Korean J Radiol.
2003 Jun;4(2):124-129. 10.3348/kjr.2003.4.2.124.
Detection of Hepatic VX2 Tumors in Rabbits: Comparison of Conventional US and Phase-Inversion Harmonic US During the Liver-Specific Late Phase of Contrast Enhancement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Chonbuk, Korea. leejm@radcom.snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine and Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1118815
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2003.4.2.124
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
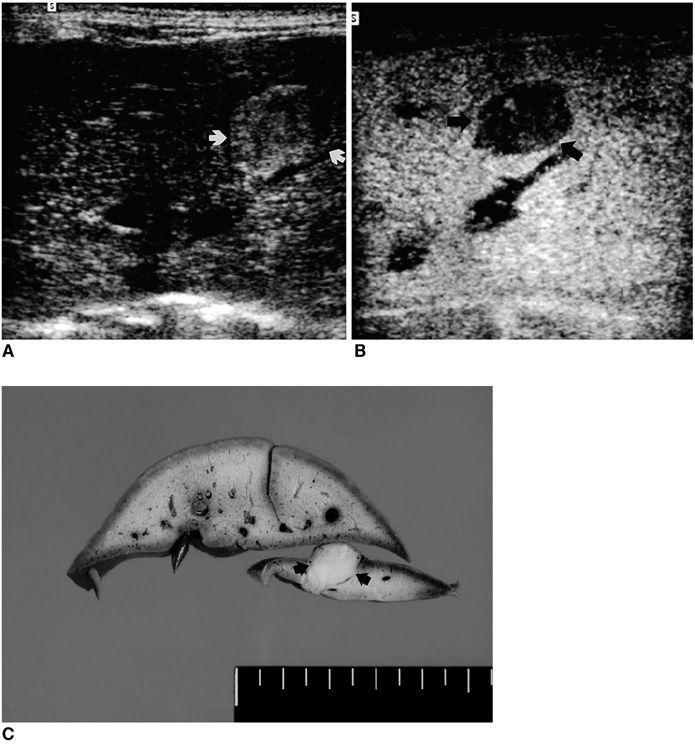
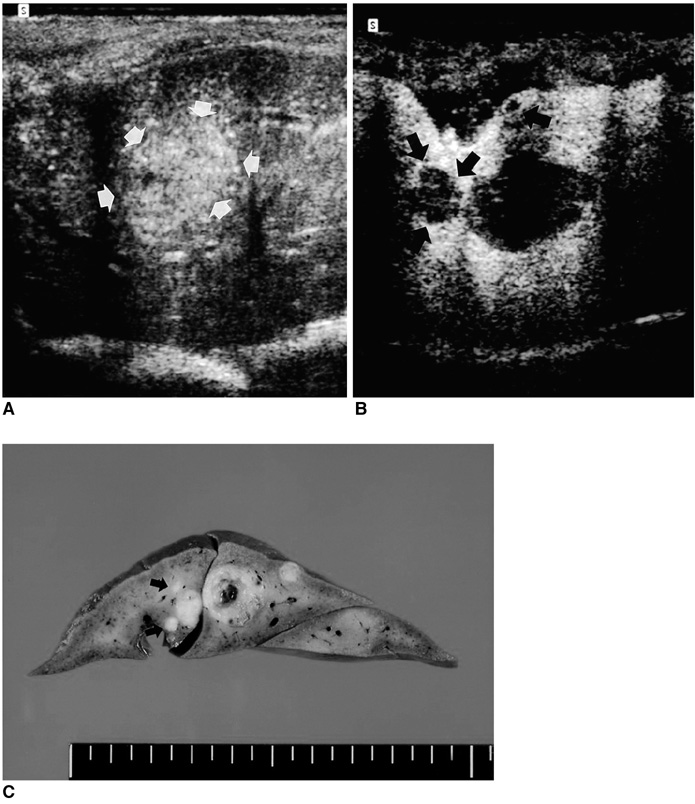
To compare phase-inversion sonography during the liver-specific phase of contrast enhancement using a microbubble contrast agent with conventional B-mode sonography for the detection of VX2 liver tumors. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Twenty-three rabbits, 18 of which had VX2 liver tumor implants, received a bolus injection of 0.6 g of Levovist (200 mg/ml). During the liver-specific phase of this agent, they were evaluated using both conventional sonography and contrast-enhanced phase-inversion harmonic imaging (CE-PIHI). Following sacrifice of the animals, pathologic analysis was performed and the reference standard thus obtained. The conspicuity, size and number of the tumors before and after contrast administration, as determined by a sonographer, were compared between the two modes and with the pathologic findings. RESULTS: CE-PIHI demonstrated marked hepatic parenchymal enhancement in all rabbits. For VX2 tumors detected at both conventional US and CE- PIHI, conspicuity was improved by contrast-enhanced PIHI. On examination of gross specimens, 52 VX2 tumors were identified. Conventional US correctly detected 18 of the 52 (34.6%), while PIHI detected 35 (67.3%) (p < 0.05). In particular, conventional US detected only three (8.3%) of the 36 tumors less than 10 mm in diameter, but CE-PIHI detected 19 such tumors (52.8%) (p < 0.05). CONCLUSION: Compared to conventional sonography, PIHI performed during the liver-specific phase after intravenous injection of Levovist is markedly better at detecting VX2 liver tumors.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bluemke DA, Paulson EK, Choti MA, DeSena S, Calvien PA. Detection of hepatic lesions in candidates for surgery. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 175:1653–1658.2. Alderson PO, Adams DF, McNeil BJ, et al. Computed tomography, ultrasound, and scintigraphy of the liver in patients with colon or breast carcinoma: a prospective comparison. Radiology. 1983. 149:225–230.3. Soyer PH, Levesque M, Elias D, Zeitoun G, Roche A. Detection of liver metastases from colorectal cancer: comparison of intraoperative ultrasound and CT during arterial portography. Radiology. 1992. 183:541–544.4. Wernecke K, Rummeny E, Bongartz G, et al. Detection of hepatic masses in patients with carcinoma: comparative sensitivities of sonography, CT, and MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991. 157:731–739.5. Clarke MP, Kane RA, Steele G Jr, et al. Prospective comparison of preoperative imaging and intraoperative ultrasonography in the detection of liver tumors. Surgery. 1989. 106:849–855.6. Ohlsson B, Tranberg KG, Lundstedt C, Ekberg H, Hederstrom E. Detection of hepatic metastases in colorectal cancer: a prospective study of laboratory and imaging methods. Eur J Surg. 1993. 159:275–281.7. Ferrucci JT. Liver tumor imaging: current concepts. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990. 155:473–484.8. Burns PN, Wilson SR, Simpson DH. Pulse-inversion imaging of liver blood flow: improved method for characterizing focal masses with microbubble contrast. Invest Radiol. 2000. 35:58–71.9. Wilson SR, Burns PN, Muradali D, Wilson JA, Lai X. Harmonic hepatic US with microbubble contrast agent: initial experience showing improved characterization of hemangioma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and metastases. Radiology. 2000. 