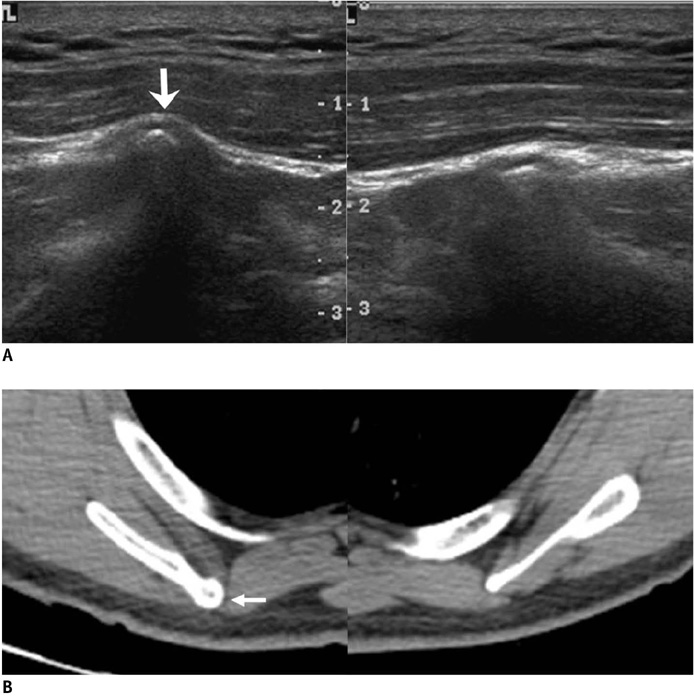
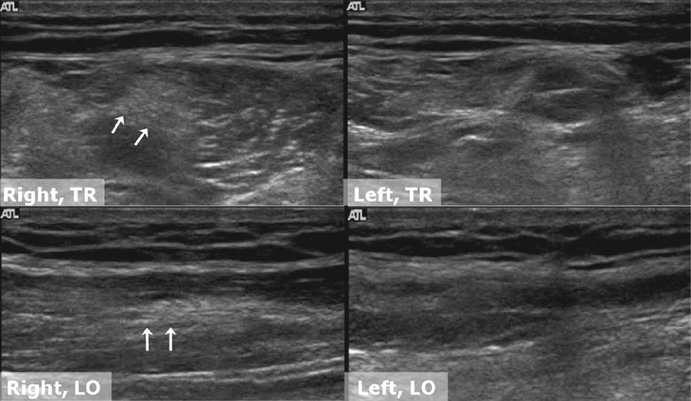
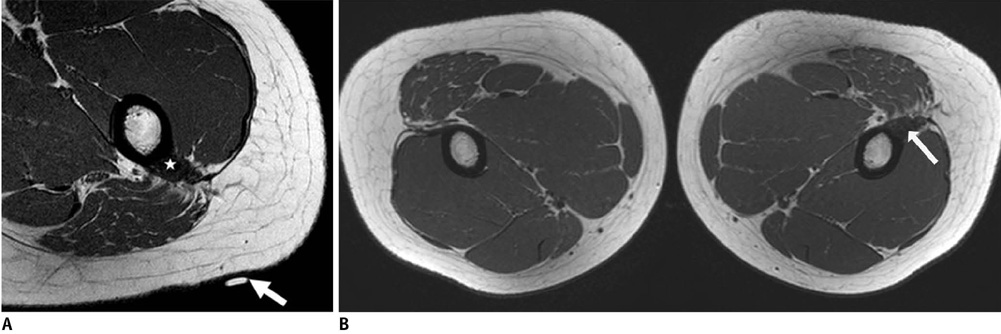
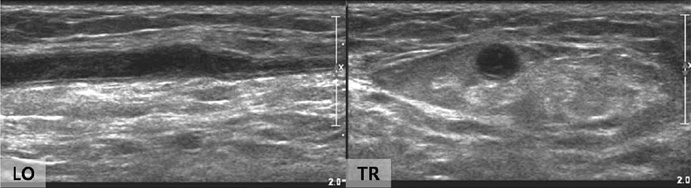
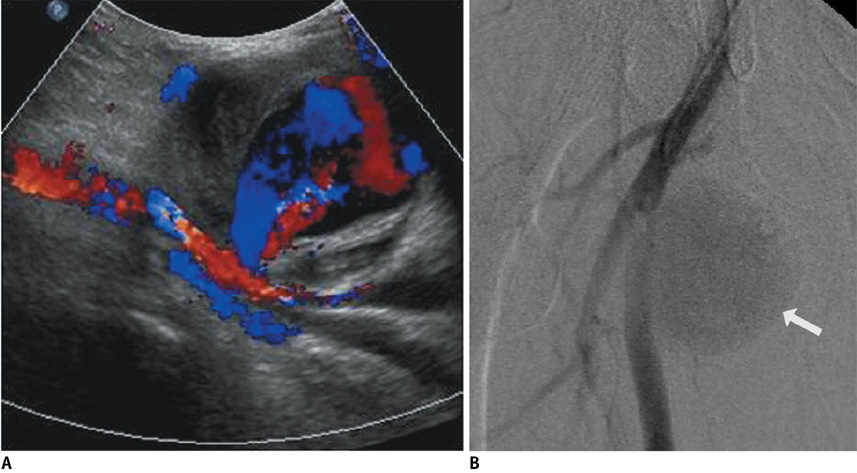
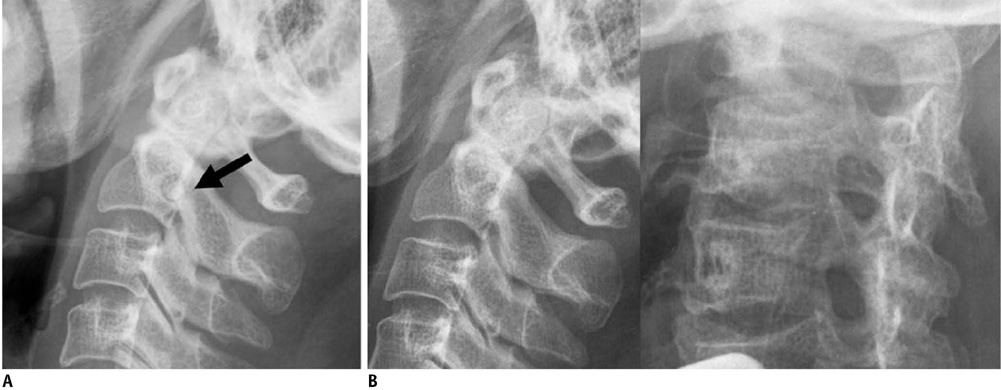
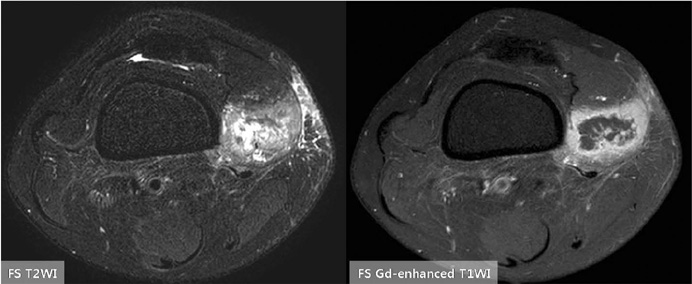
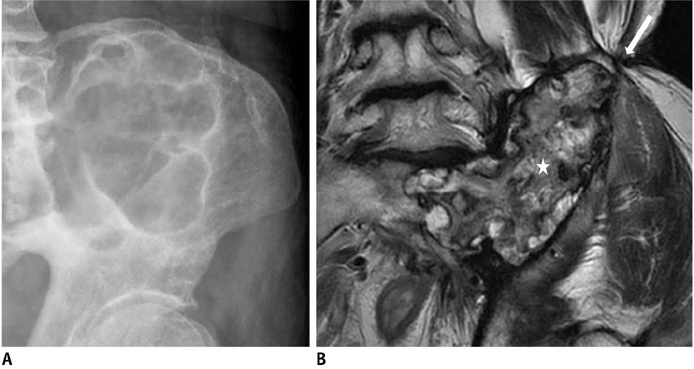
Korean J Radiol.
2011 Apr;12(2):220-231. 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.2.220.
Various Tumor-Mimicking Lesions in the Musculoskeletal System: Causes and Diagnostic Approach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Seoul 130-702, Korea. gdluck@hitel.net
- 2Department of Radiology, East-West Neo Medical Center, Kyung Hee University, Seoul 134-727, Korea.
