Yonsei Med J.
2010 May;51(3):345-353. 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.3.345.
Non-Invasive Estimation of Systolic Blood Pressure and Diastolic Blood Pressure Using Photoplethysmograph Components
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Engineering, Yonsei University, Wonju, Korea. hryoon@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anesthesiology, Yonsei University, Wonju, Korea.
- 3Department of Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery, Yonsei University, Wonju, Korea.
- KMID: 1074985
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2010.51.3.345
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Photoplethysmography (PPG) is a noninvasive optical technology that detects changes in blood volume in the vascular system. This study aimed to investigate the possibilities of monitoring the cardiovascular system status by using PPG.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
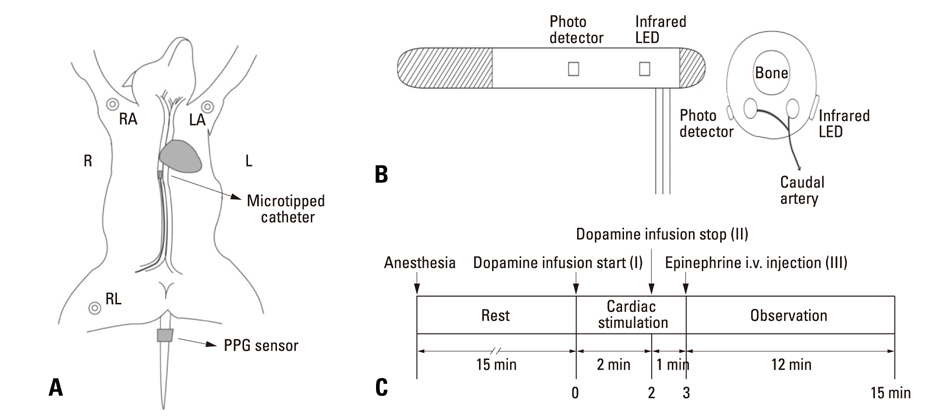
Forced hemodynamic changes were induced using cardiac stimulants; dopamine and epinephrine, and PPG components were recorded by a noninvasive method at the peripheral blood vessels. The results were compared among 6 dogs. Endotracheal intubation was performed after an intramuscular injection of 25 mg/kg ketamine sulfate, and anesthesia was maintained with 2% enflurane. After stabilizing the animals for 15 min, 16 mg/mL diluted dopamine was injected into a vein for 2 min at 20 microgram/kg.min(-1) by using an infusion pump. Thereafter, the infusion pump was stopped, and 1 mg epinephrine was injected intravenously. Fluid administration was controlled to minimize preload change in blood pressure.
RESULTS
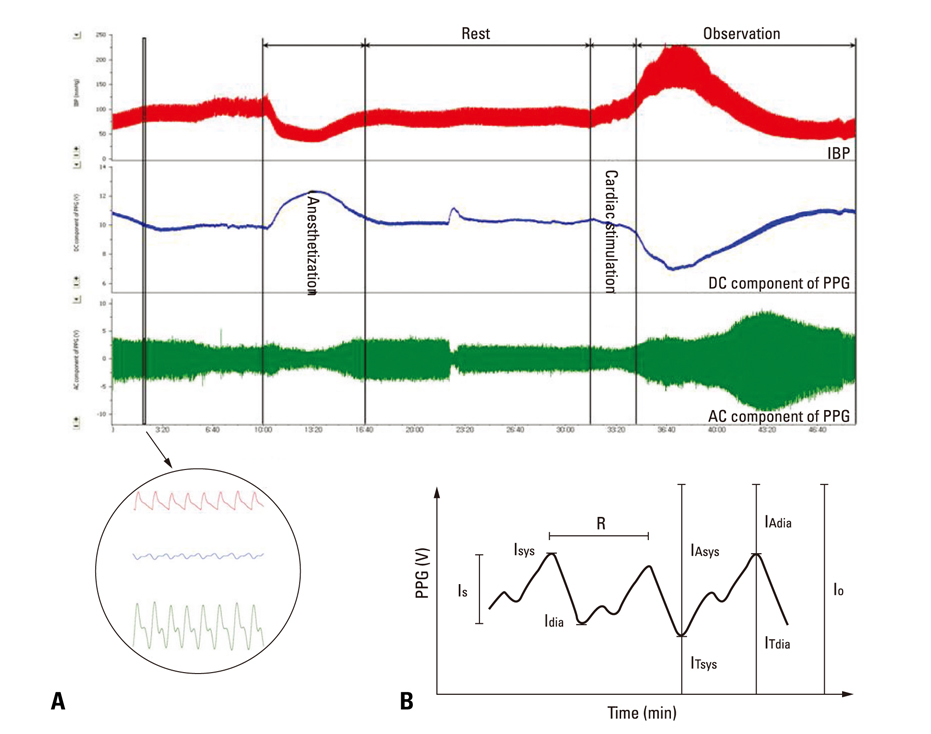
