Korean J Radiol.
2011 Oct;12(5):541-546. 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.5.541.
Application of Intraoperative Ultrasonography for Guiding Microneurosurgical Resection of Small Subcortical Lesions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ultrasound, Tangdu Hospital of the Fourth Military Medicine University, Xi an 710038, China. Duanyy@fmmu.edu.cn
- 2Institute for Functional Neurosurgery of PLA, Department of Neurosurgery, Tangdu Hospital of the Fourth Military Medicine University, Xi an 710038, China.
- KMID: 1116438
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.5.541
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
We wanted to evaluate the clinical value of intraoperative ultrasonography for real-time guidance when performing microneurosurgical resection of small subcortical lesions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
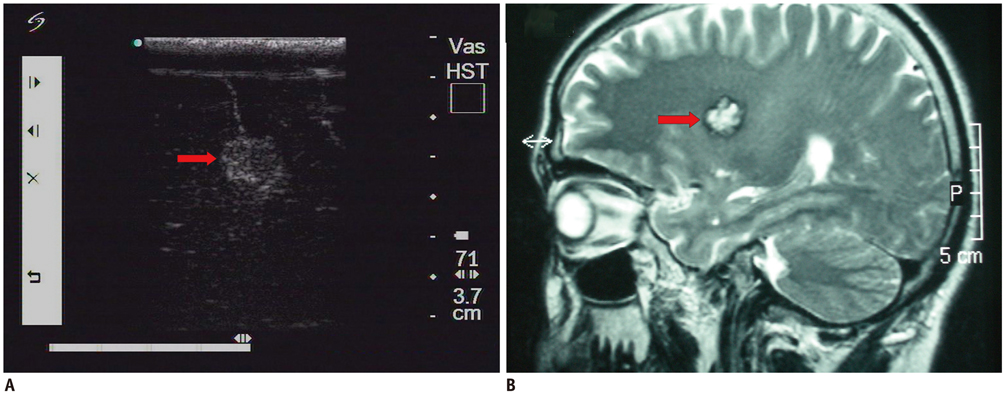
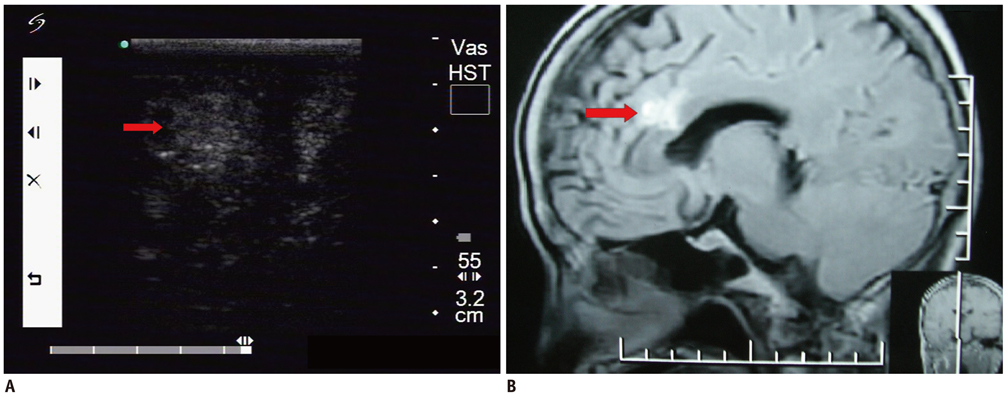
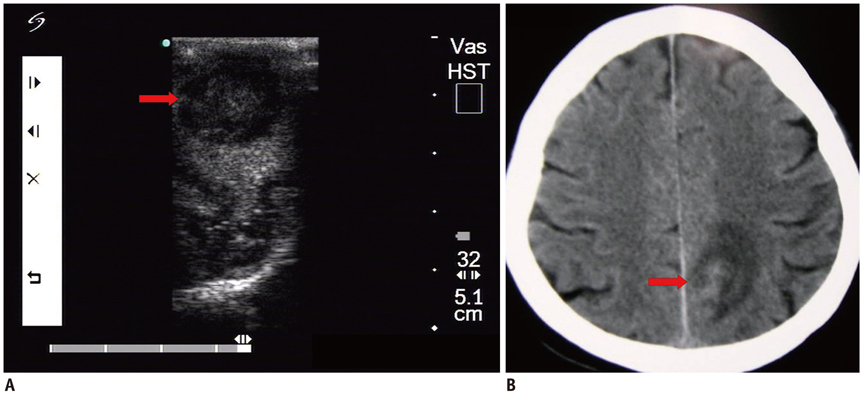
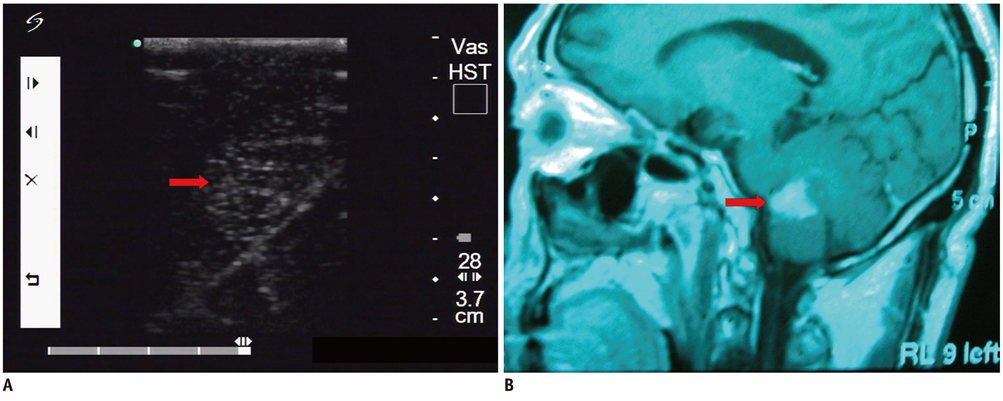
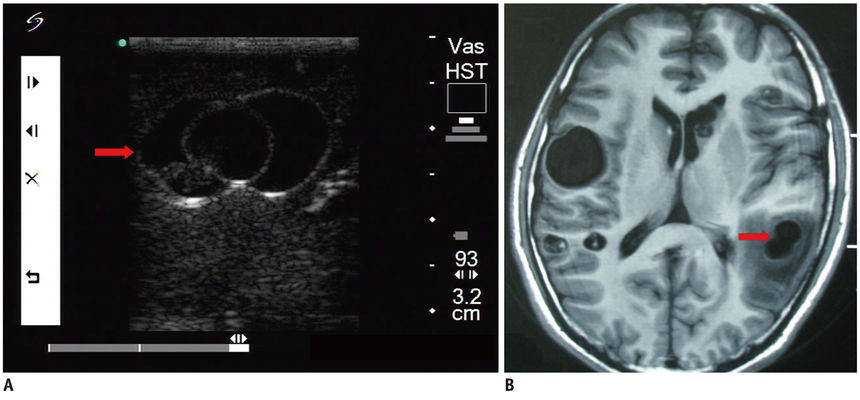
Fifty-two patients with small subcortical lesions were involved in this study. The pathological diagnoses were cavernous hemangioma in 25 cases, cerebral glioma in eight cases, abscess in eight cases, small inflammatory lesion in five cases, brain parasite infection in four cases and the presence of an intracranial foreign body in two cases. An ultrasonic probe was sterilized and lightly placed on the surface of the brain during the operation. The location, extent, characteristics and adjacent tissue of the lesion were observed by high frequency ultrasonography during the operation.
RESULTS
All the lesions were located in the cortex and their mean size was 1.3 +/- 0.2 cm. Intraoperative ultrasonography accurately located all the small subcortical lesions, and so the neurosurgeon could provide appropriate treatment. Different lesion pathologies presented with different ultrasonic appearances. Cavernous hemangioma exhibited irregular shapes with distinct margins and it was mildly hyperechoic or hyperechoic. The majority of the cerebral gliomas displayed irregular shapes with indistinct margins, and they often showed cystic and solid mixed echoes. Postoperative imaging identified that the lesions had completely disappeared, and the original symptoms of all the patients were significantly alleviated.
CONCLUSION
