J Yeungnam Med Sci.
2023 Oct;40(4):381-387. 10.12701/jyms.2022.00941.
Cortical thickness of the rostral anterior cingulate gyrus is associated with frailty in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 2Department of Psychiatry, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2547361
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00941
Abstract
- Background
Frailty is defined as a condition of being weak and delicate, and it represents a state of high vulnerability to adverse health outcomes. Recent studies have suggested that the cingulate gyrus is associated with frailty in the elderly population. However, few imaging studies have explored the relationship between frailty and the cingulate gyrus in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) undergoing hemodialysis.
Methods
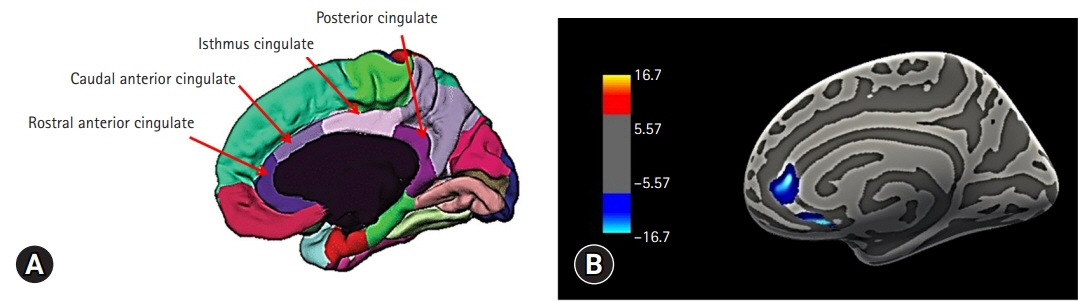
Eighteen right-handed patients with ESRD undergoing hemodialysis were enrolled in the study. We used the FreeSurfer software package to estimate the cortical thickness of the regions of interest, including the rostral anterior, caudal anterior, isthmus, and posterior cingulate gyri. The Beck Depression Inventory, Beck Anxiety Inventory, and laboratory tests were also conducted.
Results
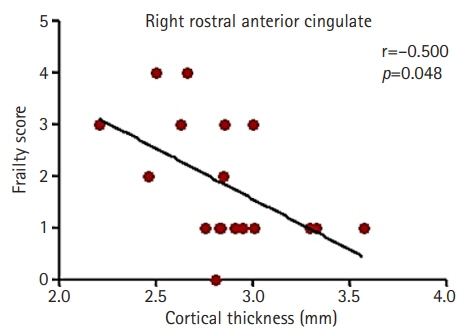
The cortical thickness of the right rostral anterior cingulate gyrus (ACG) was significantly correlated with the Fried frailty index, age, and creatinine level. Multiple regression analysis indicated that the cortical thickness of the right rostral ACG was associated with frailty after controlling for age and creatinine level.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that the cortical thickness of the rostral ACG may be associated with frailty in patients with ESRD on hemodialysis and that the rostral ACG may play a role in the frailty mechanism of this population.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lee SY, Yang DH, Hwang E, Kang SH, Park SH, Kim TW, et al. The prevalence, association, and clinical outcomes of frailty in maintenance dialysis patients. J Ren Nutr. 2017; 27:106–12.
Article2. Painter P, Roshanravan B. The association of physical activity and physical function with clinical outcomes in adults with chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2013; 22:615–23.
Article3. Roshanravan B, Khatri M, Robinson-Cohen C, Levin G, Patel KV, de Boer IH, et al. A prospective study of frailty in nephrology-referred patients with CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012; 60:912–21.
Article4. Kooman JP, Kotanko P, Schols AM, Shiels PG, Stenvinkel P. Chronic kidney disease and premature ageing. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014; 10:732–42.
Article5. Johansen KL, Chertow GM, Jin C, Kutner NG. Significance of frailty among dialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007; 18:2960–7.
Article6. McAdams-DeMarco MA, Suresh S, Law A, Salter ML, Gimenez LF, Jaar BG, et al. Frailty and falls among adult patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis: a prospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2013; 14:224.
Article7. Wilhelm-Leen ER, Hall YN, K Tamura M, Chertow GM. Frailty and chronic kidney disease: the Third National Health and Nutrition Evaluation Survey. Am J Med. 2009; 122:664–71.
Article8. Jacobs JM, Cohen A, Ein-Mor E, Maaravi Y, Stessman J. Frailty, cognitive impairment and mortality among the oldest old. J Nutr Health Aging. 2011; 15:678–82.
Article9. Fried LP, Ferrucci L, Darer J, Williamson JD, Anderson G. Untangling the concepts of disability, frailty, and comorbidity: implications for improved targeting and care. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2004; 59:255–63.
Article10. Ní Mhaoláin AM, Fan CW, Romero-Ortuno R, Cogan L, Cunningham C, Kenny RA, et al. Frailty, depression, and anxiety in later life. Int Psychogeriatr. 2012; 24:1265–74.
