Endocrinol Metab.
2024 Feb;39(1):127-139. 10.3803/EnM.2023.1826.
FoxO6-Mediated TXNIP Induces Lipid Accumulation in the Liver through NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Life Sciences, Chosun University College of Natural Science, Gwangju, Korea
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Kyungsung University College of Pharmacy, Busan, Korea
- 3Department of Food Science & Technology, Pusan National University College of Natural Resources and Life Science, Miryang, Korea
- KMID: 2552804
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1826
Abstract
- Background
Hepatic steatosis, which involves the excessive accumulation of lipid droplets in hepatocytes, presents a significant global health concern due to its association with obesity and metabolic disorders. Inflammation plays a crucial role in the progression of hepatic steatosis; however, the precise molecular mechanisms responsible for this process remain unknown.
Methods
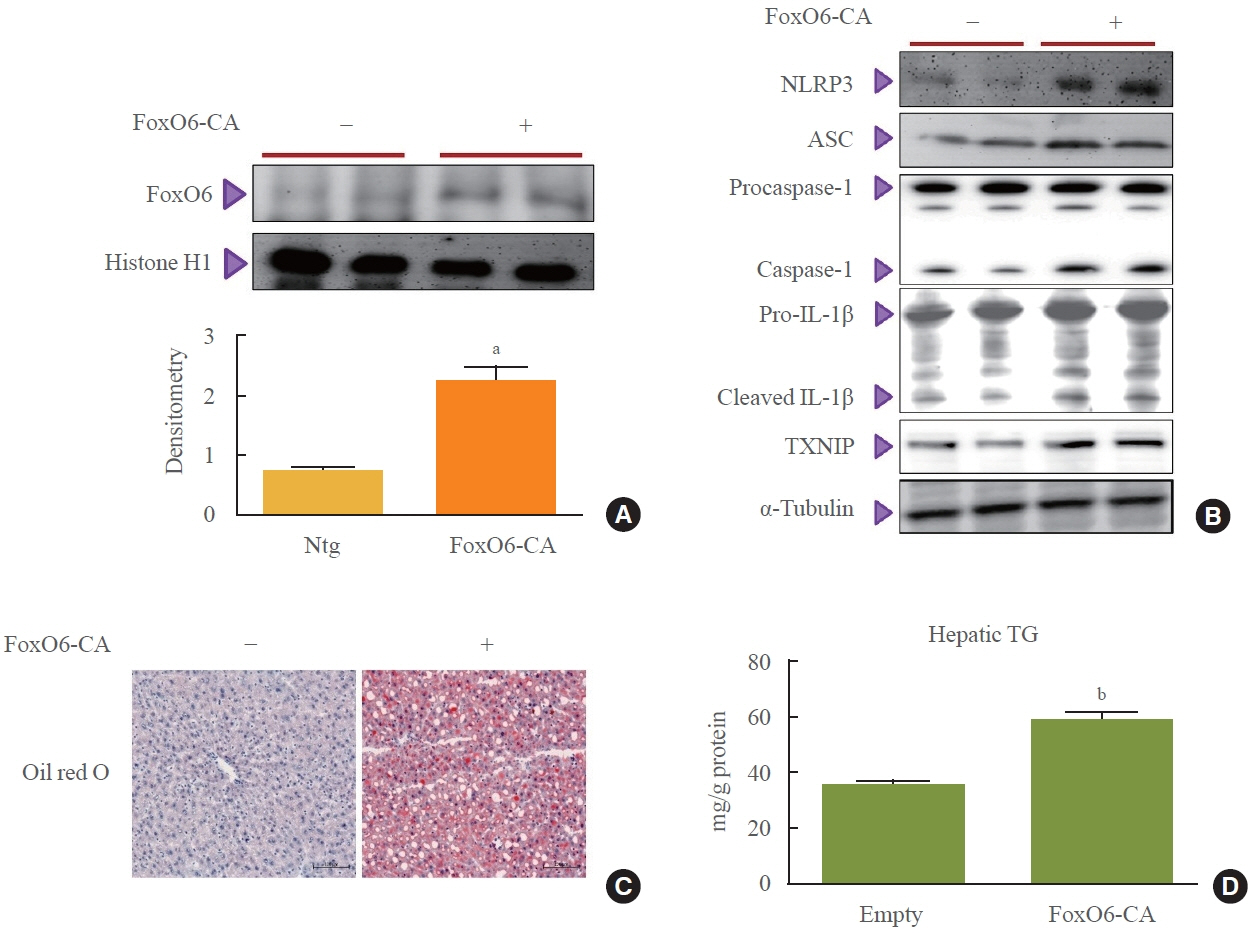
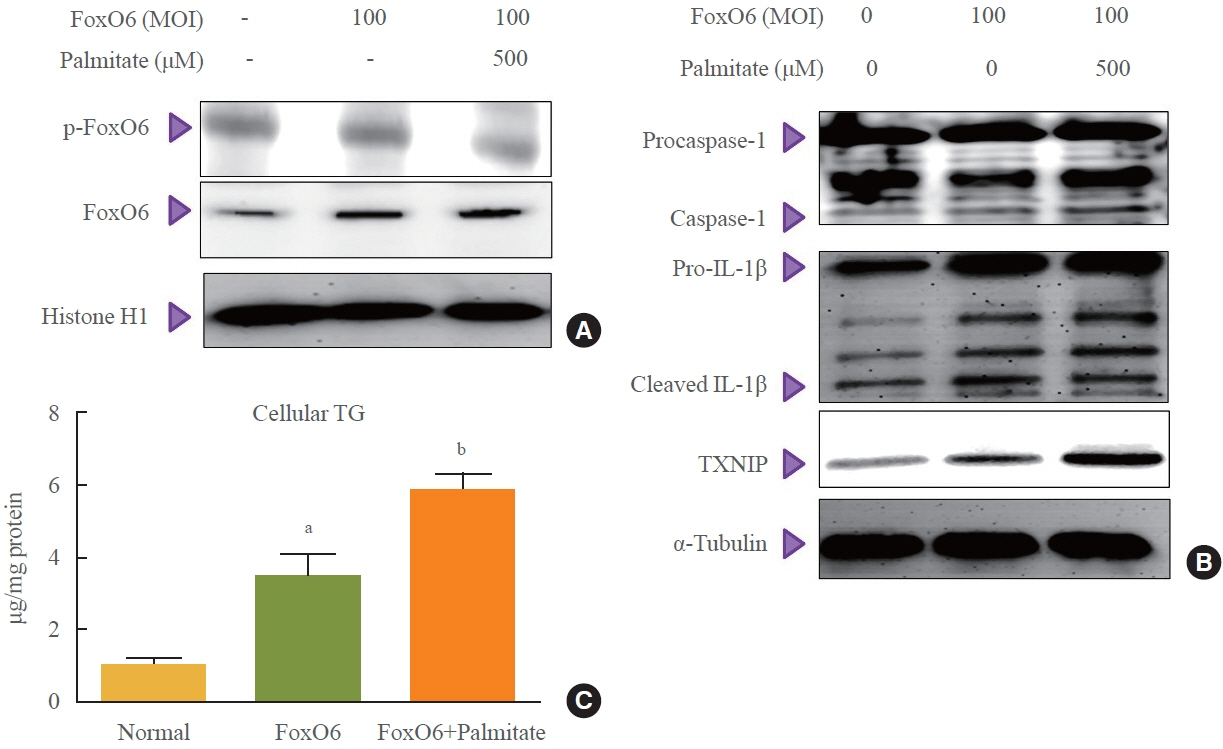
This study investigated the involvement of the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor pyrin domain-containing-3 (NLRP3) inflammasome and the forkhead box O6 (FoxO6) transcription factor in the pathogenesis of hepatic steatosis. We monitored the NLRP3 inflammasome and lipogenesis in mice overexpressing the constitutively active (CA)-FoxO6 allele and FoxO6-null mice. In an in vitro study, we administered palmitate to liver cells overexpressing CA-FoxO6 and measured changes in lipid metabolism.
