Korean J Radiol.
2007 Dec;8(6):466-474. 10.3348/kjr.2007.8.6.466.
A Correlation between the Severity of Lung Lesions on Radiographs and Clinical Findings in Patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Imaging and Intervention, Chang Gung Memorial at Linkou, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, 5 Fuhsing Rd., Kweishan, Taoyuan, Taiwan. ylw0518@adm.cgmh.org.tw
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chang Gung Memorial at Linkou, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, 5 Fuhsing Rd., Kweishan, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
- 3Department of Clinical Pathology, Chang Gung Memorial at Linkou, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, 5 Fuhsing Rd., Kweishan, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Chang Gung Memorial at Linkou, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, 5 Fuhsing Rd., Kweishan, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
- 5Department of Public Health and Center of Biostatistics, Chang Gung University, 259 Wonhua 1st Rd., Kweishan, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
- KMID: 1089433
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2007.8.6.466
Abstract
- OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this study was to quantify lesions on chest radiographs in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and analyze the severity of the lesions with clinical parameters. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Two experienced radiologists reviewed chest radiographs of 28 patients with SARS. Each lung was divided into upper, middle, and lower zones. A SARS-related lesion in each zone was scored using a four-point scale: zero to three. The mean and maximal radiographic scores were analyzed statistically to determine if the scorings were related to the laboratory data and clinical course. RESULTS: Forward stepwise multiple linear regression