J Vet Sci.
2011 Mar;12(1):99-101. 10.4142/jvs.2011.12.1.99.
Effects of anti-glaucoma drugs on resistive index of the medial long posterior ciliary artery using color Doppler imaging in Beagle dogs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Medical Imaging, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon 305-764, Korea.
- 2Research Institute of Life Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju 660-701, Korea. lhc@gnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1067344
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2011.12.1.99
Abstract
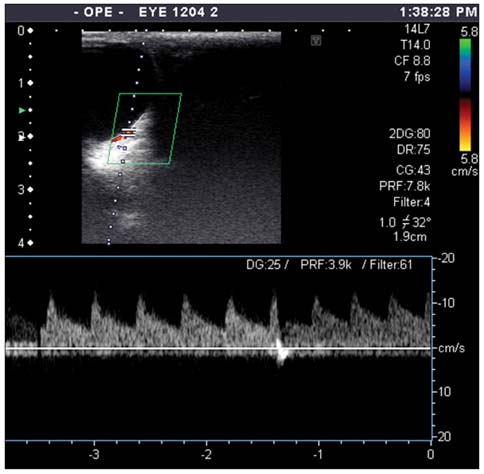
- Color Doppler imaging (CDI) was carried out to evaluate the effects of anti-glaucoma drugs on ophthalmic circulation using CDI-derived resistive index (RI) values. CDI was performed on nine Beagle dogs, and RI values were calculated for the medial long posterior ciliary artery before and after the administration of anti-glaucoma drugs. A significant increase in RI values was found after topical administration of levobunolol (p < 0.05) or dipivefrin (p < 0.05). Pilocarpine showed no effects on RI values after topical administration. The results suggest that some anti-glaucoma drugs could affect ophthalmic blood flow.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Baxter GM, Williamson TH. Color Doppler imaging of the eye: normal ranges, reproducibility, and observer variation. J Ultrasound Med. 1995. 14:91–96.
Article2. Bloom AH, Grunwald JE, DuPont JC. Effect of one week of levobunolol HCl 0.5% on the human retinal circulation. Curr Eye Res. 1997. 16:191–196.
Article3. Brightman AH. Pharmacologic management of glaucoma in the dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1980. 177:326–328.4. Brooks DE. Glaucoma in the dog and cat. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1990. 20:775–797.
Article5. Giovagnorio F, Quaranta L, Bucci MG. Color Doppler assessment of normal ocular blood flow. J Ultrasound Med. 1993. 12:473–477.
Article6. Green K, Hatchett TL. Regional ocular blood flow after chronic topical glaucoma drug treatment. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1987. 65:503–506.
Article7. Lee H, Chang D, Lee Y, Eom K, Choi H, Seo K, Choi M, Yoon J. Use of color Doppler imaging for determining the resistive index of the medial long posterior ciliary artery in clinically normal conscious dogs. Am J Vet Res. 2002. 63:211–214.
Article8. Michelson G, Groh MJ. Dipivefrin reduces blood flow in the ciliary body in humans. Ophthalmology. 1994. 101:659–664.
Article9. Schmetterer L, Strenn K, Findl O, Breiteneder H, Graselli U, Agneter E, Eichler HG, Wolzt M. Effects of antiglaucoma drugs on ocular hemodynamics in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1997. 61:583–595.
Article10. Williamson TH, Harris A. Ocular blood flow measurement. Br J Ophthalmol. 1994. 78:939–945.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Vascular Risk Factors in Normal Tension Glaucoma
- Incomplete Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
- Measurement of Blood Flow Velocity of Ophthalmic and Central Retinal Artery using Color Doppler Imaging
- Usefulness of Color Doppler Sonography in the Diagnosis of Scrotal Disease
- Resistive Indices in Acute Scrotal Inflammation on Doppler Ultrasonography