Yonsei Med J.
2010 Sep;51(5):787-789. 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.5.787.
Left Paraduodenal Hernia Presenting with Atypical Symptoms
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, Korea. linuskim@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 1071435
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2010.51.5.787
Abstract
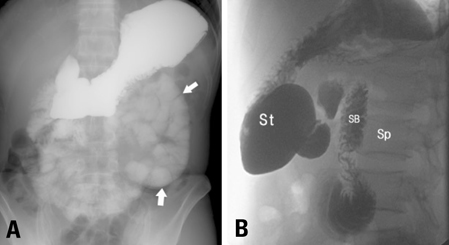
- Paraduodenal hernias are a rare congenital malformation, but they are the most common internal hernias. They develop secondary to a failure in midgut rotation, which may lead to small bowel obstruction or other clinical manifestations. The authors recently experienced a case of a left paraduodenal hernia presenting with unusual symptoms of left flank pain and vomiting.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Singh RR, Warren P, Smith P, Wilson W. Image of the month. Paraduodenal Hernia. Arch Surg. 2006. 141:711–712.2. Manji R, Warnock GL. Left paraduodenal hernia: an unusual cause of the small-bowel obstruction. Can J Surg. 2001. 44:455–457.3. Huang YM, Chou AS, Wu YK, Wu CC, Lee MC, Chen HT, et al. Left paraduodenal hernia presenting as recurrent small bowel obstruction. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. 11:6557–6559.
Article4. Dritsas ER, Ruiz OR, Kennedy GM, Blackford J, Hasl D. Paraduodenal hernia: a report of two cases. Am Surg. 2001. 67:733–736.5. Tong RS, Sengupta S, Tjandra JJ. Left paraduodenal hernia: case report and review of the literature. ANZ J Surg. 2002. 72:69–71.
Article6. Cingi A, Demirkalem P, Manukyan MN, Tuney D, Yegen C. Left-sided paraduodenal hernia: report of a case. Surg Today. 2006. 36:651–654.
Article7. Socas Macías M, Alamo Martín JM, Suárez Grau JM, Suárez Artacho G, Tejada A, Martin Cartes J, et al. Atypical left paraduodenal hernia. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2006. 98:473–475.
Article8. Rollins MD, Glasgrow RE. Left paraduodenal hernia. J Am Coll Surg. 2004. 198:492–493.
Article9. Blachar A, Federle MP, Dodson SF. Internal hernia: clinical and imaging findings in 17 patients with emphasis on CT criteria. Radiology. 2001. 218:68–74.10. Selçuk D, Kantarci F, Oğüt G, Korman U. Radiological evaluation of internal abdominal hernias. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2005. 16:57–64.11. Martin LC, Merkle EM, Thompson WM. Review of internal hernia: radiographic and clinical findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 186:703–717.12. Brigham RA, Fallon WF, Saunders JR, Harmon JW, d'Avis JC. Paraduodenal hernia: diagnosis and surgical management. Surgery. 1984. 96:498–502.13. Uematsu T, Kitamura H, Iwase M, Yamashita K, Orura H, Nakamuka T, et al. Laparoscopic repair of a paraduodenal hernia. Surg Endosc. 1998. 12:50–52.
Article