showed that the mean radiographic score correlated most significantly with the number of hospitalized days (p < 0.001). The second most significant factor was the absolute lymphocyte count (p < 0.001) and the third most significant factor was the number of days of intubation (p = 0.025). The maximal radiographic score correlated best with the percentage of lymphocytes in a leukocyte count (p < 0.001), while the second most significant factor was the number of hospitalized days (p < 0.001) and the third most significant factor was the absolute lymphocyte count (p = 0.013). The mean radiographic scores of the patients who died, with comorbidities and without a comorbidity were 11.1, 6.3 and 2.9, respectively (p = 0.032). The corresponding value for maximal radiographic scores were 17.7, 9.7 and 6.0, respectively (p = 0.033). CONCLUSION: The severity of abnormalities quantified on chest radiographs in patients with SARS correlates with the clinical parameters.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Biological Markers/blood
Blood Gas Analysis/statistics & numerical data
Female
Humans
Intubation, Intratracheal/statistics & numerical data
Length of Stay
Lung/*radiography
Lymphocyte Count/statistics & numerical data
Male
Middle Aged
Observer Variation
Predictive Value of Tests
Prognosis
Retrospective Studies
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome/blood/*diagnosis/mortality
Severity of Illness Index
Survival Analysis
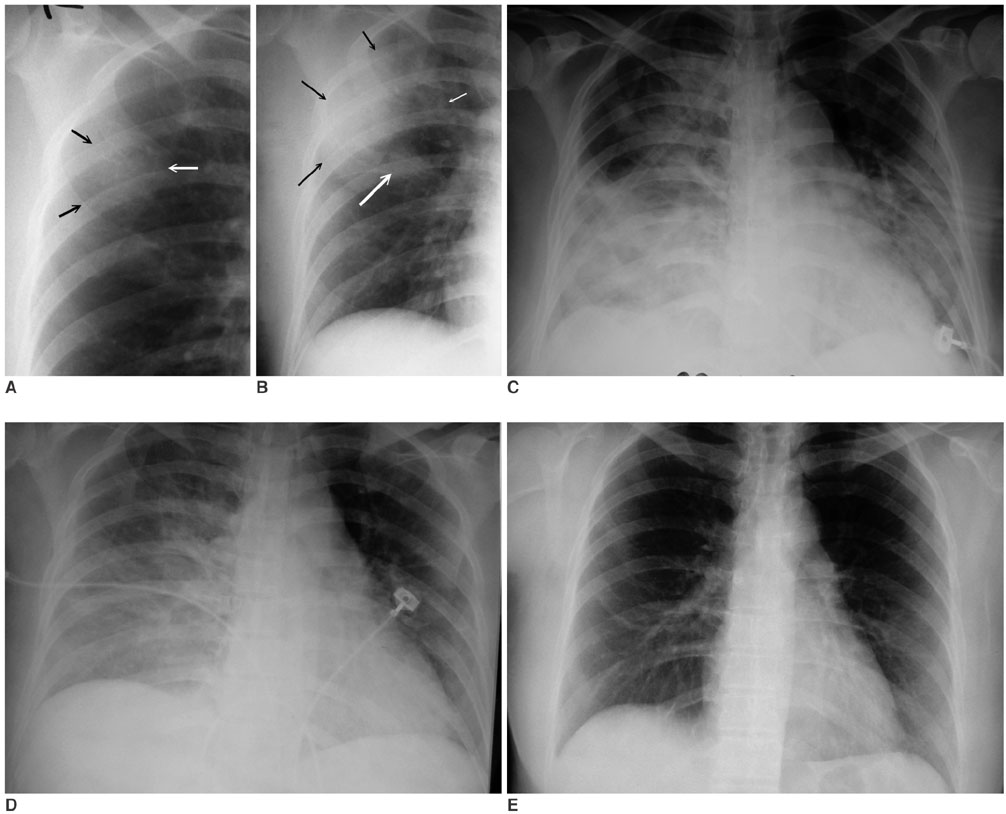
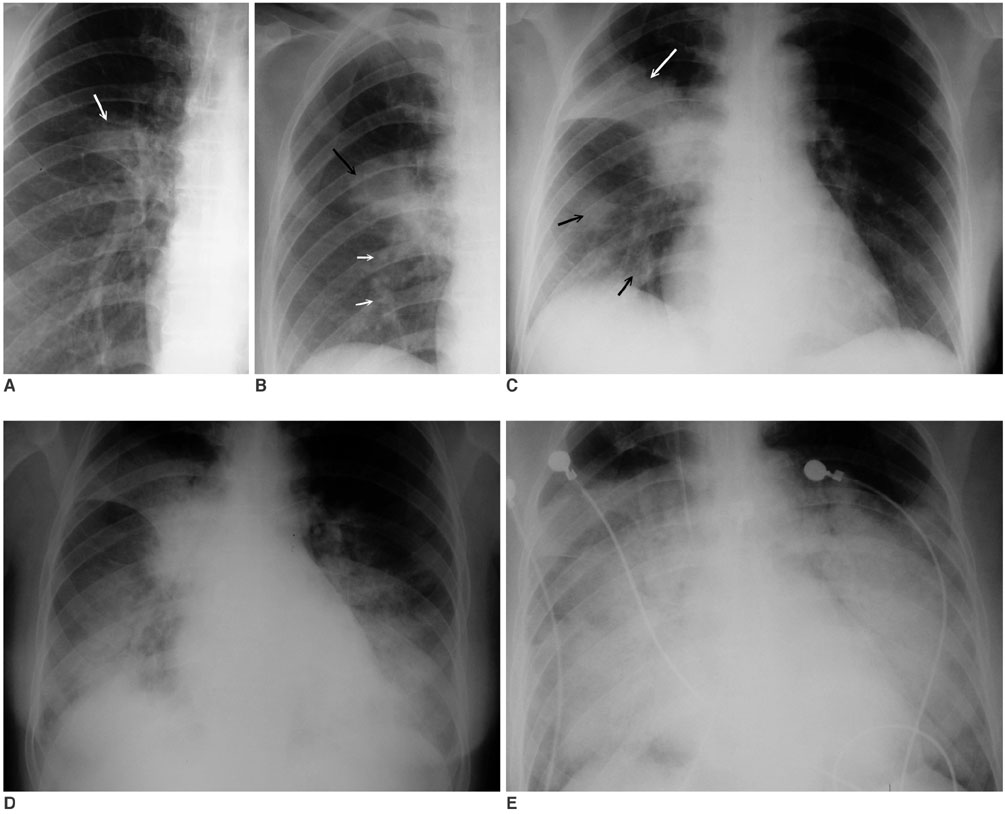
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Chest Radiographic and CT Findings of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Analysis of Nine Patients Treated in Korea
Soon Ho Yoon, Kyung Hee Lee, Jin Yong Kim, Young Kyung Lee, Hongseok Ko, Ki Hwan Kim, Chang Min Park, Yun-Hyeon Kim
Korean J Radiol. 2020;21(4):494-500. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0132.