Results
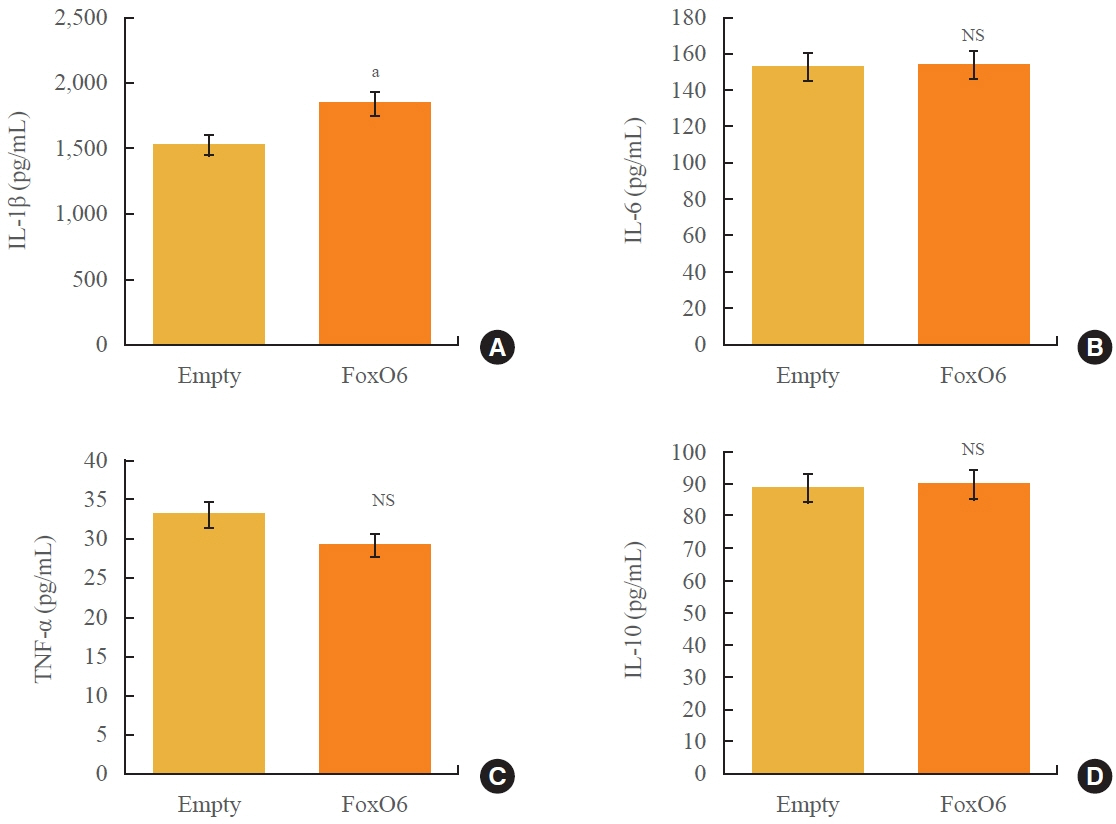
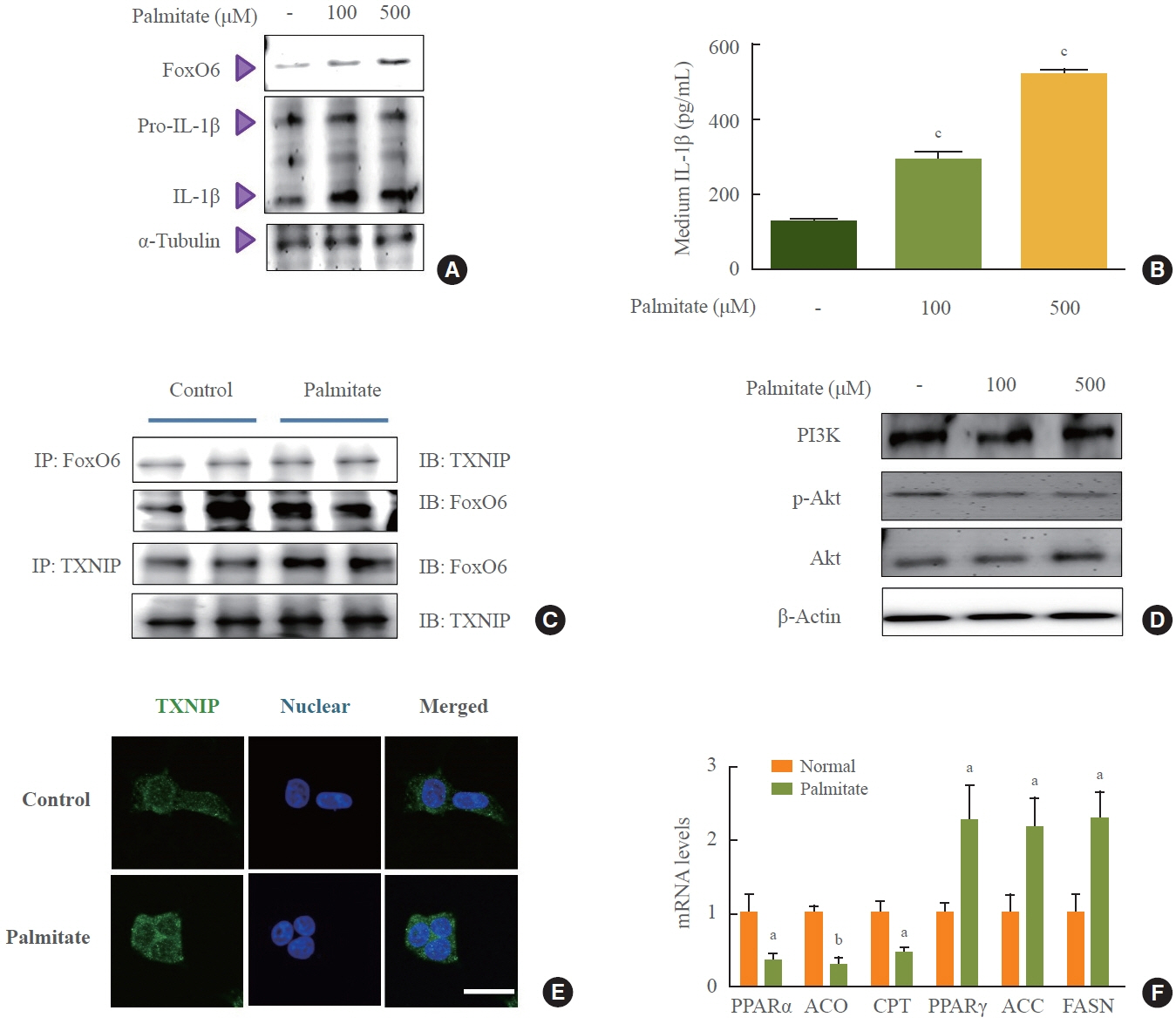
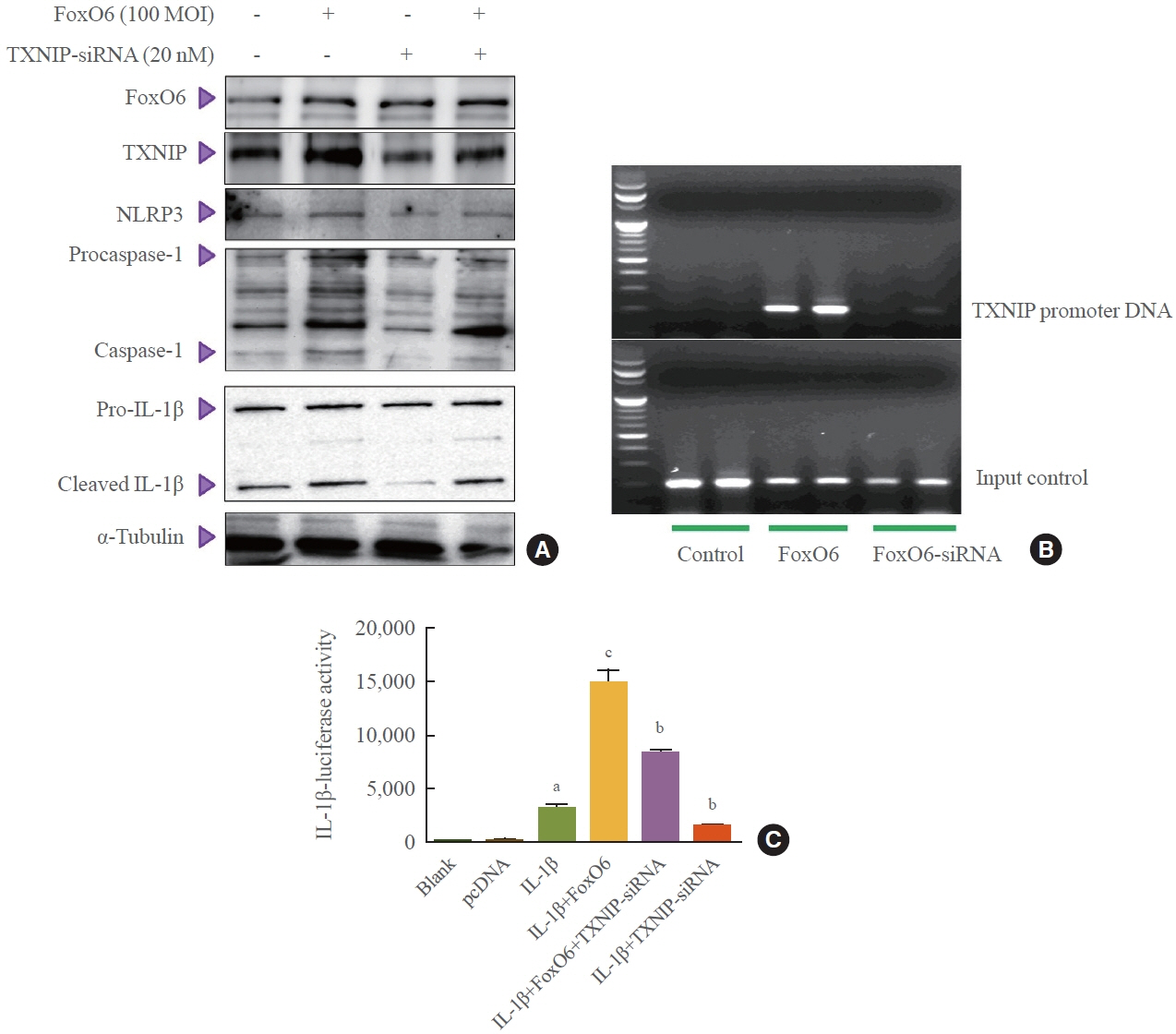
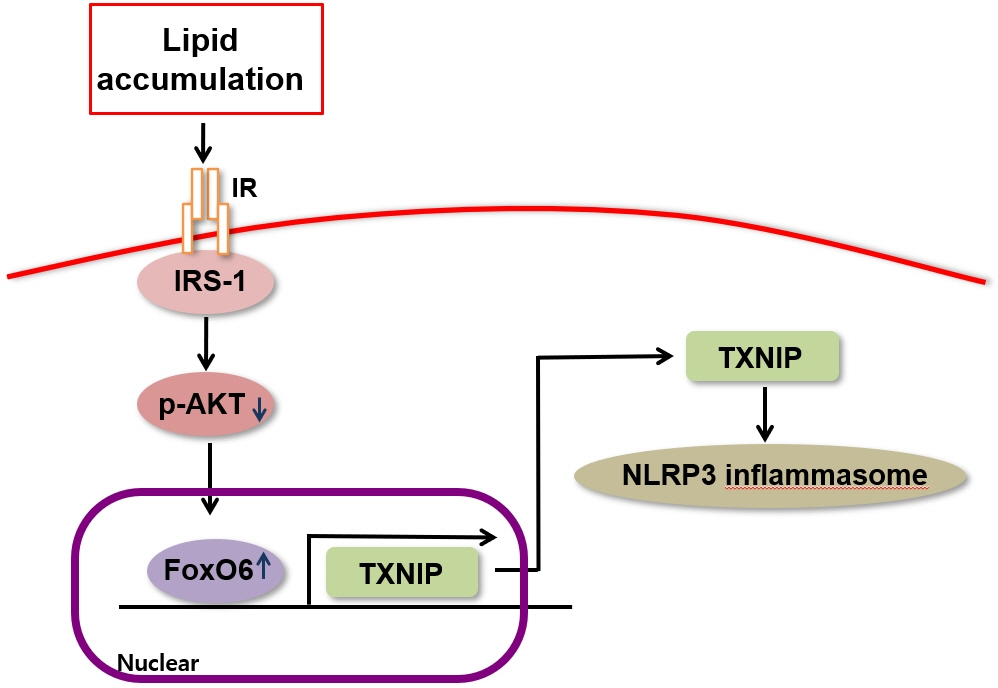
We administered palmitate treatment to clarify the mechanisms through which FoxO6 activates cytokine interleukin (IL)-1β through the NLRP3 inflammasome. The initial experiments revealed that dephosphorylation led to palmitate-induced FoxO6 transcriptional activity. Further palmitate experiments showed increased expression of IL-1β and the hepatic NLRP3 inflammasome complex, including adaptor protein apoptotic speck protein containing a caspase recruitment domain (ASC) and pro-caspase-1. Furthermore, thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP), a key regulator of cellular redox conditions upstream of the NLRP3 inflammasome, was induced by FoxO6 in the liver and HepG2 cells.
