J Vet Sci.
2007 Jun;8(2):155-161. 10.4142/jvs.2007.8.2.155.
Dissemination and tracking of Salmonella spp. in integrated broiler operation
- Affiliations
-
- 1National Veterinary Research and Quarantine Service, Ministry of Agriculture & Forestry, Anyang 430-824, Korea.
- 2College of Veterinary Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 702-701, Korea. youngju@knu.ac.kr
- 3College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 500-757, Korea.
- 4Daegu Metropolitan City Research Institute of Health & Environment, Daegu 706-732, Korea.
- KMID: 1089667
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2007.8.2.155
Abstract
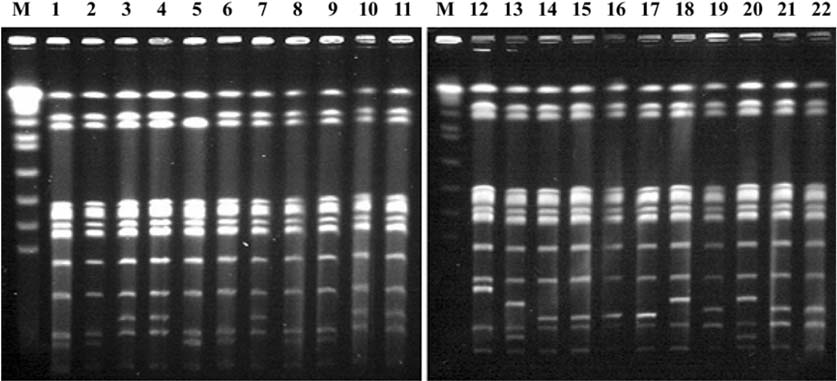
- Controlling Salmonella in integrated broiler operation is complicated because there are numerous potential sources of Salmonella contamination, including chicks, feed, rodents, wild poultry operations, and the processing plant. The objective of this study was to investigate the distribution of Salmonella through all phases of two integrated broiler operations and to determine the key areas related to the control of all known sources of infection. Two different Salmonella serotypes were observed at integrated broiler chicken company A. S. enteritidis, the predominant company A isolate, was consistently found in the breeder farm, hatcheries, broiler farms, and chicken slaughterhouse. At company B, a total of six different serotypes, S. heidelberg, S. senftenberg, S. enteritidis, S. blockley, S. gallinarum, and S. virchow, were detected. Although S. heidelberg was not found in the broiler farms, it was consistently found in the breeder farm, hatcheries, and chicken slaughterhouse. In addition, S. enteritidis was found in the hatcheries, broiler farm, and chicken slaughterhouse. In order to obtain the genetic clonality, 22 S. enteritidis isolates were digested with XbaI and analyzed by pulsed-field gel electrohporesis (PFGE). A difference in the PFGE pattern was found to be related to the origin of the integrated broiler operation. These data support the critical need to control Salmonella in breeder farms and hatcheries, and demonstrate important points related to the control of infection in large-scale poultry operations of Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animal Husbandry
Animals
*Chickens
DNA, Bacterial/chemistry/genetics
Electrophoresis, Gel, Pulsed-Field/veterinary
Female
Food Microbiology
Korea/epidemiology
Poultry Diseases/epidemiology/*microbiology/transmission
Salmonella/classification/genetics/*isolation & purification
Salmonella Infections, Animal/epidemiology/*microbiology/transmission
Figure
Reference
-
1. Angen Ø, Skov MN, Chriel M, Agger JF, Bisgaard M. A retrospective study on Salmonella infection in Danish broiler flocks. Prev Vet Med. 1996. 26:223–237.
Article2. Bailey JS. Control of Salmonella and Campylobacter in poultry production. A summary of work at Russell Research Center. Poult Sci. 1993. 72:1169–1173.
Article3. Bailey JS, Cox NA, Craven SE, Cosby DE. Serotype tracking of Salmonella through integrated broiler chicken operations. J Food Prot. 2002. 65:742–745.
Article4. Bale MJ, Bennett PM, Beringer JE, Hinton M. The survival of bacteria exposed to desiccation on surfaces associated with farm buildings. J Appl Bacteriol. 1993. 75:519–528.
