J Vet Sci.
2007 Dec;8(4):335-340. 10.4142/jvs.2007.8.4.335.
Relative biological effectiveness of fast neutrons for apoptosis in mouse hair follicles
- Affiliations
-
- 1Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Science, Seoul 139-240, Korea.
- 2College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 500-757, Korea. shokim@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 1106212
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2007.8.4.335
Abstract
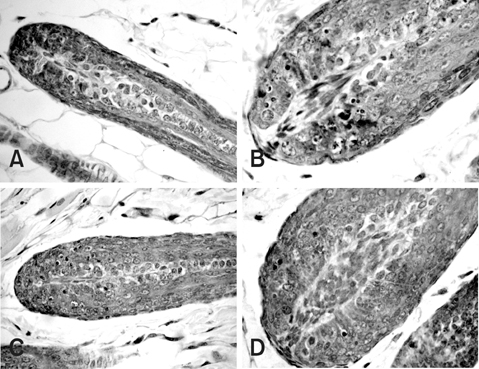
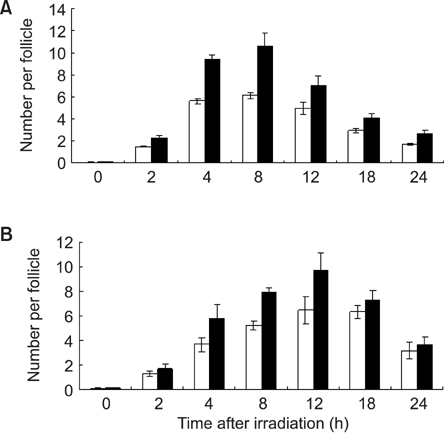
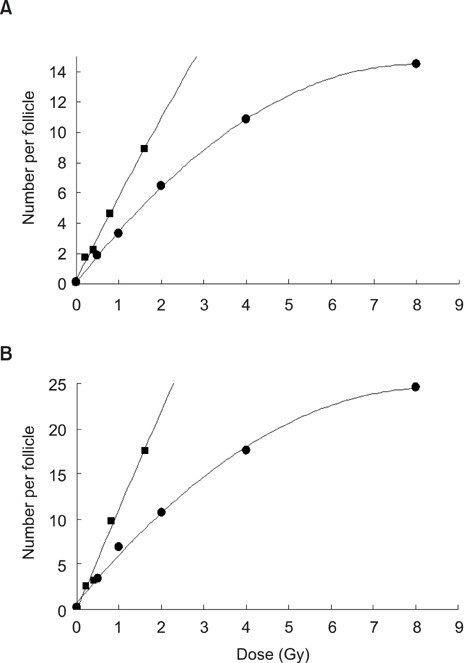
- This study compared the effects of high linear energy transfer (LET) fast neutrons on the induction of apoptosis in the hair follicles of ICR mice with those of low LET (60)Co gamma-rays. The changes that occurred from 0 to 24 h after exposing the mice to either 2 Gy of gamma-rays (2 Gy/min) or 0.8 Gy of neutrons (94 mGy/min, 35 MeV) were examined. The maximum frequency was found at 12 h (gamma-rays) or 8 h (neutrons) after irradiation. The mice that received 0-8 Gy of gamma-rays or 0-1.6 Gy of neutrons were examined 8 h after irradiation. The dose-response curves were analyzed using the best-fit curve model. The dose-response curves were linear-quadratic, and a significant relationship was found between the frequency of apoptotic cells and the dose. The morphological findings in the irradiated groups were typical apoptotic fragments in the matrix region of the hair follicle, but the spontaneous existence of apoptotic fragments was rarely observed in the control group. In the presence of an apoptosis frequency between 2 and 14 per follicle, the relative biological effectiveness values of neutrons in small and large follicles were 2.09 +/- 0.30 and 2.15 +/- 0.18, respectively.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Blöcher D. DNA double-strand break repair determines the RBE of α-particles. Int J Radiat Biol. 1988. 54:761–771.
Article2. Bonicalzi ME, Haince JF, Droit A, Poirier GG. Regulation of poly(ADP-ribose) metabolism by poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase: where and when? Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005. 62:739–750.3. Britten RA, Peters LJ, Murray D. Biological factors influencing the RBE of neutrons: implications for their past, present and future use in radiotherapy. Radiat Res. 2001. 156:125–135.
Article4. Broerse JJ, Barendsen GW. Relative biological effectiveness of fast neutrons for effects on normal Tissues. Curr Top Radiat Res Q. 1973. 8:305–350.5. Denekamp J, Joiner MC, Maughan RL. Neutron RBEs for mouse skin at low doses per fraction. Radiat Res. 1984. 98:317–331.
Article6. Fox JC, McNally NJ. The rejoining of DNA double-strand break following irradiation with 238Pu α-particles: evidence for a fast component of repair as measured by neutral filter elution. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990. 57:513–521.
Article7. Fritsch P, Richard-Le Naour H, Denis S, Ménétrier F. Kinetics of radiation-induced apoptosis in the cerebellum of 14-day-old rats after acute or during continuous exposure. Int J Radiat Biol. 1994. 66:111–117.
Article8. Fujikawa K, Hasegawa Y, Matsuzawa S, Fukunaga A, Itoh T, Kondo S. Dose and dose-rate effects of X rays and fission neutrons on lymphocyte apoptosis in p53(+/+) and p53(-/-) mice. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 2000. 41:113–127.