Conclusion
The findings of this study shed light on the molecular mechanisms underpinning the FoxO6-NLRP3 inflammasome axis in promoting inflammation and lipid accumulation in the liver.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Van Der Heide LP, Hoekman MF, Smidt MP. The ins and outs of FoxO shuttling: mechanisms of FoxO translocation and transcriptional regulation. Biochem J. 2004; 380(Pt 2):297–309.2. Accili D, Arden KC. FoxOs at the crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and transformation. Cell. 2004; 117:421–6.3. Barthel A, Schmoll D, Unterman TG. FoxO proteins in insulin action and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 16:183–9.4. Biggs WH 3rd, Meisenhelder J, Hunter T, Cavenee WK, Arden KC. Protein kinase B/Akt-mediated phosphorylation promotes nuclear exclusion of the winged helix transcription factor FKHR1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:7421–6.5. Kawamori D, Kaneto H, Nakatani Y, Matsuoka TA, Matsuhisa M, Hori M, et al. The forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 bridges the JNK pathway and the transcription factor PDX-1 through its intracellular translocation. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281:1091–8.6. Martinez SC, Tanabe K, Cras-Meneur C, Abumrad NA, Bernal-Mizrachi E, Permutt MA. Inhibition of Foxo1 protects pancreatic islet beta-cells against fatty acid and endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Diabetes. 2008; 57:846–59.7. Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature. 2006; 444:860–7.8. Schenk S, Saberi M, Olefsky JM. Insulin sensitivity: modulation by nutrients and inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2008; 118:2992–3002.9. Kamagate A, Dong HH. FoxO1 integrates insulin signaling to VLDL production. Cell Cycle. 2008; 7:3162–70.10. Kim DH, Lee B, Lee J, Kim ME, Lee JS, Chung JH, et al. FoxO6-mediated IL-1β induces hepatic insulin resistance and age-related inflammation via the TF/PAR2 pathway in aging and diabetic mice. Redox Biol. 2019; 24:101184.11. Kim DH, Perdomo G, Zhang T, Slusher S, Lee S, Phillips BE, et al. FoxO6 integrates insulin signaling with gluconeogenesis in the liver. Diabetes. 2011; 60:2763–74.12. Vandanmagsar B, Youm YH, Ravussin A, Galgani JE, Stadler K, Mynatt RL, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2011; 17:179–88.13. Donath MY. Targeting inflammation in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: time to start. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014; 13:465–76.14. Schroder K, Tschopp J. The inflammasomes. Cell. 2010; 140:821–32.15. Febbraio MA. Role of interleukins in obesity: implications for metabolic disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 25:312–9.16. Hoque R, Vodovotz Y, Mehal W. Therapeutic strategies in inflammasome mediated diseases of the liver. J Hepatol. 2013; 58:1047–52.17. Chen J, Saxena G, Mungrue IN, Lusis AJ, Shalev A. Thioredoxin-interacting protein: a critical link between glucose toxicity and beta-cell apoptosis. Diabetes. 2008; 57:938–44.18. Perrone L, Devi TS, Hosoya K, Terasaki T, Singh LP. Thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) induces inflammation through chromatin modification in retinal capillary endothelial cells under diabetic conditions. J Cell Physiol. 2009; 221:262–72.19. Zhou R, Tardivel A, Thorens B, Choi I, Tschopp J. Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol. 2010; 11:136–40.20. Minn AH, Hafele C, Shalev A. Thioredoxin-interacting protein is stimulated by glucose through a carbohydrate response element and induces beta-cell apoptosis. Endocrinology. 2005; 146:2397–405.21. Parikh H, Carlsson E, Chutkow WA, Johansson LE, Storgaard H, Poulsen P, et al. TXNIP regulates peripheral glucose metabolism in humans. PLoS Med. 2007; 4:e158.22. Li X, Rong Y, Zhang M, Wang XL, LeMaire SA, Coselli JS, et al. Up-regulation of thioredoxin interacting protein (Txnip) by p38 MAPK and FOXO1 contributes to the impaired thioredoxin activity and increased ROS in glucose-treated endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009; 381:660–5.23. Stoltzman CA, Peterson CW, Breen KT, Muoio DM, Billin AN, Ayer DE. Glucose sensing by MondoA:Mlx complexes: a role for hexokinases and direct regulation of thioredoxin-interacting protein expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105:6912–7.24. Kim DH, Kim JY, Yu BP, Chung HY. The activation of NFkappaB through Akt-induced FOXO1 phosphorylation during aging and its modulation by calorie restriction. Biogerontology. 