Korean J Radiol.
2011 Dec;12(6):745-749. 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.6.745.
Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Tenosynovitis in the Hand: Two Case Reports with the MR Imaging Findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and the Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 135-710, Korea. jwjwkwon@gmail.com
- KMID: 1101930
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.6.745
Abstract
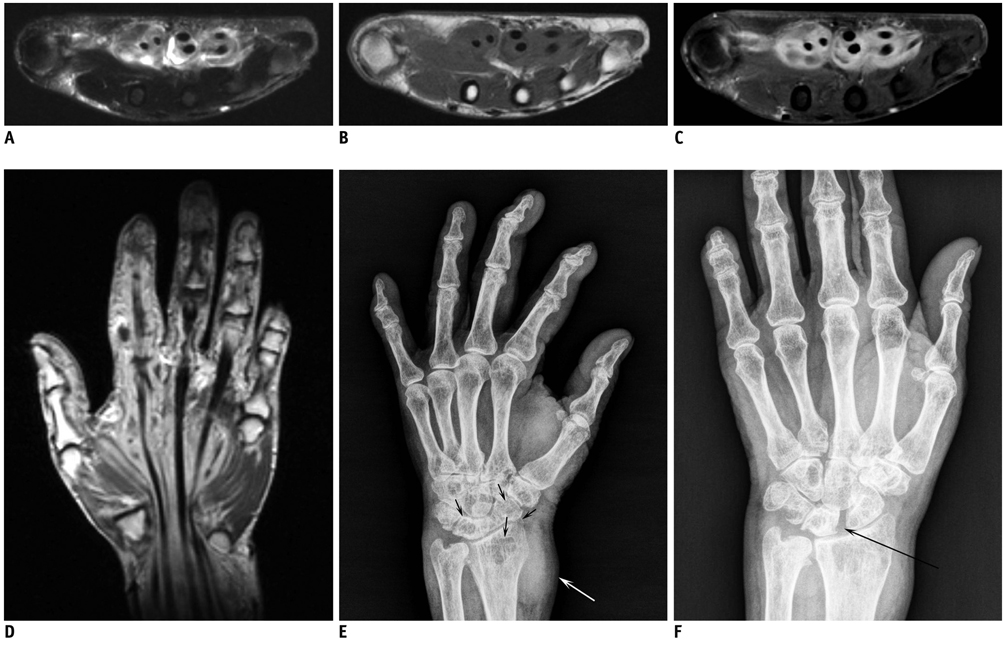
- Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections can cause destructive tenosynovitis of the hand. We report on and discuss the clinical course and distinctive radiologic findings of two patients with hand tenosynovitis secondary to M. marinum and intracellulare infection, which are different from those of the nontuberculous mycobacterial infections reported in the previous literature.
MeSH Terms
-
Female
*Hand/radiography
Humans
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Male
Middle Aged
Mycobacterium Infections, Nontuberculous/*diagnosis/etiology/radiography
Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare Infection/*diagnosis/etiology/radiography
*Mycobacterium marinum
Surgical Wound Infection/complications
Tenosynovitis/diagnosis/*microbiology/radiography
Wound Infection/complications
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Diagnosis and Treatment for Deep Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Infection of the Hand and Wrist
Ho Youn Park, Jun O Yoon, Jin-Woong Park, Jaeyoun Yoon, Jim Sam Kim
J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2015;20(3):119-126. doi: 10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.3.119.
Reference
-
1. Falkinham JO 3rd. Epidemiology of infection by nontuberculous mycobacteria. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1996. 9:177–215.2. Wallace DV, Dykewicz MS, Bernstein DI, Blessing-Moore J, Cox L, Khan DA, et al. The diagnosis and management of rhinitis: an updated practice parameter. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. 122:S1–S84.3. Zenone T, Boibieux A, Tigaud S, Fredenucci JF, Vincent V, Chidiac C, et al. Non-tuberculous mycobacterial tenosynovitis: a review. Scand J Infect Dis. 1999. 31:221–228.4. Neviaser RJ. Tenosynovitis. Hand Clin. 1989. 5:525–531.5. Wallace RJ Jr, Brown BA, Onyi GO. Skin, soft tissue, and bone infections due to Mycobacterium chelonae chelonae: importance of prior corticosteroid therapy, frequency of disseminated infections, and resistance to oral antimicrobials other than clarithromycin. J Infect Dis. 1992. 166:405–412.6. Amrami KK, Sundaram M, Shin AY, Bishop AT. Mycobacterium marinum infections of the distal upper extremities: clinical course and imaging findings in two cases with delayed diagnosis. Skeletal Radiol. 2003. 32:546–549.7. Mateo L, Rufi G, Nolla JM, Alcaide F. Mycobacterium chelonae tenosynovitis of the hand. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004. 34:617–622.8. Wongworawat MD, Holtom P, Learch TJ, Fedenko A, Stevanovic MV. A prolonged case of Mycobacterium marinum flexor tenosynovitis: radiographic and histological correlation, and review of the literature. Skeletal Radiol. 2003. 32:542–545.9. Lorenz HM, Dalpke AH, Deboben A, Ho AD, Greiner A, Jung M, et al. Mycobacterium kansasii tenosynovitis in a rheumatoid arthritis patient with long-term therapeutic immunosuppression. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. 59:900–903.10. Abdelwahab IF, Kenan S, Hermann G, Klein MJ, Lewis MM. Tuberculous peroneal tenosynovitis. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993. 75:1687–1690.11. Jaovisidha S, Chen C, Ryu KN, Siriwongpairat P, Pekanan P, Sartoris DJ, et al. Tuberculous tenosynovitis and bursitis: imaging findings in 21 cases. Radiology. 1996. 201:507–513.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Tenosynovitis Due to Mycobacterium intracellulare in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Tenosynovitis of the Hand: A 10-Year Experience at Two Centers in South Korea
- Tuberculous Tenosynovitis of Hand (A Case Report)
- Mycobacterium intracellulare Tenosynovitis with Rice Body Formation with Literature Review
- Diagnosis and Treatment for Deep Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Infection of the Hand and Wrist