Korean J Gastroenterol.
2011 Dec;58(6):357-360. 10.4166/kjg.2011.58.6.357.
A Case of Intrapancreatic Accessory Spleen Mistaken as a Pancreatic Mass due to Different Enhancing Pattern from Normal Spleen
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Gumi, Korea. netstars@empas.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Gumi, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Gumi, Korea.
- KMID: 1043337
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2011.58.6.357
Abstract
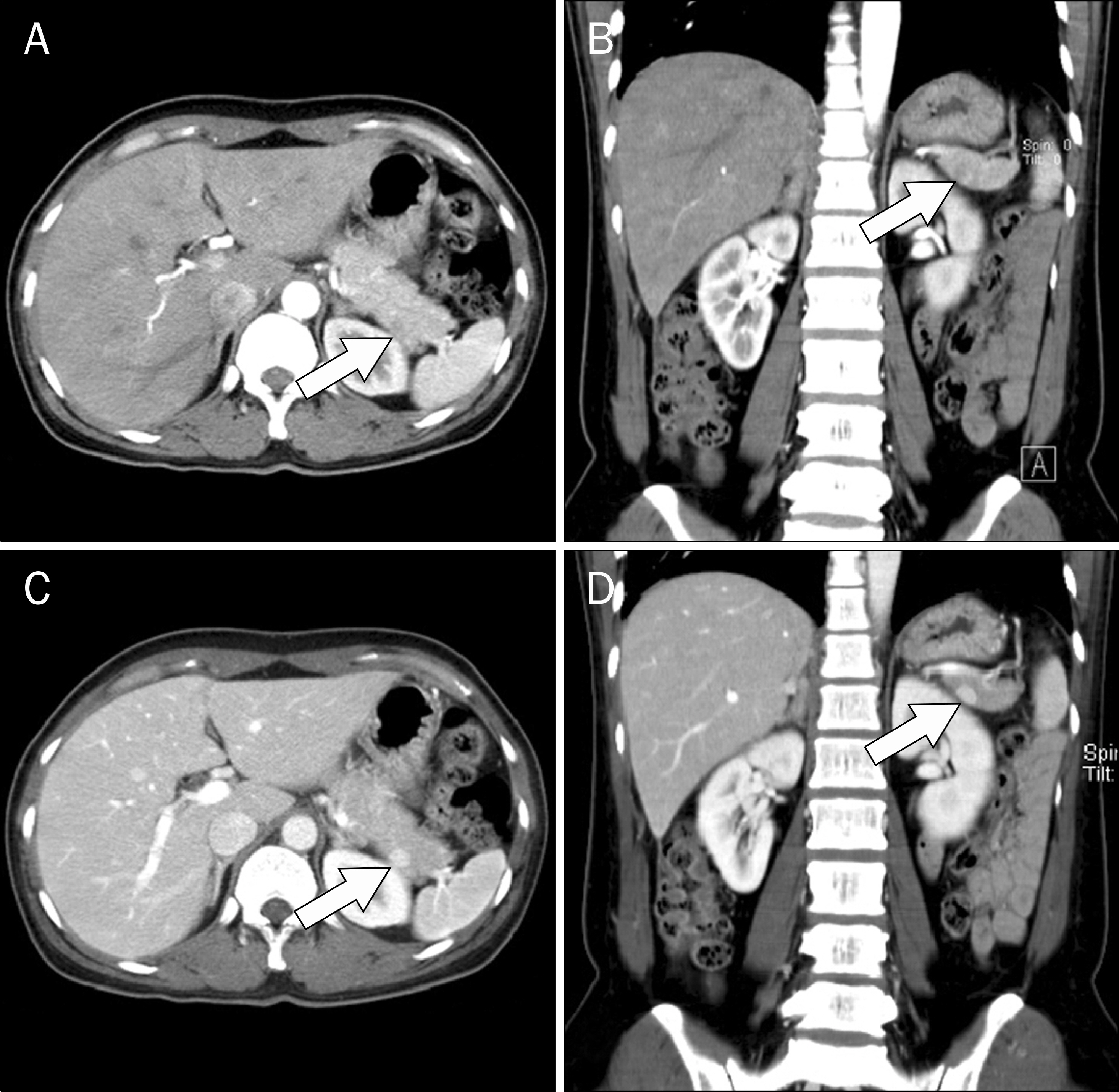
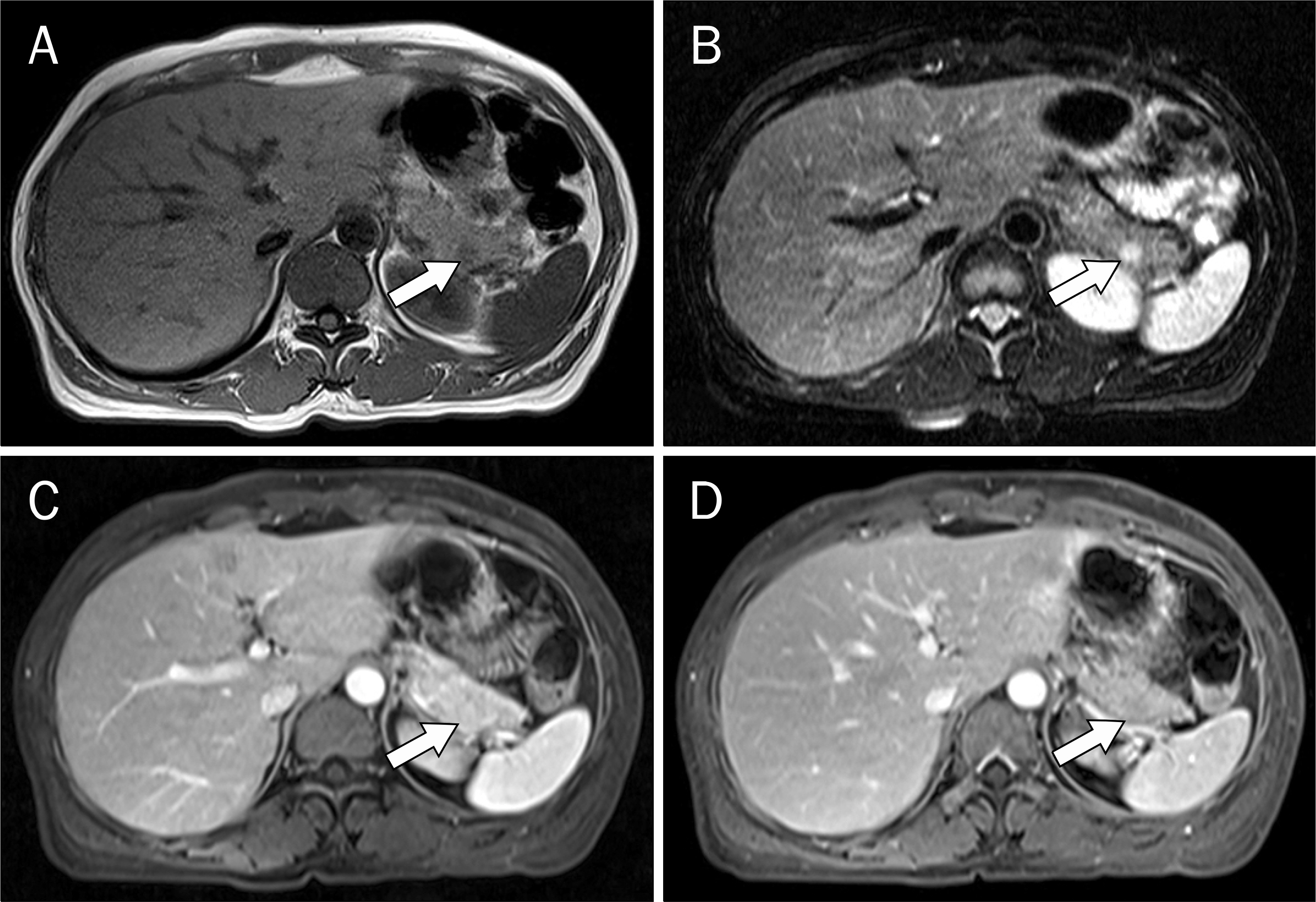
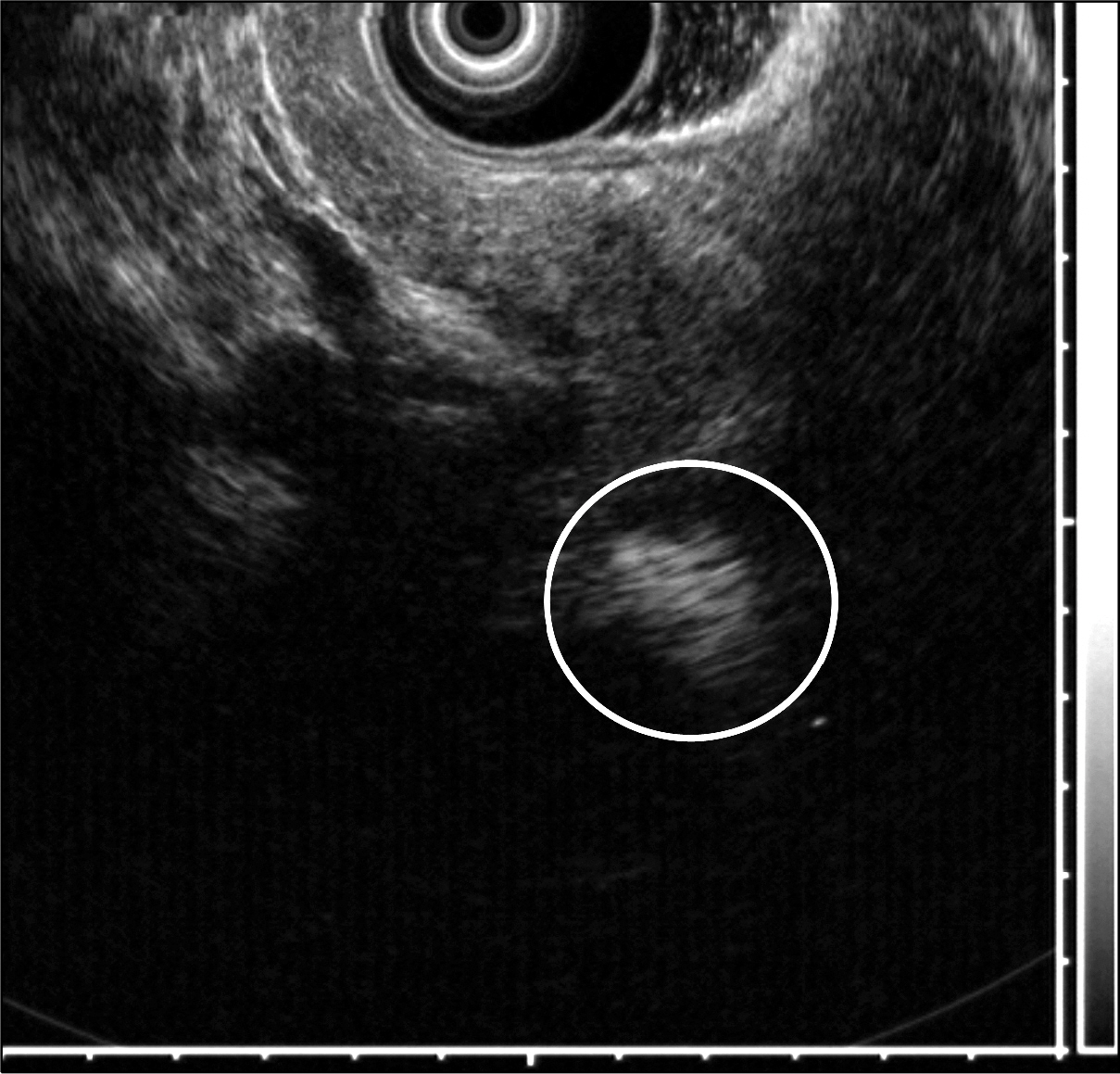
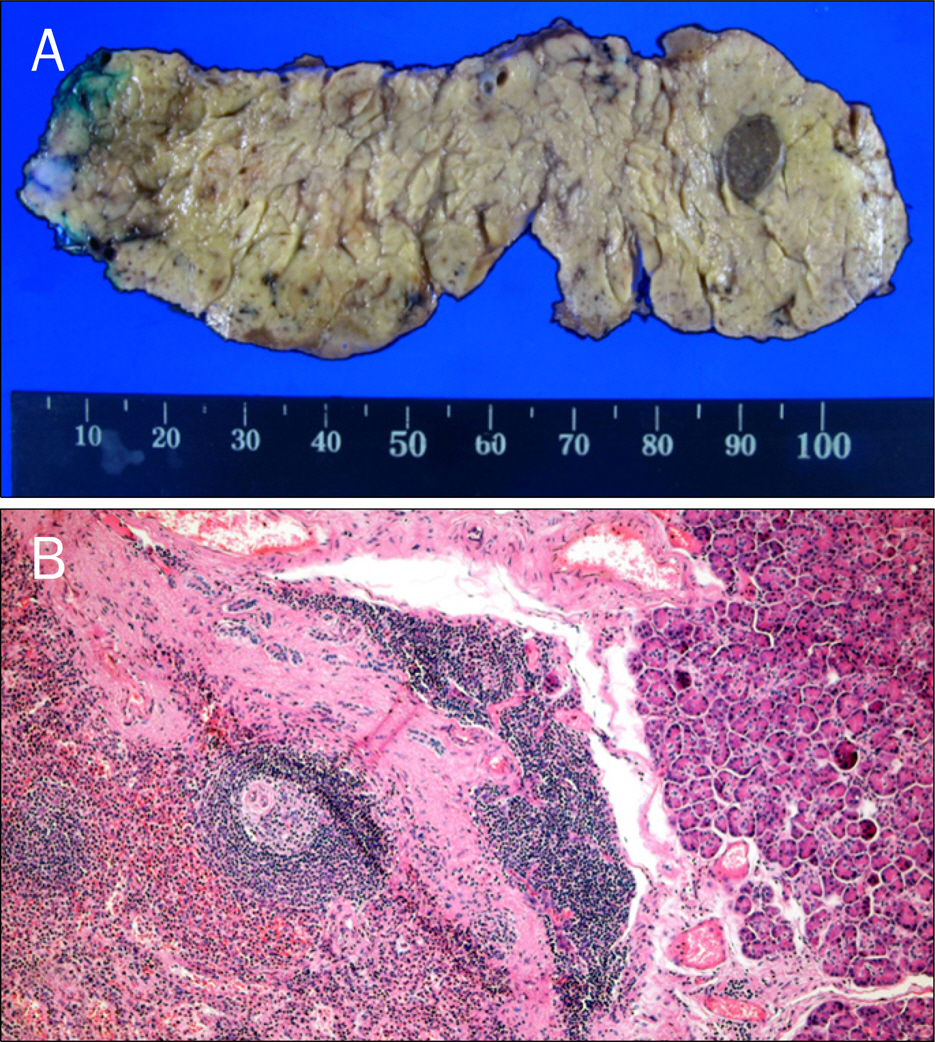