2008; 9:33–47.25. Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970; 227:680–5.26. Schulze PC, Yoshioka J, Takahashi T, He Z, King GL, Lee RT. Hyperglycemia promotes oxidative stress through inhibition of thioredoxin function by thioredoxin-interacting protein. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:30369–74.27. Nivet-Antoine V, Cottart CH, Lemarechal H, Vamy M, Margaill I, Beaudeux JL, et al. trans-Resveratrol downregulates Txnip overexpression occurring during liver ischemia-reperfusion. Biochimie. 2010; 92:1766–71.28. Chutkow WA, Patwari P, Yoshioka J, Lee RT. Thioredoxininteracting protein (Txnip) is a critical regulator of hepatic glucose production. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:2397–406.29. Boaru SG, Borkham-Kamphorst E, Tihaa L, Haas U, Weiskirchen R. Expression analysis of inflammasomes in experimental models of inflammatory and fibrotic liver disease. J Inflamm (Lond). 2012; 9:49.30. Calabuig-Navarro V, Yamauchi J, Lee S, Zhang T, Liu YZ, Sadlek K, et al. Forkhead box O6 (FoxO6) depletion attenuates hepatic gluconeogenesis and protects against fat-induced glucose disorder in mice. J Biol Chem. 2015; 290:15581–94.31. Al-Mubarak B, Soriano FX, Hardingham GE. Synaptic NMDAR activity suppresses FOXO1 expression via a cis-acting FOXO binding site: FOXO1 is a FOXO target gene. Channels (Austin). 2009; 3:233–8.32. Xuan Z, Zhang MQ. From worm to human: bioinformatics approaches to identify FOXO target genes. Mech Ageing Dev. 2005; 126:209–15.33. Yamaguchi F, Hirata Y, Akram H, Kamitori K, Dong Y, Sui L, et al. FOXO/TXNIP pathway is involved in the suppression of hepatocellular carcinoma growth by glutamate antagonist MK-801. BMC Cancer. 2013; 13:468.34. Kim DH, Zhang T, Lee S, Calabuig-Navarro V, Yamauchi J, Piccirillo A, et al. FoxO6 integrates insulin signaling with MTP for regulating VLDL production in the liver. Endocrinology. 2014; 155:1255–67.35. Goossens GH, Blaak EE, Theunissen R, Duijvestijn AM, Clement K, Tervaert JW, et al. Expression of NLRP3 inflammasome and T cell population markers in adipose tissue are associated with insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism in humans. Mol Immunol. 2012; 50:142–9.36. Csak T, Ganz M, Pespisa J, Kodys K, Dolganiuc A, Szabo G. Fatty acid and endotoxin activate inflammasomes in mouse hepatocytes that release danger signals to stimulate immune cells. Hepatology. 2011; 54:133–44.37. Wen H, Gris D, Lei Y, Jha S, Zhang L, Huang MT, et al. Fatty acid-induced NLRP3-ASC inflammasome activation interferes with insulin signaling. Nat Immunol. 2011; 12:408–15.38. Guha M, Mackman N. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinaseAkt pathway limits lipopolysaccharide activation of signaling pathways and expression of inflammatory mediators in human monocytic cells. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:32124–32.39. Molnarfi N, Gruaz L, Dayer JM, Burger D. Opposite regulation of IL-1beta and secreted IL-1 receptor antagonist production by phosphatidylinositide-3 kinases in human monocytes activated by lipopolysaccharides or contact with T cells. J Immunol. 2007; 178:446–54.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ethanol Augments Monosodium Urate-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via Regulation of AhR and TXNIP in Human Macrophages
- Loganin Prevents Hepatic Steatosis by Blocking NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
- The Mechanism of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Pathogenic Implication in the Pathogenesis of Gout
- NLRP3 Inflammasome and Host Protection against Bacterial Infection
- Extracellular Acidification Augments NLRP3-Mediated Inflammasome Signaling in Macrophages