Korean J Radiol.
2009 Feb;10(1):34-42. 10.3348/kjr.2009.10.1.34.
Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation for the Hepatocellular Carcinoma Abutting the Diaphragm: Assessment of Safety and Therapeutic Efficacy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. rhimhc@skku.edu
- KMID: 1088676
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2009.10.1.34
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
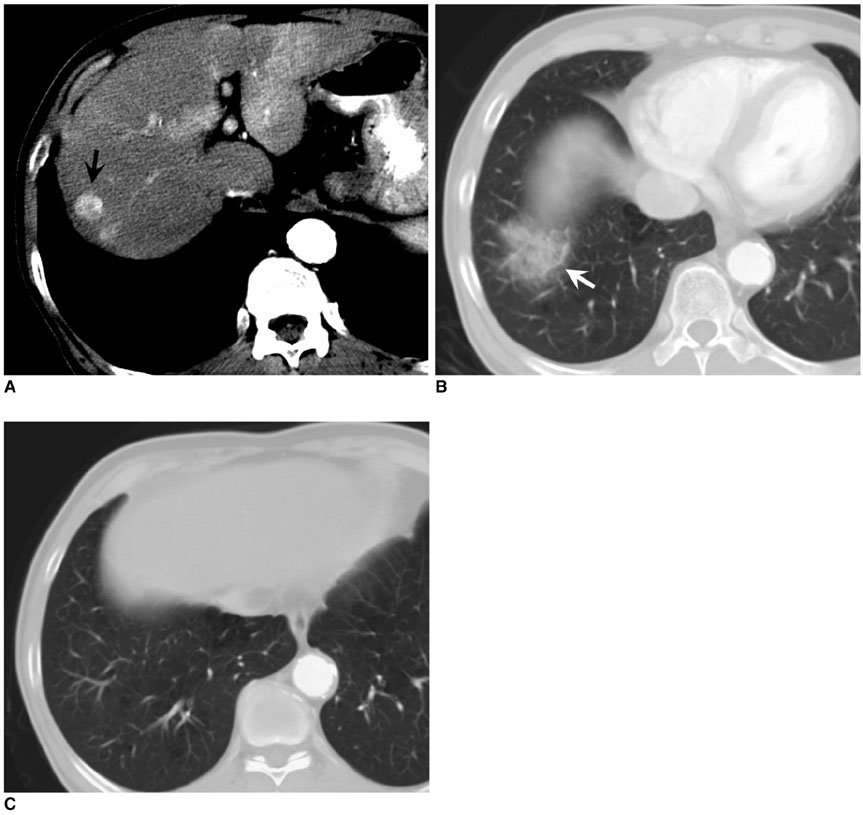
To assess the safety and therapeutic efficacy of a percutaneous radiofrequency (RF) ablation for the hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) abutting the diaphragm. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We retrospectively assessed 80 patients who underwent a percutaneous RF ablation for a single nodular (< 4 cm) HCC over the last four years. Each patient underwent an ultrasound-guided RF ablation using internally cooled electrodes for the first-line treatment. We divided patients into two subgroups based on whether the index tumor was abutting (less than 5 mm) the diaphragm or not: group A (abutting; n = 31) versus group B (non-abutting; n = 49). We compared the two subgroups for complications and therapeutic efficacy using image and the review of medical records. The statistical assessment included an independent t-test, Fisher's exact test, and chi-square test. RESULTS: The assessment of the diaphragmatic swelling at CT immediately following the procedure was more severe in group A than group B (mean thickness change:1.44 vs. 0.46 mm, p = 0.00). Further, right shoulder pain was more common in group A than B (p = 0.01). Although minor complications (hemothorax 1 case, pleural effusion 1 case) were noted only in group A, no major thoracic complication occurred in either group. The technical success rate was lower in group A than group B (84% vs. 98%, p = 0.03). As well, the primary and secondary technique effectiveness rates in group A and group B were 90% versus 98% (p = 0.29) and 79% versus 91% (p = 0.25), respectively. The local tumor progression rate was higher in group A than in group B (29% vs. 6%, p = 0.02). CONCLUSION: We found that the percutaneous RF ablation for the HCC abutting the diaphragm is a safe procedure without major complications. However, it is less effective with regard to technical success and local tumor control.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation with Multiple Electrodes for Medium-Sized Hepatocellular Carcinomas
Jung Lee, Jeong Min Lee, Jung-Hwan Yoon, Jae Young Lee, Se Hyung Kim, Jeong Eun Lee, Joon Koo Han, Byung Ihn Choi
Korean J Radiol. 2012;13(1):34-43. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.1.34.Moving-Shot versus Fixed Electrode Techniques for Radiofrequency Ablation: Comparison in an
Ex-Vivo Bovine Liver Tissue Model
Eun Ju Ha, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee
Korean J Radiol. 2014;15(6):836-843. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.836.
