
Article22. Antelmi I, de Paula RS, Shinzato AR, Peres CA, Mansur AJ, Grupi CJ. Influence of age, gender, body mass index, and functional capacity on heart rate variability in a cohort of subjects without heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 2004. 93:381–385.
Article23. Matsumoto T, Miyawaki C, Ue H, Kanda T, Yoshitake Y, Moritani T. Comparison of thermogenic sympathetic response to food intake between obese and non-obese young women. Obes Res. 2001. 9:78–85.
Article24. Lin LY, Lai LP, Lin JL, Du CC, Shau WY, Chan HL, Tseng YZ, Huang SK. Tight mechanism correlation between heart rate turbulence and baroreflex sensitivity: sequential autonomic blockade analysis. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2002. 13:427–431.
Article25. Koyama J, Watanabe J, Yamada A, Koseki Y, Konno Y, Toda S, Shinozaki T, Miura M, Fukuchi M, Ninomiya M, Kagaya Y, Shirato K. Evaluation of heart-rate turbulence as a new prognostic marker in patients with chronic heart failure. Circ J. 2002. 66:902–907.
Article26. Barthel P, Schmidt G, Schneider R, Ulm K, Malik M, Schömig A. Heart rate turbulence in patients with and without autonomic dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999. 3:Suppl A. 136A.27. Osman F, Franklyn JA, Daykin J, Chowdhary S, Holder RL, Sheppard MC, Gammage MD. Heart rate variability and turbulence in hyperthyroidism before, during, and after treatment. Am J Cardiol. 2004. 94:465–469.
Article28. Ortak J, Weitz G, Wiegand UK, Bode F, Eberhardt F, Katus HA, Richardt G, Schunkert H, Bonnemeier H. Changes in heart rate, heart rate variability, and heart rate turbulence during evolving reperfused myocardial infarction. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2005. 28:S227–S232.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationship between Heart Rate Turbulence and Heart Rate Variability in Korean Adults with Structurally Normal Heart
- The Relationship Between Hemispheric Lesion and Autonomic Function by Using Beat-to-Beat Heart Rate Variation
- Cardiac Vagal Tone as an Index of Autonomic Nervous Function in Healthy Newborn and Premature Infants
- Heart Rate Variability and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
- Anesthesia and autonomic nervous system: is measurement of heart rate variability, blood pressure variability and baroreflex sensitivity useful in anesthesiology specialty?