Article5. Baumler AJ, Hargis BM, Tsolis RM. Tracing the origins of Salmonella outbreaks. Science. 2000. 287:50–52.6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Standardized Molecular Subtyping of Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis. 2000. Atlanta: National Center for Infectious Disease.7. Corry JEL, Allen VM, Hudson WR, Breslin MF, Davies RH. Sources of Salmonella on broiler carcasses during transportation and processing: modes of contamination and methods of control. J Appl Microbiol. 2002. 92:424–432.
Article8. Cox NA, Bailey JS, Berrang ME. Bactericidal treatment of hatching eggs I. chemical immersion treatments and Salmonella. J Appl Poult Res. 1998. 7:347–350.
Article9. Davies R, Breslin M. Environmental contamination and detection of Salmonella enterica serovar enteritidis in laying flocks. Vet Rec. 2001. 149:699–704.
Article10. Davies RH, Nicholas RAJ, McLaren IM, Corkish JD, Lanning DG, Wray C. Bacteriological and serological investigation of persistent Salmonella enteritidis infection in an integrated poultry organisation. Vet Microbiol. 1997. 58:277–293.
Article11. Davies RH, Wray C. An approach to reduction of Salmonella infection in broiler chicken flocks through intensive sampling and identification of cross-contamination hazards in commercial hatcheries. Int J Food Microbiol. 1994. 24:147–160.
Article12. Gast RK. Understanding Salmonella enteritidis in laying chickens: the contributions of experimental infections. Int J Food Microbiol. 1994. 21:107–116.
Article13. Holt PS, Gast RK, Porter RE Jr, Stone HD. Hyporesponsiveness of the systemic and mucosal humoral immune systems in chickens infected with Salmonella enterica serovar enteritidis at one day of age. Poult Sci. 1999. 78:1510–1517.
Article14. Keller LH, Schifferli DM, Benson CE, Aslam S, Eckroade RJ. Invasion of chicken reproductive tissues and forming eggs is not unique to Salmonella enteritidis. Avian Dis. 1997. 41:535–539.
Article15. Lachoncha I, Baggesen DL, Rementeria A, Garaizar J. Genotypic characterisation by PFGE of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis phage types 1, 4, 6, and 8 isolated from animal and human sources in three European countries. Vet Microbiol. 2000. 75:155–165.16. Lahellec C, Colin P. Relationship between serotypes of Salmonellae from hatcheries and rearing farms and those from processed poultry carcases. Br Poult Sci. 1985. 26:179–186.
Article17. Mackey BM, Derrick CM. The effect of sublethal injury by heating, freezing, drying and gamma radiation on the duration of the lag phase of Salmonella typhimurium. J Appl Bacteriol. 1982. 53:243–251.18. O'Brien JPD. Aspect of Salmonella enteritidis control in poultry. Worlds Poult Sci J. 1990. 46:119–124.19. Plym-Forshell L, Ekesbo I. Survival of Salmonellas in urine and dry faeces form cattle-an experimental study. Acta Vet Scand. 1996. 37:127–131.
Article20. Rose N, Beaudeau F, Drouin P, Toux JY, Rose V, Colin P. Risk factors for Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica contamination in French broiler-chicken flocks at the end of the rearing period. Prev Vet Med. 1999. 39:265–277.
Article21. van de Giessen AW, Peters R, Berkers PA, Jansen WH, Notermans SH. Salmonella contamination of poultry flocks in The Netherlands. Vet Q. 1991. 13:41–46.
Article22. Wilson S. Control of Salmonella enteritidis in poultry. Vet Rec. 1989. 125:465–466.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence of Salmonella spp. in pet turtles and their environment
- Usefulness of selenite F enrichment broth for the isolation of Salmonella from stool
- Prevalence of Lawsonia intracellularis, Brachyspira hyodysenteriae and Salmonella in swine herds
- Characteristics of Non-typhoidal Salmonella Isolates from Human and Broiler-chickens in Southwestern Seoul, Korea
- Application of SYBR Green real-time PCR assay for the specific detection of Salmonella spp