Korean J Lab Med.
2010 Apr;30(2):133-137. 10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.2.133.
Development and Evaluation of the Quick Anaero-system-A New Disposable Anaerobic Culture System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, Chosun University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Chosun University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chosun University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. sjbjang@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 1096798
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.2.133
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
We developed a new disposable anaerobic culture system, namely, the Quick anaero-system, for easy culturing of obligate anaerobes.
METHODS
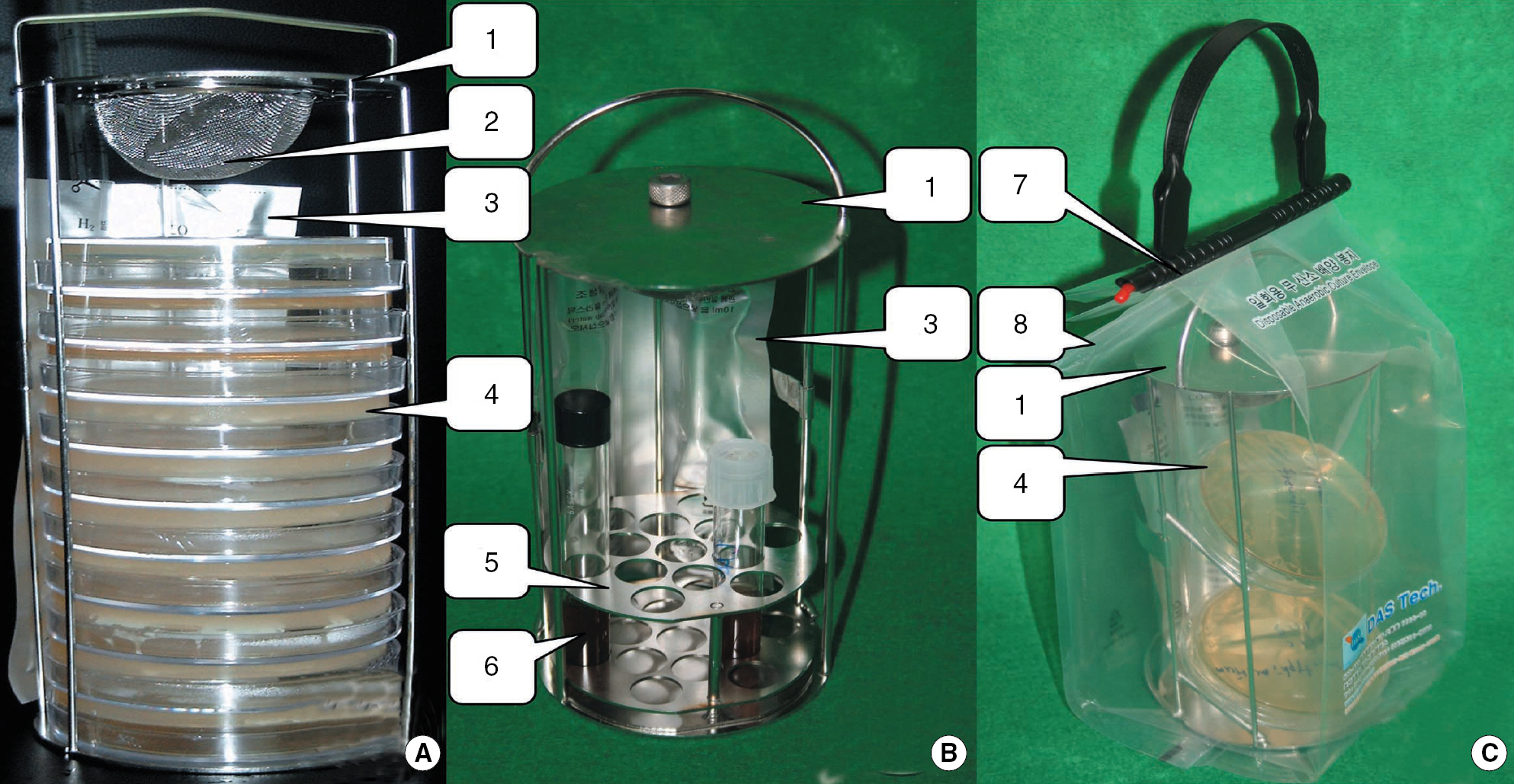
Our system consists of 3 components: 1) new disposable anaerobic gas pack, 2) disposable culture-envelope and sealer, and 3) reusable stainless plate rack with mesh containing 10 g of palladium catalyst pellets. To evaluate the efficiency of our system, we used 12 anaerobic bacteria. We prepared 2 sets of ten-fold serial dilutions of the 12 anaerobes, and inoculated these samples on Luria-Bertani (LB) broth and LB blood agar plate (LB-BAP) (BD Diagnostic Systems, USA). Each set was incubated in the Quick anaero-system (DAS Tech, Korea) and BBL GasPak jar with BD GasPak EZ Anaerobe Container System (BD Diagnostic Systems) at 35-37degrees C for 48 hr. The minimal inoculum size showing visible growth of 12 anaerobes when incubated in both the systems was compared.
RESULTS
The minimal inoculum size showing visible growth for 2 out of the 12 anaerobes in the LB broth and 9 out of the 12 anaerobes on LB-BAP was lower for the Quick anaero-system than in the BD GasPak EZ Anaerobe Container System. The mean time (+/-SD) required to achieve absolute anaerobic conditions of the Quick anaero-system was 17 min and 56 sec (+/-3 min and 25 sec).
CONCLUSIONS
The Quick anaero-system is a simple and effective method of culturing obligate anaerobes, and its performance is superior to that of the BD GasPak EZ Anaerobe Container System.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Comparison of the Vitek 2, API 20A, and 16s rRNA Gene Sequencing for the Identification of Anaerobic Bacteria
Gyun Cheol Park, Sook Jin Jang, Min Jung Lee, Joong-Ki Kook, Min Jung Kim, Young Sook Kim, Nam Woong Yang, Hye Soo Lee, Seong Ho Kang, Geon Park, Dae Soo Moon
Ann Clin Microbiol. 2015;18(1):20-26. doi: 10.5145/ACM.2015.18.1.20.The Growth Inhibition Effect on the Causative Bacteria of Bacterial Vaginosis by Bacterial Strains Isolated from the Vagina of a Healthy Woman
Wan-Jin Sihn, Nam-Woong Yang
J Bacteriol Virol. 2014;44(3):244-251. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2014.44.3.244.
Reference
-
1.Loesche WJ. Oxygen sensitivity of various anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1969. 18:723–7.
Article2.Citron DM. Specimen collection and transport, anaerobic culture techniques, and identification of anaerobes. Rev Infect Dis. 1984. 6(S1):51–8.
Article3.Bennett GN., Hickford JG., Zhou H. Convenient anaerobic techniques, science from the supermarket shelf. Anaerobe. 2006. 12:49–51.
Article4.Strobel HJ. Basic laboratory culture methods for anaerobic bacteria. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. 581:247–61.
Article5.Imhof A., Heinzer I. Continuous monitoring of oxygen concentrations in several systems for cultivation of anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1996. 34:1646–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of rapID ANA II system for identification of anaerobic bacteria
- Evaluation of vitek ANI system for identification of anaerobic bacteria
- Evaluation of a commercial microdilution (ATB ANA) system forsusceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria
- Single Use (disposable) Duodenoscope: Recent Development and Future
- Evaluation of the BacT/Alert Blood Culture System for Culturing Sterile Body Fluids other than Blood