Korean J Ophthalmol.
2007 Jun;21(2):95-99. 10.3341/kjo.2007.21.2.95.
Diabetic Macular Edema Before and After Intravitreal Triamcinolone Injection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Ophthalmic Research Center, Shaheed Beheshti Medical University, Tehran, Iran. arramezani@gmail.com
- KMID: 1101911
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2007.21.2.95
Abstract
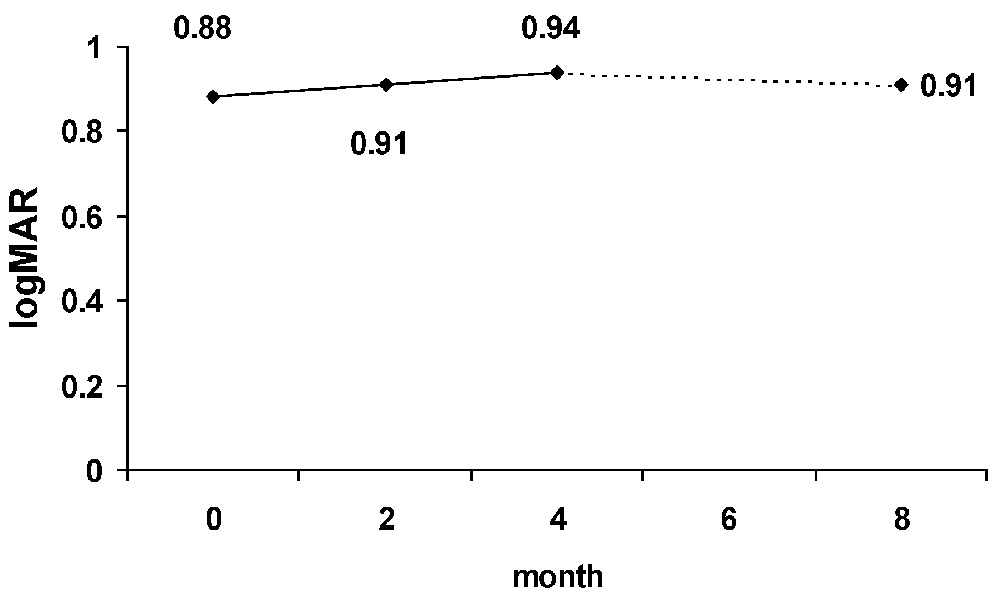
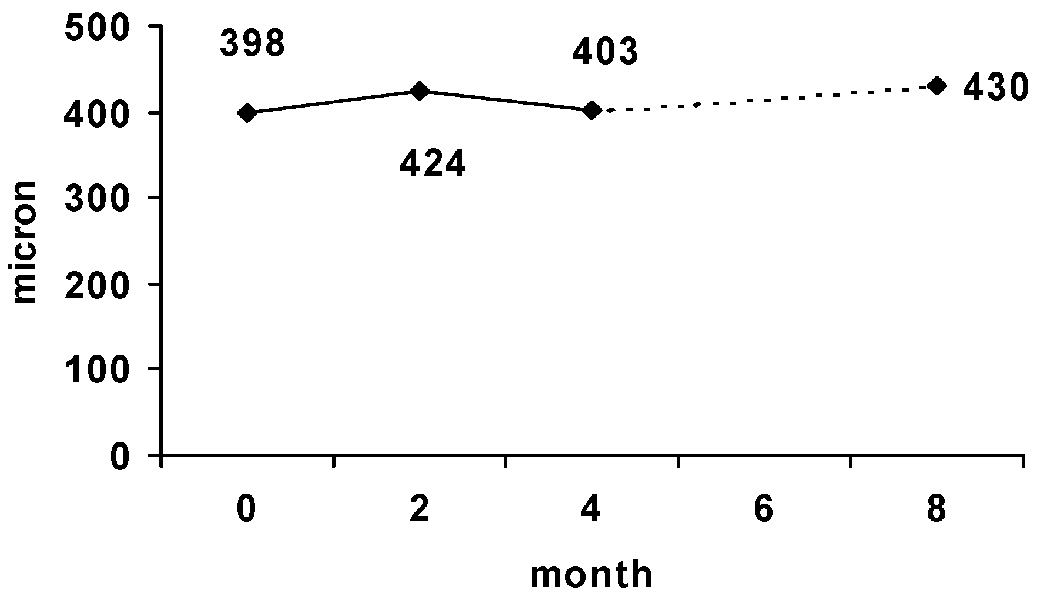
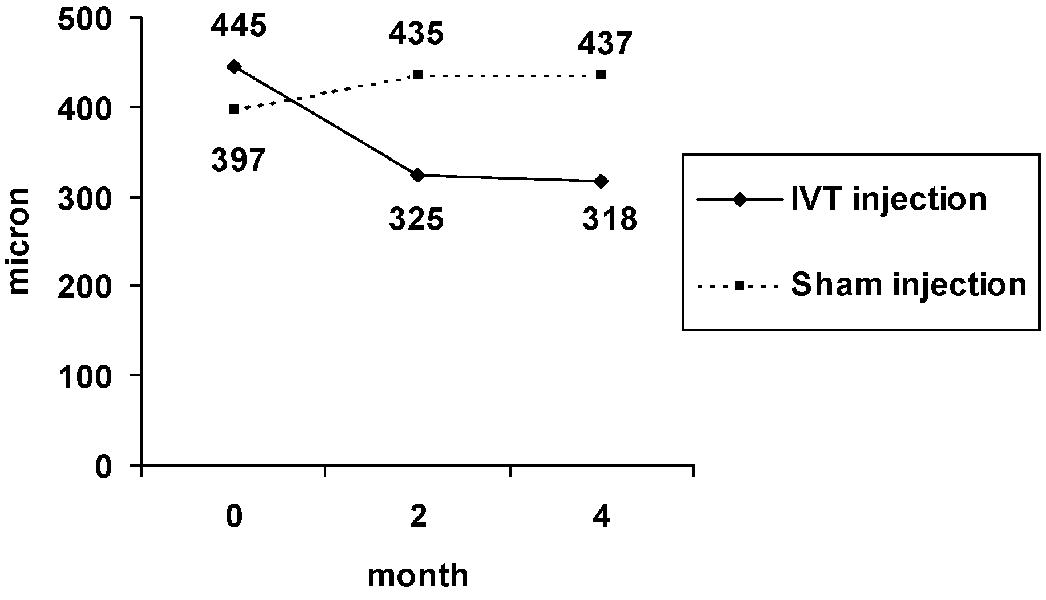
- PURPOSE: To compare intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide (IVT) versus natural course in refractory diabetic macular edema. METHODS: In a prospective interventional case series, twenty five eyes with refractory DME which had been allocated to the sham group of a previous clinical trial underwent new examination and optical coherence tomography about 9 months after their first enrollment. Twenty eyes that met the inclusion criteria, visual acuity (VA) < 20/50 and central macular thickness (CMT) > 200 micrometer, were treated by 4 mg IVT. Evaluations were repeated at 2 and 4 months post-injection to imitate the similar examination intervals after sham injection. Corrected visual acuity and macular thickness changes following IVT were compared to the corresponding changes after sham injection (the natural course). RESULTS: Visual acuity changes within and between each period were not statistically significant. Visual acuity decreased 0.08 & 0.09 logMAR by 2 months and 0.06 & 0.04 logMAR by 4 months after sham and IVT injections, respectively. The changes of macular thickness after IVT and sham intervention were not meaningful either. However, the difference between thickness changes by 4 months (52+/-50 micrometer increase after sham vs. 262+/-115 micrometer reduction after IVT) was significant (P=0.014). CONCLUSIONS: Concerning macular thickness, IVT has beneficial effect on refractory diabetic macular edema as opposed to observation. However, considering visual acuity, it does not induce significant difference in comparison to the natural course of the disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Diabetic Retinopathy/*complications/pathology
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Glucocorticoids/*administration & dosage
Humans
Injections
Macula Lutea/drug effects/*pathology
Macular Edema/*drug therapy/etiology/pathology
Male
Middle Aged
Prospective Studies
Time Factors
Tomography, Optical Coherence
Treatment Outcome
Triamcinolone Acetonide/*administration & dosage
Visual Acuity
Vitreous Body
Figure
Reference
-
