Korean J Radiol.
2004 Mar;5(1):25-30. 10.3348/kjr.2004.5.1.25.
MR Imaging Findings of Clonorchiasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Chonnam National University Medical School. yjeong@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Namkwang Hospital, Seonam University Medical School.
- KMID: 1066242
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2004.5.1.25
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
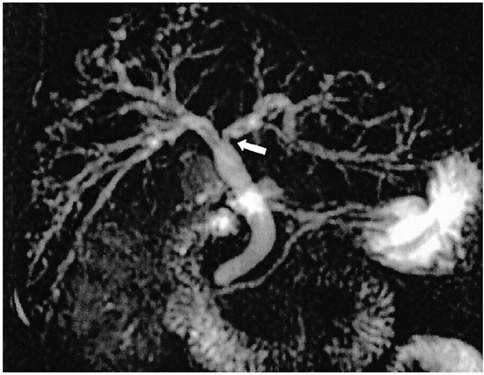
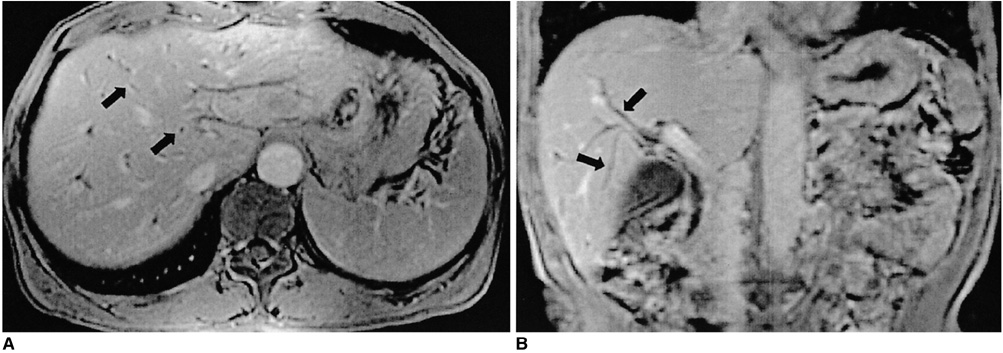
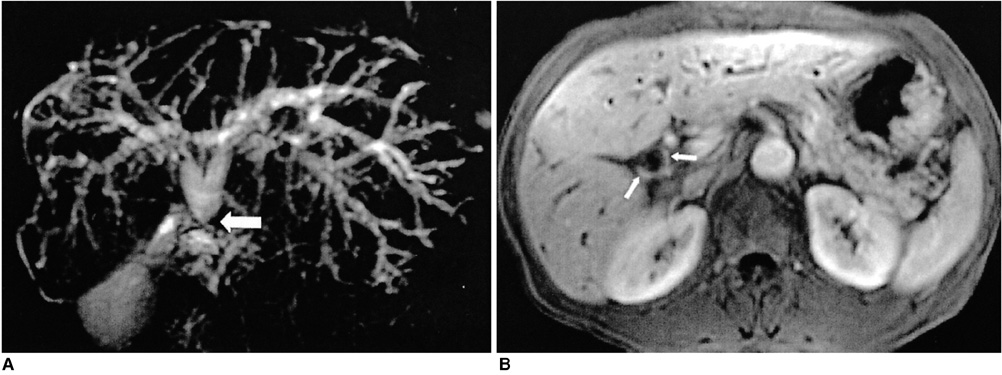
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the MR spectrum and MR cholangiographic imaging findings of clonorchiasis. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We reviewed 26 patients with confirmed clonorchiasis by either stool tests (n=24) or surgery (n=2). MR imaging was performed on a 1.5 T system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI) with a torso coil. Axial T1-and T2-weighted, gadolinium-enhanced dynamic images and MR cholangiography were obtained. Image analyses were used to identify abnormalities of the intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts and the presence of hepatobiliary malignancy. All MR examinations were reviewed by the consensus of two abdominal radiologists. RESULT: Intrahepatic bile duct abnormalities were seen in 23 (89%) of the 26 patients. The most common finding was mild dilatation of the intrahepatic bile duct which was found in 21 (81%). "Too many intrahepatic ducts" were found in 16 (62%), wall enhancement and thickening in 21 (81%) and filling defects and ductal stricture in the intrahepatic bile duct in 6 (24%) and 3 (12%) patients, respectively. Extrahepatic ductal dilation was found in 5 (19%) and 9 (35%) revealed hepatobiliary malignancy. CONCLUSION: MR imaging revealed various findings of clonorchiasis, including dilatation, wall enhancement, stricture of the intrahepatic ducts and filling defect within the intrahepatic bile duct.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yamaguchi T. Clinical parasitology. 1981. London: Wolfe Medical;50–57.2. Rim HJ. The current pathobiology and chemotherapy of clonorchiasis. Korean J Parasitol. 1986. 24:7–20.3. Hou PC. The relationship between primary carcinoma of the liver and infestation with Clonorchiasis sinensis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1956. 72:239–246.4. Flavell DJ. Liver-fluke infection as an aetiological factor in bile duct carcinoma of man. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1981. 75:814–824.5. Belmaric J. Intrahepatic bile duct carcinoma and clonorchiasis infection in Hong Kong. Cancer. 1973. 31:468–473.6. Choi TK, Wong KP, Woong J. Cholangiographic appearance in clonorchiasis. Br J Radiol. 1984. 57:681–684.7. Lim JH. Radiologic findings of clonorchiasis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990. 155:1001–1008.8. Choi BI, Kim HJ, Do YS, Han MH, Lee SH. CT findings of clonorchiasis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989. 