Korean J Radiol.
2011 Oct;12(5):641-645. 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.5.641.
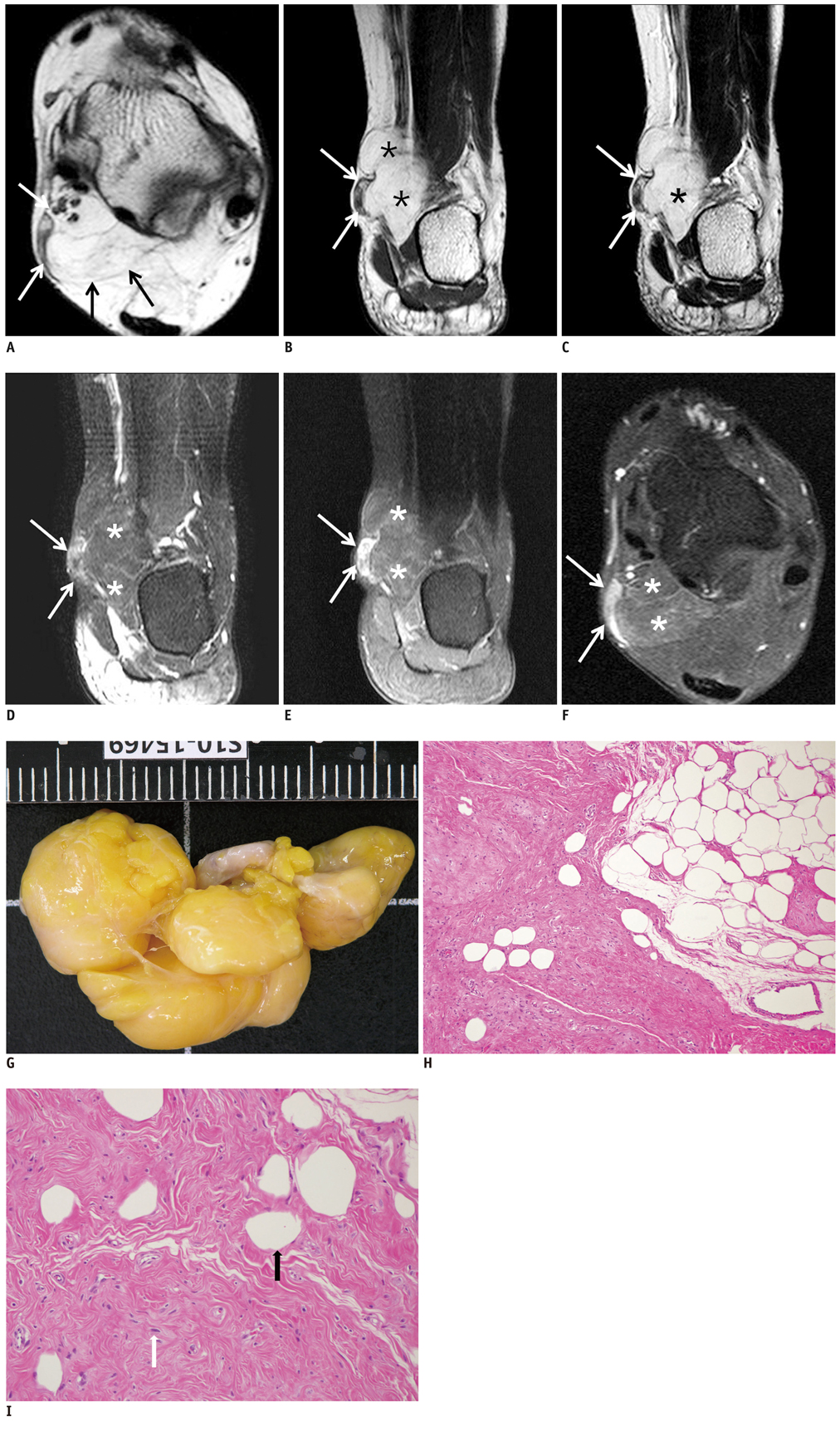
MRI of a Subcutaneous Myolipoma in the Ankle: a Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon 301-723, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon 301-723, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon 301-723, Korea.
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon 301-723, Korea. ces612@nate.com
- KMID: 1116453
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.5.641
Abstract
- Myolipoma is a rare benign tumor, composed of irregularly admixed adipose tissue and smooth muscle fibers. Few literature studies have described the radiologic appearance of myolipoma, especially in the soft tissue. No MRI findings in subcutaneous myolipoma of an extremity have been reported. Here, we report on the case of a 34-year-old woman with myolipoma in the subcutaneous tissue of the ankle and describe MRI features of the lesion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Meis JM, Enzinger FM. Myolipoma of soft tissue. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991. 15:121–125.2. Behranwala KA, Chettiar K, El-Bahrawy M, Stamp G, Kakkar AK. Retroperitoneal myolipoma. World J Surg Oncol. 2005. 3:72.3. Takahashi Y, Imamura T, Irie H, Tanaka F, Fukushima J, Fukusato T, et al. Myolipoma of the retroperitoneum. Pathol Int. 2004. 54:460–463.4. Nagayama A, Miyamura N, Lu Z, Tsuda Y, Kitaoka T, Amemiya T, et al. Light and electron microscopic findings in a patient with orbital myolipoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2003. 241:773–776.5. Ben-Izhak O, Elmalach I, Kerner H, Best LA. Pericardial myolipoma: a tumour presenting as a mediastinal mass and containing oestrogen receptors. Histopathology. 1996. 29:184–186.6. Kransdorf MJ, Murphey MD. Imaging of soft tissue tumors. 2006. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;80–149.7. Guillou L, Coindre JM. Newly described adipocytic lesions. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2001. 18:238–249.8. Parratt MT, Gokaraju K, Spiegelberg BG, Miles J, Cannon SR, Briggs TW. Myolipoma affecting the erector spinae: a case report in a child. Case Report Med. 2009. 2009:520126.9. Murphey MD, Carroll JF, Flemming DJ, Pope TL, Gannon FH, Kransdorf MJ. From the archives of the AFIP: benign musculoskeletal lipomatous lesions. Radiographics. 2004. 24:1433–1466.10. Pereira JM, Sirlin CB, Pinto PS, Casola G. CT and MR imaging of extrahepatic fatty masses of the abdomen and pelvis: techniques, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and pitfalls. Radiographics. 2005. 25:69–85.