Intraoperative ultrasonography can help accurately locate small subcortical lesions and it is helpful for selecting the proper approach and guiding thorough resection of these lesions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moller-Hartmann W, Herminghaus S, Krings T, Marquardt G, Lanfermann H, Pilatus U, et al. Clinical application of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the diagnosis of intracranial mass lesions. Neuroradiology. 2002. 44:371–381.2. Kawamata T, Iseki H, Hori T. [Navigation systems for neurosurgery at present and in the future]. No Shinkei Geka. 2003. 31:609–618.3. Erdogan N, Tucer B, Mavili E, Menku A, Kurtsoy A. Ultrasound guidance in intracranial tumor resection: correlation with postoperative magnetic resonance findings. Acta Radiol. 2005. 46:743–749.4. Shen TZ, Zhang YL, Chen XR. Advances of WHO classification of brain tumors. Chin Comput Med Imag. 2000. 6:219–231.5. van Velthoven V. Intraoperative ultrasound imaging: comparison of pathomorphological findings in US versus CT, MRI and intraoperative findings. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2003. 85:95–99.6. Cokluk C, Iyigun O, Senel A, Celik F, Rakunt C. The guidance of intraoperative ultrasonography in the surgical treatment of arteriovenous malformation. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2003. 46:169–172.7. Wang J, Liu X, Hou WH, Dong G, Wei Z, Zhou H, et al. The relationship between intra-operative ultrasonography and pathological grade in cerebral glioma. J Int Med Res. 2008. 36:1426–1434.8. Janson M, Michael K, Berg J, Anderson J. The role of intraoperative sonography in neurosurgery. J Diagn Med Sono. 2005. 21:148–151.9. Becker G, Perez J, Krone A, Demuth K, Lindner A, Hofmann E, et al. Transcranial color-coded real-time sonography in the evaluation of intracranial neoplasms and arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery. 1992. 31:420–428.10. Lunardi P, Acqui M. The echo-guided removal of cerebral cavernous angiomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1993. 123:113–117.11. Sun H, Zhao JZ. Application of intraoperative ultrasound in neurological surgery. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2007. 50:155–159.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intraoperative neurosonography revisited: effective neuronavigation in pediatric neurosurgery
- Non-enhancing gliomas: does intraoperative ultrasonography improve resections?
- Navigated intraoperative ultrasonography for brain tumors: a pictorial essay on the technique, its utility, and its benefits in neuro-oncology
- Stereotactic Craniotomy and Trans-Sulcal Approach for Small Subcortical Lesions
- The role of intraoperative ultrasonography in the diagnosis and management of focal hepatic lesions