- KMID: 1088568
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.2.220
Abstract
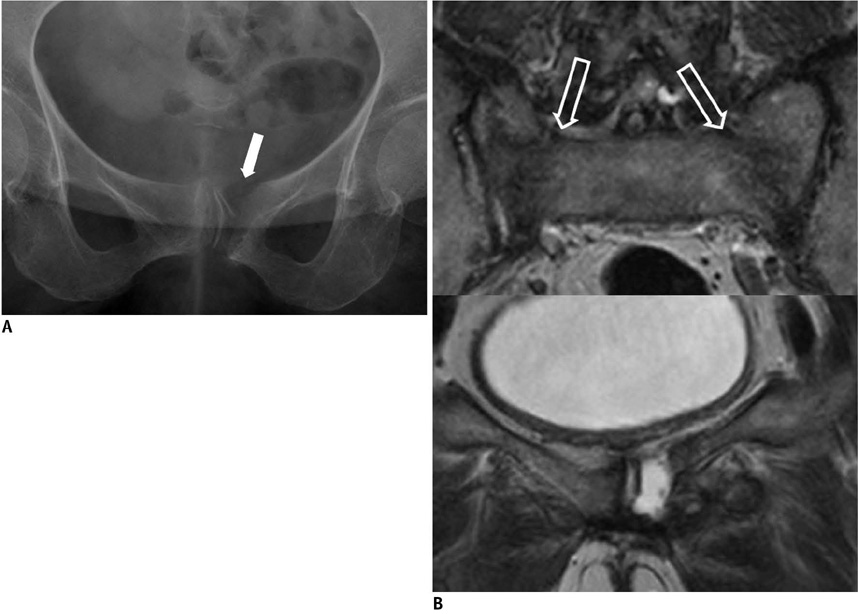
- Tumor-mimicking lesions in the musculoskeletal system can be defined as lesions mistaken as tumors due to the presence of palpation upon physical examination or a tumor-like appearance upon radiological examination. Moreover, tumor-mimicking lesions show diverse etiologies and anatomic locations. We illustrated the various tumor-mimicking lesions involving bone and soft tissue. In this review, the tumor-mimicking lesions were classified into those based on clinical examination and those based on radiological examination in musculoskeletal radiology. Awareness of the various causes of tumor-mimicking lesions, correctly obtaining clinical information, and the proper selection of imaging modality are important for the differentiation of tumor-mimicking lesions from true neoplasms.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
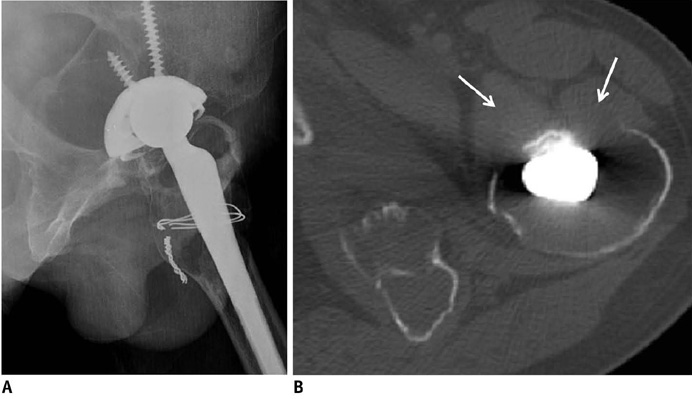
1. Vessal S, Rai SB. Accessory extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle, a pseudomass of the distal forearm: ultrasound and MR appearances - case report and literature review. Clin Radiol. 2006. 61:442–445.2. Mattle HP, Hess CW, Ludin HP, Mumenthaler M. Isolated muscle hypertrophy as a sign of radicular or peripheral nerve injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991. 54:325–329.3. Polesuk BS, Helms CA. Hypertrophied palmaris longus muscle, a pseudomass of the forearm: MR appearance--case report and review of the literature. Radiology. 1998. 207:361–362.4. Anderson MW, Benedetti P, Walter J, Steinberg DR. MR appearance of the extensor digitorum manus brevis muscle: a pseudotumor of the hand. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995. 164:1477–1479.5. Capelastegui A, Astigarraga E, Fernandez-Canton G, Saralegui I, Larena JA, Merino A. Masses and pseudomasses of the hand and wrist: MR findings in 134 cases. Skeletal Radiol. 1999. 28:498–507.6. Kalbermatten DF, Kalbermatten NT, Hertel R. Cotton-induced pseudotumor of the femur. Skeletal Radiol. 2001. 30:415–417.7. Resnick D. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders. 1995. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders.8. Mellado JM, Ramos A, Salvadó E, Camins A, Danús M, Saurí A. Accessory ossicles and sesamoid bones of the ankle and foot: imaging findings, clinical significance and differential diagnosis. Eur Radiol. 2003. 13:Suppl 6. L164–L177.9. Anderson SE, Johnston JO, Steinbach LS. Pseudotumors of the shoulder invited review. Eur J Radiol. 2008. 68:147–158.10. Useche JN, de Castro AM, Galvis GE, Mantilla RA, Ariza A. Use of US in the evaluation of patients with symptoms of deep venous thrombosis of the lower extremities. Radiographics. 