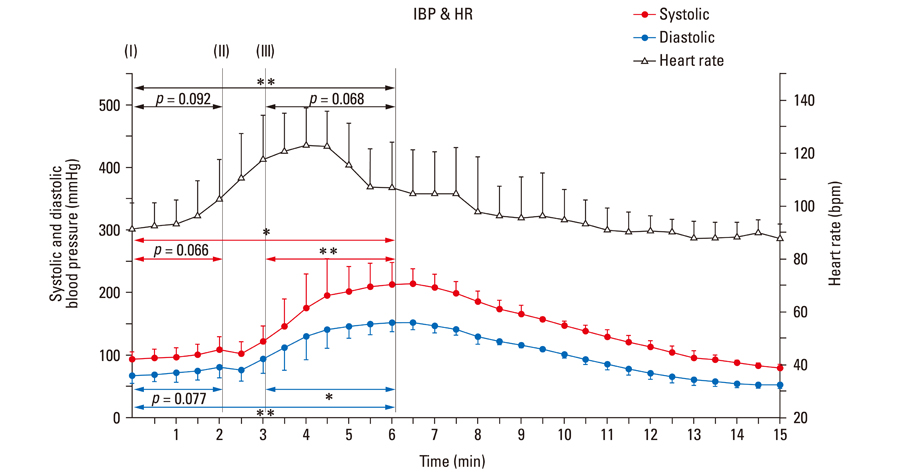
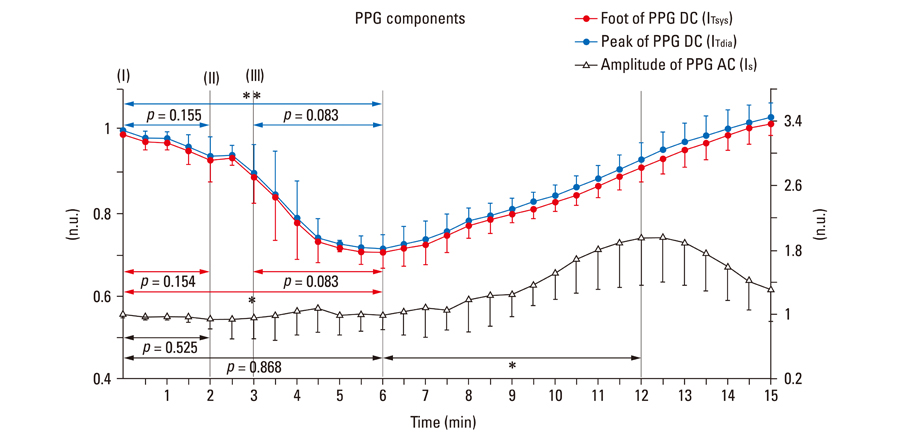
After stimulant administration, systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressures (DBP) increased. The direct current (DC) component, which reflects changes in blood volume, decreased while the alternating current (AC) component, which reflects changes in vascular compliance and resistance, increased. The correlation coefficient between SBP and the foot of the DC component was 0.939 (p < 0.01), while it was 0.942 (p < 0.01) for DBP and the peak of the DC component. The AC component could predict the increase in vascular resistance from a stable pulse blood volume, even with increased pulse pressure. Conclusions: These results support the possibility that PPG components may be used for easy and noninvasive measurement of hemodynamic changes in the cardiovascular system.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Beevers G, Lip GY, O'Brien E. ABC of hypertension: The pathophysiology of hypertension. BMJ. 2001. 322:912–916.
Article2. Pickering TG, Hall JE, Appel LJ, Falkner BE, Graves J, Hill MN, et al. Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals: Part 1: blood pressure measurement in humans: a statement for professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension. 2005. 45:142–161.3. Vander AJ, Sherman JH, Luciano DS. Human Physiology: The mechanisms of body function. 2001. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.4. Allen J, Murray A. Similarity in bilateral photoplethysmographic peripheral pulse wave characteristics at the ears, thumbs and toes. Physiol Meas. 2000. 21:369–377.
Article5. Allen J. Photoplethysmography and its application in clinical physiological measurement. Physiol Meas. 2007. 28:R1–R39.