Reference
-
1. Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, Zaki SR, Peret T, Emery S, et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:1953–1966.2. Peiris JS, Lai ST, Poon LL, Guan Y, Yam LY, Lim W, et al. Coronavirus as a possible cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet. 2003. 361:1319–1325.3. Drosten C, Gunther S, Preiser W, van der Werf S, Brodt HR, Becker S, et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:1967–1976.4. Wan YL, Kuo HP, Tsai YH, Wu YK, Wang CH, Liu CY, et al. Eight cases of severe acute respiratory syndrome presenting as round pneumonia. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 182:1567–1570.5. Lee N, Hui D, Wu A, Chan P, Cameron P, Joynt GM, et al. A major outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:1986–1994.6. Peiris JS, Chu CM, Cheng VC, Chan KS, Hung IF, Poon LL, et al. Clinical progression and viral load in a community outbreak of coronavirus-associated severe acute respiratory syndrome pneumonia: a prospective study. Lancet. 2003. 361:1767–1772.7. Poutanen SM, Low DE, Henry B, Finkelstein S, Rose D, Green K, et al. Identification of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Canada. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:1995–2005.8. Hsu LY, Lee CC, Green JA, Ang B, Paton NI, Lee L, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Singapore: clinical features of index patient and initial contacts. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003. 9:713–717.9. Booth CM, Matukas LM, Tomlinson GA, Rachlis AR, Rose DB, Dwosh HA, et al. Clinical features and short-term outcomes of 144 patients with SARS in the greater Toronto area. JAMA. 2003. 289:2801–2809.10. Wong KT, Antonio GE, Hui DS, Lee N, Yuen EH, Wu A, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome: radiographic appearances and pattern of progression in 138 patients. Radiology. 2003. 228:401–406.11. Wong KT, Antonio GE, Hui DS, Lee N, Yuen EH, Wu A, et al. Thin-Section CT of severe acute respiratory syndrome: evaluation of 73 patients exposed to or with the disease. Radiology. 2003. 228:395–400.12. Nicolaou S, Al-Nakshabandi NA, Muller NL. SARS: Imaging of severe acute respiratory syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 180:1247–1249.13. Muller N, Ooi GC, Khong PL, Nicolaou S. Severe acute respiratory syndrome: radiographic and CT findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 181:3–8.14. Grinblat L, Shulman H, Glickman A, Matukas L, Paul N. Severe acute respiratory syndrome: radiographic review of 40 probable cases in Toronto, Canada. Radiology. 2003. 228:802–809.15. Paul NS, Roberts H, Butany J, Chung T, Gold W, Mehta S, et al. Radiologic pattern of disease in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome: the Toronto experience. Radiographics. 2004. 24:553–563.16. Antonio GE, Wong KT, Hui DS, Wu A, Lee N, Yuen EH, et al. Thin-section CT in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome following hospital discharge: preliminary experience. Radiology. 2003. 228:810–815.17. Zou Z, Yang Y, Chen J, Xin S, Zhang W, Zhou X, et al. Prognostic factors for severe acute respiratory syndrome: a clinical analysis of 165 cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 38:483–489.18. Choi KW, Chau TN, Tsang O, Tso E, Chiu MC, Tong WL, et al. Outcomes and prognostic factors in 267 patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. Ann Intern Med. 2003. 139:715–723.19. Chan JW, Ng CK, Chan YH, Mok TY, Lee S, Chu SY, et al. Short term outcome and risk factors for adverse clinical outcomes in adults with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Thorax. 2003. 58:686–689.20. Tsui PT, Kwok ML, Yuen H, Lai ST. Severe acute respiratory syndrome: clinical outcome and prognostic correlates. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003. 9:1064–1069.21. Chan KS, Zheng JP, Mok YW, Li YM, Liu YN, Chu CM, et al. SARS: prognosis, outcome and sequelae. Respirology. 2003. 