2008. 28:1785–1797.11. Ramon FA, Degryse HR, De Schepper AM, Van Marck EA. Calcific tendinitis of the vastus lateralis muscle. A report of three cases. Skeletal Radiol. 1991. 20:21–23.12. Thiele RG, Schlesinger N. Diagnosis of gout by ultrasound. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007. 46:1116–1121.13. Schwartzfarb EM, Hametti JM, Romanelli P, Ricotti C. Foreign body granuloma formation secondary to silicone injection. Dermatol Online J. 2008. 14:20.14. Catalano OA, Dal Pozzo F, Grifi DN, Menchi I, Rosenthal DI. Paraffinoma of the knee. Skeletal Radiol. 2003. 32:485–488.15. De Wilde V, De Maeseneer M, Lenchik L, Van Roy P, Beeckman P, Osteaux M. Normal osseous variants presenting as cystic or lucent areas on radiography and CT imaging: a pictorial overview. Eur J Radiol. 2004. 51:77–84.16. Hammond I, Sheikh A, Rasuli P, Souza CA. Vertebral pseudolesion on lateral chest radiograph. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008. 190:W240–W241.17. Kransdorf MJ, Meis JM. From the archives of the AFIP. Extraskeletal osseous and cartilaginous tumors of the extremities. Radiographics. 1993. 13:853–884.18. De Smet AA, Norris MA, Fisher DR. Magnetic resonance imaging of myositis ossificans: analysis of seven cases. Skeletal Radiol. 1992. 21:503–507.19. Kransdorf MJ, Meis JM, Jelinek JS. Myositis ossificans: MR appearance with radiologic-pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991. 157:1243–1248.20. Gaeta M, Mazziotti S, Minutoli F, Genitori A, Toscano A, Rodolico C, et al. MR imaging findings of focal myositis: a pseudotumour that may mimic muscle neoplasm. Skeletal Radiol. 2009. 38:571–578.21. Kransdorf MJ, Temple HT, Sweet DE. Focal myositis. Skeletal Radiol. 1998. 27:283–287.22. Son JM, Jee WH, Jung CK, Kim SI, Ha KY. Aspergillus spondylitis involving the cervico-thoraco-lumbar spine in an immunocompromised patient: a case report. Korean J Radiol. 2007. 8:448–451.23. Urban BA, Fishman EK, Goldman SM, Scott WW Jr, Jones B, Humphrey RL, et al. CT evaluation of amyloidosis: spectrum of disease. Radiographics. 1993. 13:1295–1308.24. Park JS, Ryu KN, Hong HP, Park YK, Chun YS, Yoo MC. Focal osteolysis in total hip replacement: CT findings. Skeletal Radiol. 2004. 33:632–640.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Musculoskeletal Applications of Elastography: a Pictorial Essay of Our Initial Experience
- Incidental Musculoskeletal Lesions Detected on Abdominopelvic CT Scans: A Pictorial Essay
- Primary Extracranial Meningioma Mimicking Musculoskeletal Malignancy: A Case Report
- Clinical Situations in which Musculoskeletal Ultrasound is Helpful
- Usefulness of strain elastography of the musculoskeletal system