Article6. Nilsson L, Johansson A, Kalman S. Respiratory variations in the reflection mode photoplethysmographic signal. Relationships to peripheral venous pressure. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2003. 41:249–254.
Article7. Webster JG. Design of Pulse Oximeters. 1997. New York: Taylor & Francis.8. Nitzan M, Vatine JJ, Babchenko A, Khanokh B, Tsenter J, Stessman J. Simultaneous measurement of the photoplethysmographic signal variability in the right and left hands. Lasers Med Sci. 1998. 13:189–195.
Article9. Kraitl J, Ewald H, Gehring H. An optical device to measure blood components by a photoplethysmographic method. J Pure Appl Opt. 2005. 7:S318–S324.
Article10. Teng XF, Zhang YT. The effect of contacting force on photoplethysmographic signals. Physiol Meas. 2004. 25:1323–1335.
Article11. Ito Y, Fujimoto Y, Obara T. The role of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine in blood pressure disturbances in patients with pheochromocytoma. World J Surg. 1992. 16:759–763.
Article12. Hollenberg SM, Ahrens TS, Annane D, Astiz ME, Chalfin DB, Dasta JF, et al. Practice parameters for hemodynamic support of sepsis in adult patients: 2004 update. Crit Care Med. 2004. 32:1928–1948.
Article13. De Backer D, Creteur J, Silva E, Vincent JL. Effects of dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine on the splanchnic circulation in septic shock: which is best? Crit Care Med. 2003. 31:1659–1667.14. Kuchel OG, Kuchel GA. Peripheral dopamine in pathophysiology of hypertension. Interaction with aging and lifestyle. Hypertension. 1991. 18:709–721.
Article15. Blad KD, Lookinland S, Measom G, Bond AE, Williams M. Assessing dopamine concentrations: an evidence-based approach. Am J Crit Care. 2000. 9:130–139.16. Horn PT, Murphy MB. Dopamine receptor agonists in cardiovascular medicine. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1991. 1:103–107.
Article17. Murphy MB, Elliott WJ. Dopamine and dopamine receptor agonists in cardiovascular therapy. Crit Care Med. 1990. 18:S14–S18.
Article18. Lee WJ, Kim KH. Pharmacology of Leewoojoo. 2001. 4th ed. Seoul: Medical Munhaksa.19. Craig CR, Stitzel RE. Modern Pharmacology. 1994. 4th ed. Boston: Little Brown.20. Goldstein DS, Golczynska A, Stuhlmuller J, Holmes C, Rea RF, Grossman E, et al. A test of the "epinephrine hypothesis" in humans. hypertension. 1999. 33:36–43.
Article21. Webb-Peploe MM, Shepherd JT. Responses of the superficial limb veins of the dog to changes in temperature. Circ Res. 1968. 22:737–746.
Article22. Köhler BU, Hennig C, Orglmeister R. The principles of software QRS detection. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 2002. 21:42–57.
Article23. Akselrod S, Gordon D, Madwed JB, Snidman NC, Shannon DC, Cohen RJ. Hemodynamic regulation: investigation by spectral analysis. Am J Physiol. 1985. 249:H867–H875.
Article24. Guyton AC. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 1982. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders.25. Bramwell JC, Hill AV. The velocity of the pulse wave in man. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. 1922. 93:298–306.26. Nitzan M, Babchenko A, Khanokh B. Very low frequency variability in arterial blood pressure and blood volume pulse. Med Biol Eng Comput. 1999. 37:54–58.27. Pinna GD, Maestri R, Mortara A. Estimation of arterial blood pressure variability by spectral analysis: comparison between Finapres and invasive measurements. Physiol Meas. 1996. 17:147–149.
Article28. Wesseling KH. Finger arterial pressure measurement with Finapres. Z Kardiol. 1996. 85:Suppl 3. 38–44.29. Clemmesen JO, Galatius S, Skak C, Dalgaard P, Larsen FS, Ott P. The effect of increasing blood pressure with dopamine on systemic, splanchnic, and lower extremity hemodynamics in patients with acute liver failure. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1999. 34:921–927.30. Shaltis P, Reisner A, Asada H. Calibration of the photoplethysmogram to arterial blood pressure: capabilities and limitations for continuous pressure monitoring. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2005. 4:3970–3973.
Article31. Hashimoto J, Chonan K, Aoki Y, Nishimura T, Ohkubo T, Hozawa A, et al. Pulse wave velocity and the second derivative of the finger photoplethysmogram in treated hypertensive patients: their relationship and associating factors. J Hypertens. 2002. 20:2415–2422.
Article