8:S36–S40.22. Booth CM, Matukas LM, Tomlinson GA, Rachlis AR, Rose DB, Dwosh HA, et al. Clinical features and short-term outcomes of 144 patients with SARS in the greater Toronto area. JAMA. 2003. 289:2801–2809.23. Ng EK, Hui DS, Chan KC, Hung EC, Chiu RW, Lee N, et al. Quantitative analysis and prognostic implication of SARS coronavirus RNA in the plasma and serum of patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Clin Chem. 2003. 49:1976–1980.24. Tan YM, Chow PK, Soo KC. Severe acute respiratory syndrome: clinical outcome after inpatient outbreak of SARS in Singapore. BMJ. 2003. 326:1394.25. Wong KT, Antonio GE, Hui DS, Ho C, Chan PN, Ng WH, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome: thin-section computed tomography features, temporal changes, and clinicoradiologic correlation during the convalescent period. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2004. 28:790–795.26. Wang CH, Liu CY, Wan YL, Chou CL, Huang KH, Lin HC, et al. Persistence of lung inflammation and lung cytokines with high-resolution CT abnormalities during recovery from SARS. Respir Res. 2005. 6:42.27. Antonio GE, Ooi CG, Wong KT, Tsui EL, Wong JS, Sy AN, et al. Radiographic-clinical correlation in severe acute respiratory syndrome: study of 1373 patients in Hong Kong. Radiology. 2005. 237:1081–1090.28. Lai EK, Deif H, LaMere EA, Pham DH, Wolff B, Ward S, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome: quantitative assessment from chest radiographs with clinical and prognostic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005. 184:255–263.29. Ooi CG, Khong PL, Lam B, Ho JC, Yiu WC, Wong WM, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome: relationship between radiologic and clinical parameters. Radiology. 2003. 229:492–499.30. Ooi CG, Khong PL, Ho JC, Lam B, Wong WM, Yiu WC, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome: radiographic evaluation and clinical outcome measures. Radiology. 2003. 229:500–506.31. Paul NS, Chung T, Konen E, Roberts HC, Rao TN, Gold WL, et al. Prognostic significance of the radiographic pattern of disease in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 182:493–498.32. Ko SF, Lee TY, Huang CC, Cheng YF, Ng SH, Kuo YL, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome: prognostic implications of chest radiographic findings in 52 patients. Radiology. 2004. 233:173–181.33. Chang YC, Yu CJ, Chang SC, Galvin JR, Liu HM, Hsiao CH, et al. Pulmonary sequelae in convalescent patients after severe acute respiratory syndrome: evaluation with thin-section CT. Radiology. 2005. 236:1067–1075.34. Antonio GE, Wong KT, Tsui EL, Chan DP, Hui DS, Ng AW, et al. Chest radiograph scores as potential prognostic indicators in severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005. 184:734–741.35. Hui DS, Wong KT, Antonio GE, Lee N, Wu A, Wong V, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome: correlation between clinical outcome and radiologic features. Radiology. 2004. 233:579–585.36. Chau TN, Lee PO, Choi KW, Lee CM, Ma KF, Tsang TY, et al. Value of initial chest radiographs for predicting clinical outcomes in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Am J Med. 2004. 117:249–254.37. Hsieh SC, Chan WP, Chien JC, Lee WS, Yao MS, Choi WM, et al. Radiographic appearance and clinical outcome correlates in 26 patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 182:1119–1122.38. Chu WC, Li AM, Ng AW, So HK, Lam WW, Lo KL, et al. Thin-section CT 12 months after the diagnosis of severe acute respiratory syndrome in pediatric patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 186:1707–1714.39. Peiris JS, Chu CM, Cheng VC, Chan KS, Hung IF, Poon LL, et al. Clinical progression and viral load in a community outbreak of corona-associated SARS pneumonia: a prospective study. Lancet. 2003. 361:1767–1772.40. Wong RS, Wu A, To KF, Lee N, Lam CW, Wong CK, et al. Haematological manifestations in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome: retrospective analysis. BMJ. 2003. 326:1358–1362.