Korean J Radiol.
2005 Sep;6(3):196-199. 10.3348/kjr.2005.6.3.196.
Functional MR Imaging of Psychogenic Amnesia: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Korea. gwjeong@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Korea.
- 3Department of Psychiatry, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Korea.
- KMID: 1102717
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2005.6.3.196
Abstract
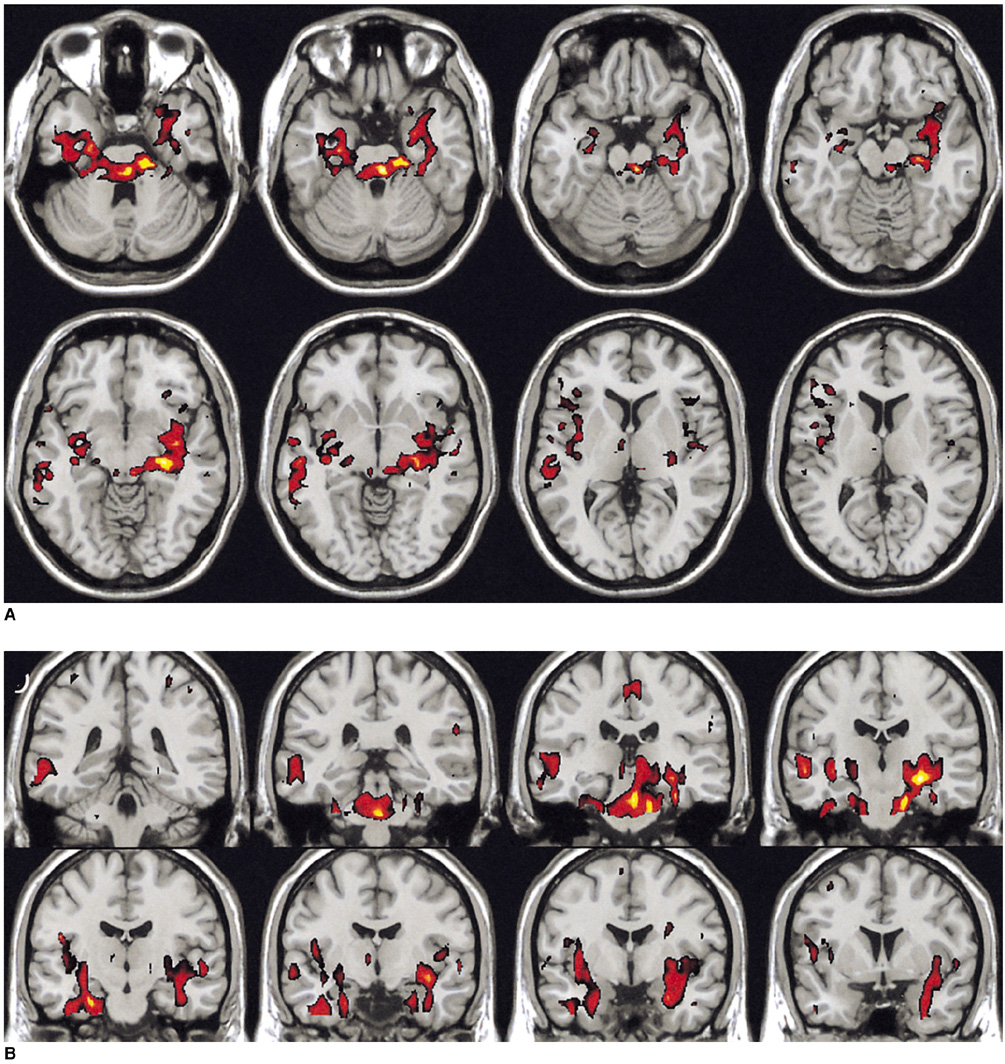
- We present here a case in which functional MR imaging (fMRI) was done for a patient who developed retrograde psychogenic amnesia for a four year period of her life history after a severe stressful event. We performed the fMRI study for a face recognition task using stimulation with three kinds of face photographs: recognizable familiar faces, unrecognizable friends' faces due to the psychogenic amnesia, and unfamiliar control faces. Different activation patterns between the recognizable faces and unrecognizable faces were found in the limbic area, and especially in the amygdala and hippocampus.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kaplan HI, Sadock BJ. Comprehensive textbook of psychiatry. 1995. 6th ed. New York: William & Wilkins;650–653.2. Pujol M, Kopelman MD. Psychogenic amnesia. Practical Neurology. 2003. 3:292–299.3. Lee SH. Brain mechanism of memory and psychiatry. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1998. 37:14–37.4. Markowitsch HJ. Psychogenic amnesia. Neuroimage. 2003. 20:132–138.5. Yasuno F, Nishigawa T, Nakagawa Y, Ikejiri Y, Tokunaga H, Mizuta I, et al. Functional anatomical study of psychogenic amnesia. Psychiatry Res. 2000. 99:43–57.6. Markowitsch HJ, Calabrese P, Fink GR, Durwen HF, Kessler J, Harting C, et al. Impaired episodic memory retrieval in a case of probable psychogenic amnesia. Psychiatry Res. 1997. 74:119–126.7. Phillips ML, Drevets WC, Rauch SL, Lane R. Neurobiology of emotion perception: the neural basis of normal emotion perception. Biol Psychiatry. 2003. 54:504–514.8. Ledoux JE, Muller J. Emotional memory and psychopathology. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1997. 352:1719–1726.9. Calabrese P, Markowitsch HJ. Memory and brain: neurobiological correlates of memory disturbances. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2003. 71:211–219.10. Kapur N, Friston KJ, Young A, Frith CD, Frackowiak RS. Activation of human hippocampal formation during memory for faces: a PET study. Cortex. 1995. 31:99–108.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pure Retrograde Amnesia: Is This Real Organic or Psychogenic?
- Retrograde Amnesia as a Predominant Symptom of Transient Global Amnesia
- Anterograde Amnesia after Acute Glufosinate Ammonium Intoxication
- Transient global amnesia associated with multiple lesions in the corpus callosum and hippocampus
- Hippocampal Lesions of Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Image in Patients with Headache without Symptoms of Transient Global Amnesia