- Most cases of accessory spleen show similar features as normal spleen in imaging studies. However, some accessory spleen has unusual scan feature which can be misdiagnosed. We present a case of intrapancreatic accessory spleen that was discovered incidentally during a workup for abdominal pain in a 47-year-old woman. CT and MRI revealed a different enhancing pattern from that of the spleen. Further evaluation with endoscopic ultrasonography failed to identify the pancreatic mass. Therefore, it was surgically removed and diagnosed pathologically as an accessory spleen.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sica GT, Reed MF. Case 27: intrapancreatic accessory spleen. Radiology. 2000; 217:134–137.
Article2. Buetow PC, Buck JL, Pantongrag-Brown L, Beck KG, Ros PR, Adair CF. Solid and papillary epithelial neoplasm of the pancreas: imaging-pathologic correlation on 56 cases. Radiology. 1996; 199:707–711.
Article3. Adsay NV, Basturk O, Klimstra DS, Klöppel G. Pancreatic pseudo-tumors: non-neoplastic solid lesions of the pancreas that clinically mimic pancreas cancer. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2004; 21:260–267.
Article4. Movitz D. Accessory spleens and experimental splenosis. Principles of growth. Chic Med Sch Q. 1967; 26:183–187.5. Halpert B, Gyorkey F. Lesions observed in accessory spleens of 311 patients. Am J Clin Pathol. 1959; 32:165–168.
Article6. Kim SH, Lee JM, Han JK, et al. Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: findings on MR Imaging, CT, US and scintigraphy, and the pathologic analysis. Korean J Radiol. 2008; 9:162–174.
Article7. Tozbikian G, Bloomston M, Stevens R, Ellison EC, Frankel WL. Accessory spleen presenting as a mass in the tail of the pancreas. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2007; 11:277–281.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Epidermoid Cysts in the Intrapancreatic Accessory Spleen Mimicking Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasm
- Epithelial Cysts in the Intrapancreatic Accessory Spleen that Clinically Mimic Pancreatic Cystic Tumor: A Report of Two Cases
- A Case of Epidermoid Cyst in the Intrapancreatic Accessory Spleen Mimicking Pancreas Mucinous Cystic Neoplasm
- Unusual Infarction of the Accessory Spleen or Polysplenia in Two Children: Case Report
- An epidermoid cyst in an intrapancreatic accessory spleen