152:281–284.9. Kim MS, Yoo HS, Lee JT, Jung SH. Radiologic imaging of bile duct change by clonorchiasis. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1988. 24:878–882.10. Lim JH, Ko YT, Lee DH, Lee KS, Suh SJ, Woo SK. Clonorchiasis and its complications: cholangiogram revisited. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1992. 28:229–235.11. Becker CD, Grossholz M, Becker M, Mentha G, de Peyer R, Terruer F. Choledocholithiasis and bile duct stenosis: diagnostic accuracy of MR cholangiopancreatography. Radiology. 1997. 205:523–530.12. Barish MA, Soto JA. MR cholangiopancreatography: technique and clinical applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997. 169:1295–1303.13. Kim MJ, Mitchell MJ, Ito K, Outwater EK. Biliary dilatation: differentiation of benign from malignant causes-value of adding conventional MR imaging to MR cholangiopancreatography. Radiology. 2000. 214:173–181.14. Guibaud L, Bret PM, Reinold C, Atri M, Barkun ANG. Diagnosis of choledocholithiasis: value of MR cholangiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994. 163:847–850.15. Choi BI, Kim TK, Han JK. MRI of Clonorchiasis and cholangiocarcinoma. JMRI. 1998. 8:359–366.16. Park MS, Yu JS, Kim KW, et al. Recurrent pyogenic cholangitis: comparison between MR cholangiography and direct cholangiography. Radiology. 2001. 220:677–682.17. Lim JH, Ko YT, Lee DH, Kim SY. Clonorchiasis: sonographic findings in 59 proved cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989. 152:761–764.18. Teefey SA, Baron RL, Rohrmann CA, Shuman WP, Freeny PC. Sclerosing cholangitis: CT findings. Radiology. 1988. 169:635–639.19. Ito K, Mitchell DB, Outwater EK, Blasbalg R. Primary sclerosing cholangitis: MR imaging features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999. 172:1527–1533.20. Okuda K, Emura T, Morokuma K, Kojima S, Yokagawa M. Clonorchiasis studies by percutaneous cholangiography and a therapeutic trial of toluene-2, 4-diiso-thiocyante. Gastroenterology. 1973. 65:457–461.21. Hou PC. The pathology of Clonorchiasis sinensis infestation of the liver. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955. 70:53–64.22. Lee SH, Shim TS, Lee SM, Chi JG. Studies on pathological changes of the liver in albino rats infected with Clonorchiasis sinensis. Korean J Parasitol. 1978. 16:148–155.23. Chung CS, Lee SK. An epidemiological study of primary liver carcinoma in Busan area with special reference to clonorchiasis. Korean J Pathol. 1976. 10:33–46.24. Hou PC. Hepatic clonorchiasis and carcinoma of the bile duct in a dog. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965. 89:365–367.25. Kim MJ, Cha SW, Mitchell DG, Chung JJ, Park S, Chung JB. MR imaging findings in recurrent pyogenic cholangitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999. 173:1545–1549.26. Fulcher AS, Yurner MA, Franklin KJ, et al. Primary sclerosing cholangitis: evaluation with MR cholangiography-a case-control study. Radiology. 2000. 215:71–80.