Korean J Ophthalmol.
2008 Sep;22(3):164-168. 10.3341/kjo.2008.22.3.164.
Comparison between Anterior Corneal Aberration and Ocular Aberration in Laser Refractive Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Pusan, Korea. wcpark@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 1070751
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2008.22.3.164
Abstract
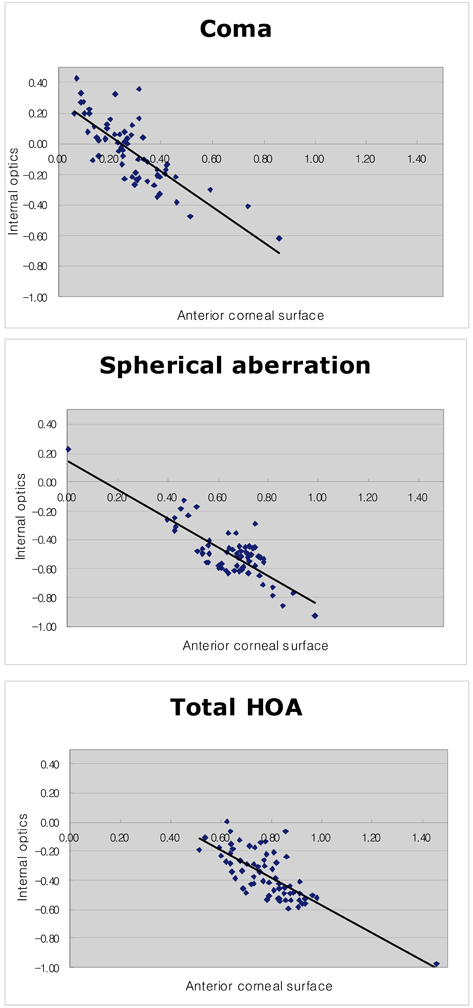
- PURPOSE: To compare changes of anterior corneal aberration (Pentacam(R)) and ocular aberration (aberrometer, LADARWave(R)) after laser refractive surgery. METHODS: Sixty-six eyes underwent laser refractive surgery and were retrospectively reviewed. Anterior corneal aberration and ocular aberration were measured by Pentacam(R) and an aberrometer (LADARWave(R)) respectively. Changes of root mean square (RMS) values of coma, spherical aberration, and total high order aberration (HOA) were evaluated before, 1 month, and 3 months after surgery RESULTS: Ocular aberrations displayed low preoperative values, but after laser refractive surgery, anterior corneal aberration and ocular aberration increased equally. There were no statistically significant differences of internal optics aberration values (ocular aberration minus anterior corneal aberration) in coma, spherical aberration, and total HOA. Anterior corneal aberration and ocular aberration showed statistically significant correlations at 1 and 3 months after surgery. CONCLUSIONS: Internal optics aberration compensated the anterior corneal aberration effectively before surgery, but the increase of anterior corneal aberration after laser refractive surgery exceeded the compensation of internal optics. As a result, anterior corneal aberration and ocular aberration increased equally. The correlation between anterior corneal aberration and ocular aberration after surgery was statistically significant due to the increased proportion of anterior corneal aberration in ocular aberration.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee DH, Choi TH, Lee HB. Short follow-up results of LASIK for correction of high myopia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1997. 38:1527–1536.2. Helmy SA, Salah A, Badawy TT, Sidky AN. Photorefractive keratectomy and laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia between 6.00 and 10.00 diopters. J Refract Surg. 1996. 12:417–421.3. Aizawa D, Shimizu K, Komatsu M, et al. Clinical outcomes of wavefront-guided laser in situ keratomileusis: 6-month follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003. 29:1507–1513.4. Lee SW, Choi TH, Lee HB. Comparison of wavefront guided customized ablation vs. conventional ablation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003. 44:2607–2614.5. Seiler T, Reckmann W, Maloney RK. Effective spherical aberration of the cornea as a quantitative descriptor in corneal topography. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993. 19:155–165.6. Williams D, Yoon GY, Porter J, et al. Visual benefit of correcting higher order aberrations of the eye. J Refract Surg. 2000. 16:S554–S559.7. Oshika T, Klyce SD, Applegate RA, et al. Comparison of corneal wavefront aberrations after photorefractive keratectomy and laser in situ keratomileusis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999. 127:1–7.8. McCormick GJ, Porter J, Cox IG, et al. Higher-order aberrations in eyes with irregular corneas after laser refractive surgery. Ophthalmology. 2005. 112:1699–1709.9. Pablo A, Antonio G, Esther B, David RW. Compensation of corneal aberrations by the internal optics in the human eye. J Vis. 2001. 1:1–8.10. Jennifer EK, Toshifumi M, Howard CH. Compensation of corneal horizontal/vertical astigmatism, lateral coma, and spherical aberration by internal optics of the eye. J Vis. 2004. 4:262–271.11. Thibos LN. Wavefront data reporting and terminology. J Refract Surg. 2001. 17:S563–S565.12. Schwiegerling J, Greivenkamp JE, Miller JM. Representation of videokeratoscopic height data with Zernike polynomials. J Opt Soc Am. 1995. 12:2105–2113.13. Marcos S, Barbero S, Llorente L. Optical response to LASIK surgery formyopia from total and corneal aberration measurements. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001. 42:3349–3356.14. Oh JR, Kim JS, Lee DH. The change of ocular aberration after LASIK surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003. 44:278–283.15. Yang SJ, Kim TI, Tchah HW. Comparison of wave-front guided LASIK and conventional LASIK. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004. 45:117–124.16. Panagopoulou SI, Pallikaris IG. Wavefront customized ablations with the WASCA Asclepion workstation. J Refract Surg. 2001. 17:S608–S612.17. Mrochen M, Kaemmerer M, Seiler T. Clinical results of wavefront-guided laser in situ keratomileusis 3 months after surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001. 27:201–207.18. Kwon HS, Koh IH, Kim EK. The effect of larger and blend zone ablation on optical aberrations in laser epithelial keratomileusis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003. 44:555–561.19. Lee SJ, Kim HJ, Joo CK. Change of high-order aberration after wavefront-guided LASIK and LASEK. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005. 46:1848–1854.20. Winkler von Mohrenfels C, Huber A, Gabler B, et al. Wavefront-guided laser epithelial keratomileusis with the wavelight concept system 500. J Refract Surg. 2004. 20:S565–S569.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Changes of the Corneal Aberration Following Cataract Surgery
- Anterior and Posterior Corneal Spherical Aberration Measured With Pentacam in the Korean
- Clinical Outcomes of Cataract Surgery with Correction of Corneal Spherical Aberration
- Comparison of Laser Refractive Cataract Surgery with a Femtosecond Laser Versus Conventional Phacoemulsification
- Comparison of Corneal Wavefront-optimized and Wavefront-guided Alcohol-assisted Photorefractive Keratectomy Using Schwind Amaris 750S Laser for Myopia