J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Feb;27(2):207-210. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.2.207.
A Case of Isolated Light Chain Deposition Disease in the Duodenum
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hemato-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. epark@cau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1120160
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.2.207
Abstract
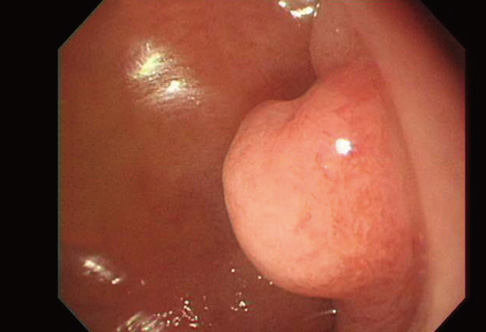
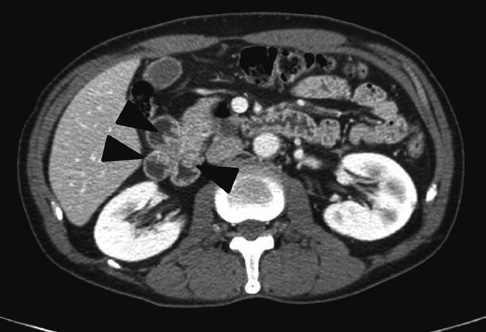
- Light chain deposition disease (LCDD) is a rare disorder associated with a clonal proliferation of plasma cells, which synthesize abnormal monoclonal immunoglobulin light chains. LCDD is characterized by systemic deposition of light chains in various organs, with the kidneys being most commonly affected. There have been few reports of isolated LCDD. We report a rare case of LCDD limited to a duodenal polyp. A 63-yr-old man visited our hospital for health screening without symptoms in 2009. On gastrofiberscopy, a duodenal polyp was observed. The biopsy showed diffuse infiltration by atypical plasma cells, which were positive for kappa-type light chains by immunohistochemistry. While the patient refused further management, we could find no evidence of recurrence until 2 yr after the initial diagnosis. It has been reported that isolated LCDD has relatively good prognosis compared to systemic LCDD. However, treatment for this disease has not been established yet.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pozzi C, D'Amico M, Fogazzi GB, Curioni S, Ferrario F, Pasquali S, Quattrocchio G, Rollino C, Segagni S, Locatelli F. Light chain deposition disease with renal involvement: clinical characteristics and prognostic factors. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003. 42:1154–1163.2. Buxbaum JN, Chuba JV, Hellman GC, Solomon A, Gallo GR. Monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease: light chain and light and heavy chain deposition diseases and their relation to light chain amyloidosis. Clinical features, immunopathology, and molecular analysis. Ann Intern Med. 1990. 112:455–464.3. Popovic M, Tavcar R, Glavac D, Volavsek M, Pirtosek Z, Vizjak A. Light chain deposition disease restricted to the brain: the first case report. Hum Pathol. 2007. 38:179–184.4. Piard F, Yaziji N, Jarry O, Assem M, Martin L, Bernard A, Jacquot JP, Justrabo E. Solitary plasmacytoma of the lung with light chain extracellular deposits: a case report and review of the literature. Histopathology. 1998. 32:356–361.5. Rostagno A, Frizzera G, Ylagan L, Kumar A, Ghiso J, Gallo G. Tumoral non-amyloidotic monoclonal immunoglobulin light chain deposits ('aggregoma'): presenting feature of B-cell dyscrasia in three cases with immunohistochemical and biochemical analyses. Br J Haematol. 2002. 119:62–69.6. Zidar N, Zver S, Jurcic V. Extraosseus plasmacytoma of the pharynx with localized light chain deposition. Case report. Pathol Oncol Res. 2010. 16:249–252.7. Buxbaum J, Gallo G. Nonamyloidotic monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease. Light-chain, heavy-chain, and light- and heavy-chain deposition diseases. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1999. 13:1235–1248.8. Lin J, Markowitz GS, Valeri AM, Kambham N, Sherman WH, Appel GB, D'Agati VD. Renal monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease: the disease spectrum. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001. 12:1482–1492.9. McKenna RW, Kyle RA, Kuehl WM, Grogan TM, Harris NL, Coupland RW. Plasma cell neoplasms in WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2008. Lyon:10. Khoor A, Myers JL, Tazelaar HD, Kurtin PJ. Amyloid-like pulmonary nodules, including localized light-chain deposition: clinicopathologic analysis of three cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004. 121:200–204.11. Rivest C, Turgeon PP, Senecal JL. Lambda light chain deposition disease presenting as an amyloid-like arthropathy. J Rheumatol. 1993. 20:880–884.12. Pozzi C, Locatelli F. Kidney and liver involvement in monoclonal light chain disorders. Semin Nephrol. 2002. 22:319–330.13. Faa G, Van Eyken P, De Vos R, Fevery J, Van Damme B, De Groote J, Desmet VJ. Light chain deposition disease of the liver associated with AL-type amyloidosis and severe cholestasis. A case report and literature review. J Hepatol. 1991. 12:75–82.14. Buxbaum JN, Chuba JV, Hellmann GC, Solomon A, Gallo GR. Monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease: light chain and light and heavy chain deposition disease and their relation to light chain amyloidosis. Ann Intern Med. 1990. 112:455–464.15. Heilman RL, Velosa JA, Holley KE, Offord KP, Kyle RA. Long-term follow-up and response to chemotherapy in patients with light-chain deposition disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1992. 20:34–41.16. Royer B, Arnulf B, Martinez F, Roy L, Flageul B, Etienne I, Ronco P, Brouet JC, Fermand JP. High dose chemotherapy in light chain or light and heavy chain deposition disease. Kidney Int. 2004. 65:642–648.17. Lorenz EC, Gertz MA, Fervenza FC, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Hayman SR, Gastineau DA, Leung N. Long-term outcome of autologous stem cell transplantation in light chain deposition disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008. 23:2052–2057.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Seven Cases of Monoclonal Gammopathies Involving Kidney
- De Novo Light Chain Deposition Disease in Long-term Survived Renal Allograft
- A Case of Localized Amyloid Light-Chain Amyloidosis in the Small Intestine
- Monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance from the perspective of nephrologists
- A Case of lambda-type Light Chain Deposition Disease Manifested as Acute Renal Failure and Multiple Organ Dysfunction by Embolic Events