Article9. Hale AJ, Smith CA, Sutherland LC, Stoneman VE, Longthorne VL, Culhane AC, Williams GT. Apoptosis: molecular regulation of cell death. Eur J Biochem. 1996. 236:1–26.
Article10. Hendry JH, Potten CS, Chadwick C, Bianchi M. Cell death (apoptosis) in the mouse small intestine after low doses: effects of dose-rate, 14.7 MeV neutrons, and 600 MeV (maximum energy) neutrons. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1982. 42:611–620.
Article11. Hendry JH, Potten CS, Merritt A. Apoptosis induced by high- and low-LET radiations. Radiat Environ Biophys. 1995. 34:59–62.
Article12. Hopewell JW. The skin: its structure and response to ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990. 57:751–773.
Article13. IARC. Neutrons. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 2000. 75 Pt 1:363–448.14. Ijiri K, Potten CS. Response of intestinal cells of differing topographical and hierarchical status to ten cytotoxic drugs and five sources of radiation. Br J Cancer. 1983. 47:175–185.
Article15. Ijiri K, Potten CS. Further studies on the response of intestinal crypt cells of different hierarchical status to eighteen different cytotoxic agents. Br J Cancer. 1987. 55:113–123.
Article16. Ishida Y, Ohmachi Y, Nakata Y, Hiraoka T, Hamano T, Fushiki S, Ogiu T. Dose-response and large relative biological effectiveness of fast neutrons with regard to mouse fetal cerebral neuron apoptosis. J Radiat Res. 2006. 47:41–47.
Article17. Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 1972. 26:239–257.
Article18. Kim SH, Chung CY, Son CH. Cell death by apoptosis in the neonatal mouse cerebellum following gamma-irradiation. Anticancer Res. 1998. 18:1629–1632.19. Kim SH, Kim SR, Lee HJ, Oh H, Ryu SY, Lee YS, Kim TH, Jo SK. Apoptosis in growing hair follicles following gamma-irradiation and application for the evaluation of radioprotective agents. In Vivo. 2003. 17:211–214.20. Konings AW. Dose-rate effects on lymphocyte survival. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 1981. 22:282–285.
Article21. Kysela BP, Arrand JE, Michael BD. Relative contribution of levels of initial damage and repair of double-strand breaks to the ionizing radiation-sensitive phenotype of the Chinese hamster cell mutant, XR-V15B. Part II. Neutrons. Int J Radiat Biol. 1993. 64:531–538.
Article22. Maity A, McKenna WG, Muschel RJ. The molecular basis for cell cycle delays following ionizing radiation: a review. Radiother Oncol. 1994. 31:1–13.
Article23. Newman HC, Prise KM, Folkard M, Michael BD. DNA double-strand break distributions in X-ray and α-particle irradiated V79 cells: evidence for non-random breakage. Int J Radiat Biol. 1997. 71:347–363.24. Potten CS. Biological dosimetry of local radiation accidents of skin: possible cytological and biochemical methods. Br J Radiol Suppl. 1986. 19:82–85.25. Potten CS. A comprehensive study of the radiobiological response of the murine (BDF1) small intestine. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990. 58:925–973.
Article26. Potten CS, Geng L, Taylor P. Hair medullary cell counts: a simple and sensitive indicator of radiation exposure. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990. 57:13–21.
Article27. Ramakrishnan N, McClain DE, Catravas GN. Membranes as sensitive targets in thymocyte apoptosis. Int J Radiat Biol. 1993. 63:693–701.
Article28. Ritter MA, Cleaver JE, Tobias CA. High-LET radiations induce a large proportion of non-rejoining DNA breaks. Nature. 1977. 266:653–655.
Article29. Ryan LA, Wilkins RC, McFarlane NM, Sung MM, McNamee JP, Boreham DR. Relative biological effectiveness of 280 keV neutrons for apoptosis in human lymphocytes. Health Phys. 2006. 91:68–75.
Article30. Sieber VK, Sugden EM, Alcock CJ, Belton RR. Reduction in the diameter of human hairs following irradiation. Br J Radiol. 1992. 65:148–151.
Article31. Song S, Lambert PF. Different responses of epidermal and hair follicular cells to radiation correlate with distinct patterns of p53 and p21 induction. Am J Pathol. 1999. 155:1121–1127.
Article32. Van der Sachans GP, Paterson MC, Cross WG. DNA strand break and rejoining in cultured human fibroblasts exposed to fast neutrons or gamma-rays. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1983. 44:75–85.33. Vral A, Cornelissen M, Thierens H, Louagie H, Philippé J, Strijckmans K, De Ridder L. Apoptosis induced by fast neutrons versus 60Co gamma-rays in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Int J Radiat Biol. 1998. 73:289–295.34. Warenius HM, Down JD. RBE of fast neutrons for apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Int J Radiat Biol. 1995. 68:625–629.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Frequency of Micronuclei in Lymphocytes Following Gamma and Fast-neutron Irradiations
- Trichofolliculoma
- The RBE of Fractionated Fast Neutron on Walker 256 Carcinosarcoma with KCCH-Cyclotron
- Growth Factors Influencing the Morphology and Growth Rate of Hair Follicles in a Human Hair Organ Culture
- A Case of Trichofolliculoma