Reference
-
1. Iannitti DA, Dupuy DE, Mayo-Smith WW, Murphy B. Hepatic radiofrequency ablation. Arch Surg. 2002. 137:422–426.2. Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Ierace T, Solbiati L, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: radio-frequency ablation of medium and large lesions. Radiology. 2000. 214:761–768.3. Chen MH, Yang W, Yan K, Gao W, Dai Y, Wang YB, et al. Treatment efficacy of radiofrequency ablation of 338 patients with hepatic malignant tumor and the relevant complications. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. 11:6395–6401.4. de Baere T, Risse O, Kuoch V, Dromain C, Sengel C, Smayra T, et al. Adverse events during radiofrequency treatment of 582 hepatic tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 181:695–700.5. Rhim H, Dodd GD 3rd, Chintapalli KN, Wood BJ, Dupuy DE, Hvizda JL, et al. Radiofrequency thermal ablation of abdominal tumors: lessons learned from complications. Radiographics. 2004. 24:41–52.6. Rhim H, Yoon KH, Lee JM, Cho Y, Cho JS, Kim SH, et al. Major complications after radio-frequency thermal ablation of hepatic tumors: spectrum of imaging findings. Radiographics. 2003. 23:123–134.7. Choi D, Lim HK, Kim MJ, Kim SH, Lee WJ, Kim SH, et al. Therapeutic efficacy and safety of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma abutting the gastrointestinal tract. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 183:1417–1424.8. Livraghi T, Solbiati L, Meloni MF, Gazelle GS, Halpern EF, Goldberg SN. Treatment of focal liver tumors with percutaneous radio-frequency ablation: complications encountered in a multicenter study. Radiology. 2003. 226:441–451.9. Ohmoto K, Tsuduki M, Shibata N, Takesue M, Kunieda T, Yamamoto S. Percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma located on the surface of the liver. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999. 173:1231–1233.10. Ohmoto K, Yamamoto S. Percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy for superficial hepatocellular carcinoma on the liver surface. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000. 95:2401–2403.11. Hori T, Nagata K, Hasuike S, Onaga M, Motoda M, Moriuchi A, et al. Risk factors for the local recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after a single session of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. J Gastroenterol. 2003. 38:977–981.12. Komorizono Y, Oketani M, Sako K, Yamasaki N, Shibatou T, Maeda M, et al. Risk factors for local recurrence of small hepatocellular carcinoma tumors after a single session, single application of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Cancer. 2003. 97:1253–1262.13. Kim YJ, Raman SS, Yu NC, Busuttil RW, Tong M, Lu DS. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: can subcapsular tumors be safely ablated? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008. 190:1029–1034.14. Koda M, Ueki M, Maeda N, Murawaki Y. Diaphragmatic perforation and hernia after hepatic radiofrequency ablation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 180:1561–1562.15. Rhim H, Lim HK, Kim YS, Choi D. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation with artificial ascites for hepatocellular carcinoma in the hepatic dome: initial experience. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008. 190:91–98.16. Teratani T, Yoshida H, Shiina S, Obi S, Sato S, Tateishi R, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in so-called high-risk locations. Hepatology. 2006. 43:1101–1108.17. Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF, Charboneau JW, Dodd GD 3rd, Dupuy DE, et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. Radiology. 2005. 235:728–739.18. Bolser DC, Hobbs SF, Chandler MJ, Ammons WS, Brennan TJ, Foreman RD. Convergence of phrenic and cardiopulmonary spinal afferent information on cervical and thoracic spinothalamic tract neurons in the monkey: implications for referred pain from the diaphragm and heart. J Neurophysiol. 1991. 65:1042–1054.19. Demling RH. The burn edema process: current concepts. J Burn Care Rehabil. 2005. 26:207–227.20. Lund T, Onarheim H, Reed RK. Pathogenesis of edema formation in burn injuries. World J Surg. 1992. 16:2–9.21. Head HW, Dodd GD 3rd, Dalrymple NC, Prasad SR, El-Merhi FM, Freckleton MW, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors against the diaphragm: frequency of diaphragmatic injury. Radiology. 2007. 243:877–884.22. Cho YK, Rhim H, Ahn YS, Kim MY, Lim HK. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma using multitined expandable electrodes: comparison of subcapsular and nonsubcapsular tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 186:S269–S274.23. Sartori S, Tombesi P, Macario F, Nielsen I, Tassinari D, Catellani M, et al. Subcapsular liver tumors treated with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: a prospective comparison with nonsubcapsular liver tumors for safety and effectiveness. Radiology. 2008. 248:670–679.24. Kapoor BS, Hunter DW. Injection of subphrenic saline during radiofrequency ablation to minimize diaphragmatic injury. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2003. 26:302–304.25. Kim YS, Rhim H, Paik SS. Radiofrequency ablation of the liver in a rabbit model: creation of artificial ascites to minimize collateral thermal injury to the diaphragm and stomach. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006. 17:541–547.26. Minami Y, Kudo M, Kawasaki T, Chung H, Ogawa C, Shiozaki H. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation guided by contrast-enhanced harmonic sonography with artificial pleural effusion for hepatocellular carcinoma in the hepatic dome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 182:1224–1226.27. Ohmoto K, Tsuzuki M, Yamamoto S. Percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy with intraperitoneal saline infusion for hepatocellular carcinoma in the hepatic dome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999. 172:65–66.28. Raman SS, Aziz D, Chang X, Sayre J, Lassman C, Lu D. Minimizing diaphragmatic injury during radiofrequency ablation: efficacy of intraabdominal carbon dioxide insufflation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 183:197–200.29. Raman SS, Lu DS, Vodopich DJ, Sayre J, Lassman C. Minimizing diaphragmatic injury during radio-frequency ablation: efficacy of subphrenic peritoneal saline injection in a porcine model. Radiology. 2002. 222:819–823.30. Koda M, Ueki M, Maeda Y, Mimura K, Okamoto K, Matsunaga Y, et al. Percutaneous sonographically guided radiofrequency ablation with artificial pleural effusion for hepatocellular carcinoma located under the diaphragm. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 183:583–588.31. Iochum S, Ludig T, Walter F, Sebbag H, Grosdidier G, Blum AG. Imaging of diaphragmatic injury: a diagnostic challenge? Radiographics. 2002. 22:S103–S116.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Percutaneous cryoablation for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Completely Ablated Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Percutaneous Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation
- Current status and future of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma
- The Role of Combination of Transarterial Chemoebolization and Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment
- Microwave thermosphere versus radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Are we approaching the time to end the debate?