215:153–161.10. Blomley MJK, Albrecht T, Cosgrove D, Jayaram V, Butler-Barnes J, Eckersley R. Stimulated acoustic emission in liver parenchyma with Levovist (letter). Lancet. 1998. 351:568.11. Blomley MJK, Albrecht T, Cosgrove DO, et al. The use of stimulated acoustic emission to image a late liver-specific phase of Levovist: an investigation in normal volunteers and in patients with and without liver disease. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1999. 25:1341–1352.12. Blomley MJK, Albrecht T, Cosgrove DO, et al. Improved imaging of liver metastases with stimulated acoustic emission in the late phase of enhancement with the US contrast agent SHU 508A: early experience. Radiology. 1999. 210:409–416.13. Forsberg F, Liu JB, Merton DA, Rawool NM, Johnson DK, Goldberg BB. Gray-scale second harmonic imaging of acoustic emission signals improves detection of liver tumors in rabbits. J Ultrasound Med. 2000. 19:557–563.14. Forsberg F, Piccoli CW, Rawool NM, Merton DA, Mitchell DG, Goldberg BB. Hepatic tumor detection: MR imaging and conventional US versus pulse-inversion harmonic US of NC100100 during its reticuloendothelial system-specific phase. Radiology. 2002. 222:824–829.15. Albrecht T, Hoffmann CW, Schettler S, et al. B-mode enhancement at phase-inversion US with air-based microbubble contrast agent: initial experience in humans. Radiology. 2000. 216:273–278.16. Albrecht T, Hoffmann CW, Schmitz SA, et al. Phase-inversion sonography during the liver-specific late phase of contrast enhancement: improved detection of liver metastases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001. 176:1191–1198.17. Lang TM, Secic M. How to report statistics in medicine: annotated guidelines for authors, editors, and reviewers. 2000. 1st ed. Philadelphia: ACP;127–132.18. Finlay IG, McArdle CS. Effect of occult hepatic metastases on survival after curative resection for colorectal carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 1983. 85:596–599.19. Hughes KS, Sugarbaker PH. Rosenberg SA, editor. Treatment of metastatic liver tumors. Surgical cure of metastatic cancer. 1987. Philadelphia: Lippincott;125–164.20. Bauer A, Schlief R, Zomack M, Urbank A, Niendorf HP. Nanda N, Schlief R, Goldberg BB, editors. Acoustically stimulated microbubbles in diagnostic ultrasound: properties and implications for diagnostic use. Advances in echo imaging using contrast enhancement. 1997. 2nd ed. London: Kluwer;669–684.21. Simpson DH, Chin CT, Burns PN. Pulse-inversion Doppler: a new method for detecting nonlinear echoes from microbubble contrast agents. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 1999. 46:372–382.22. Forsberg F, Liu JB, Chiou HJ, Rawool NM, Parker L, Goldberg BB. Comparison of fundamental and wideband harmonic contrast imaging of liver tumors. Ultrasonics. 2000. 38:110–113.23. Simpson DH, Burns PN. Pulse-inversion Doppler: a new method for detecting nonlinear echoes from microbubble contrast agents. IEEE Ultrasonic Symposium. 1997. 1597–1600.24. Quaia E, Blomley MJK, Patel S, et al. Initial observations on the effect of irradiation on the liver-specific uptake of Levovist. Eur J Radiol. 2002. 41:192–199.25. Mitsuzaki K, Yamashita Y, Ogata I, et al. Multiple-phase helical CT of the liver for detecting small hepatomas in patients with liver cirrhosis: contrast-injection protocol and optimal timing. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996. 167:753–757.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Detectability of Hepatic Metastases in Candidates of Radiofrequency Ablation: Comparison for Helical CT Scanning and Late-Phase Pulse-Inversion Harmonic Imaging
- Comparison of Enhancenent Patterns and Detection Rate of IV etastatic Adenocarcinoma of the Liver in Early and Late Phase of Spiral CT
- Hepatic CT Enhancement: Comparison between Dimeric and Monomeric Nonionic Contrast Agents in Rabbits
- Focal Hepatic Lesions: Contrast-Enhancement Patterns at Pulse-Inversion Harmonic US using a Microbubble Contrast Agent
- Assessment of Neoplastic Angiogenesis Using Perfusion-Weighted MR Imaging: Experimental Study in VX2 Carcinoma in Rabbits