1. Benson William E.. Diabetic Retinopathy. Duane's Clinical Ophthalmology. [Book on CD-ROM]. 2004. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Publishers;chap 30.2. Ciardella AP, Klancnik J, Schiff W, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone for the treatment of refractory diabetic macular oedema with hard exudates: an optical coherence tomography study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004. 88:1131–1136.3. Jonas JB, Kreissig I, Sofker A, Degenring RF. Intravitreal injection of triamcinolone for diabetic macular edema. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003. 121:57–61.4. Martidis A, Duker JS, Greenberg PB, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone for refractory diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. 2002. 109:920–927.5. Cardillo JA, Melo LA Jr, Costa RA, et al. Comparison of intravitreal versus posterior sub-Tenon's capsule injection of triamcinolone acetonide for diffuse diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. 2005. 112:1557–1563.6. Lam DS, Chan CK, Tang EW, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone for diabetic macular oedema in Chinese patients: six-month prospective longitudinal pilot study. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2004. 32:569–572.7. Krepler K, Wagner J, Sacu S, Wedrich A. The effect of intravitreal triamcinolone on diabetic macular oedema. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005. 243:478–481.8. Massin P, Audren F, Haouchine B, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide for diabetic diffuse macular edema: preliminary results of a prospective controlled trial. Ophthalmology. 2004. 111:218–224.9. Parolini B, Panozzo G, Gusson E, et al. Diode laser, vitrectomy and intravitreal triamcinolone. A comparative study for the treatment of diffuse non tractional diabetic macular edema. Semin Ophthalmol. 2004. 19:1–12.10. Jonas JB, Akkoyun I, Kreissig I, Degenring RF. Diffuse diabetic macular oedema treated by intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide: a comparative, non-randomised study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005. 89:321–326.11. Ozkiris A, Evereklioglu C, Erkilic K, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide injection as primary treatment for diabetic macular edema. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2004. 14:543–549.12. Jonas JB, Degenring RF, Kreissig I, et al. Intraocular pressure elevation after intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide injection. Ophthalmology. 2005. 112:593–598.13. Larsson J, Zhu M, Sutter F, Gillies MC. Relation between reduction of foveal thickness and visual acuity in diabetic macular edema treated with intravitreal triamcinolone. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005. 139:802–806.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intravitreal and Additional Posterior Subtenon Triamcinolone Injection in Diabetic Macular Edema
- The Effect of Intravitreal Triamcinolone Acetonide Injection according to the Diabetic Macular Edema Type
- Comparison of Intravitreal Bevacizumab Alone Injection and Intravitreal Combination Low-Dose Bevacizumab-Triamcinolone Injection or Diabetic Macular Edema
- Intravitreal versus Posterior Subtenon Injection of Triamcinolone Acetonide for Diabetic Macular Edema
- Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema: A Comparative Study