Article11. Qiu Y, Lv X, Su H, Jiang G, Li C, Tian J. Structural and functional brain alterations in end stage renal disease patients on routine hemodialysis: a voxel-based morphometry and resting state functional connectivity study. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e98346.
Article12. Papoiu AD, Emerson NM, Patel TS, Kraft RA, Valdes-Rodriguez R, Nattkemper LA, et al. Voxel-based morphometry and arterial spin labeling fMRI reveal neuropathic and neuroplastic features of brain processing of itch in end-stage renal disease. J Neurophysiol. 2014; 112:1729–38.
Article13. Hadland KA, Rushworth MF, Gaffan D, Passingham RE. The effect of cingulate lesions on social behaviour and emotion. Neuropsychologia. 2003; 41:919–31.
Article14. Sutherland RJ, Whishaw IQ, Kolb B. Contributions of cingulate cortex to two forms of spatial learning and memory. J Neurosci. 1988; 8:1863–72.
Article15. Hayden BY, Platt ML. Neurons in anterior cingulate cortex multiplex information about reward and action. J Neurosci. 2010; 30:3339–46.
Article16. Paus T. Primate anterior cingulate cortex: where motor control, drive and cognition interface. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001; 2:417–24.
Article17. Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, et al. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001; 56:M146–56.
Article18. Wang YP, Gorenstein C. Assessment of depression in medical patients: a systematic review of the utility of the Beck Depression Inventory-II. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2013; 68:1274–87.
Article19. Beck AT, Epstein N, Brown G, Steer RA. An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: psychometric properties. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1988; 56:893–7.
Article20. Hagler DJ Jr, Saygin AP, Sereno MI. Smoothing and cluster thresholding for cortical surface-based group analysis of fMRI data. Neuroimage. 2006; 33:1093–103.
Article21. Kim JC, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple JD. Frailty and protein-energy wasting in elderly patients with end stage kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013; 24:337–51.
Article22. Wei K, Nyunt MS, Gao Q, Wee SL, Yap KB, Ng TP. Association of frailty and malnutrition with long-term functional and mortality outcomes among community-dwelling older adults: results from the Singapore Longitudinal Aging Study 1. JAMA Netw Open. 2018; 1:e180650.23. Wei K, Nyunt MS, Gao Q, Wee SL, Ng TP. Frailty and malnutrition: related and distinct syndrome prevalence and association among community-dwelling older adults: Singapore Longitudinal Ageing Studies. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017; 18:1019–28.
Article24. Zhang Z, Pereira SL, Luo M, Matheson EM. Evaluation of blood biomarkers associated with risk of malnutrition in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2017; 9:829.
Article25. Omran ML, Morley JE. Assessment of protein energy malnutrition in older persons, part II: laboratory evaluation. Nutrition. 2000; 16:131–40.
Article26. Canaud B, Granger Vallée A, Molinari N, Chenine L, Leray-Moragues H, Rodriguez A, et al. Creatinine index as a surrogate of lean body mass derived from urea Kt/V, pre-dialysis serum levels and anthropometric characteristics of haemodialysis patients. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e93286.
Article27. Robertson DA, Savva GM, Kenny RA. Frailty and cognitive impairment: a review of the evidence and causal mechanisms. Ageing Res Rev. 2013; 12:840–51.28. Lee YC. A study of the relationship between depression symptom and physical performance in elderly women. J Exerc Rehabil. 2015; 11:367–71.
Article29. Kang JY, Kim CH, Sung EJ, Shin HC, Shin WJ, Jung KH. The association between frailty and cognition in elderly women. Korean J Fam Med. 2016; 37:164–70.
Article30. Brigola AG, Rossetti ES, Dos Santos BR, Neri AL, Zazzetta MS, Inouye K, et al. Relationship between cognition and frailty in elderly: a systematic review. Dement Neuropsychol. 2015; 9:110–9.
Article31. Kurella M, Chertow GM, Luan J, Yaffe K. Cognitive impairment in chronic kidney disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004; 52:1863–9.
Article32. Cukor D, Peterson RA, Cohen SD, Kimmel PL. Depression in end-stage renal disease hemodialysis patients. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2006; 2:678–87.
Article33. Kimmel PL, Peterson RA. Depression in end-stage renal disease patients treated with hemodialysis: tools, correlates, outcomes, and needs. Semin Dial. 2005; 18:91–7.34. Maddock RJ, Garrett AS, Buonocore MH. Posterior cingulate cortex activation by emotional words: fMRI evidence from a valence decision task. Hum Brain Mapp. 2003; 18:30–41.
Article35. Mayberg HS, Brannan SK, Mahurin RK, Jerabek PA, Brickman JS, Tekell JL, et al. Cingulate function in depression: a potential predictor of treatment response. Neuroreport. 1997; 8:1057–61.36. Devinsky O, Morrell MJ, Vogt BA. Contributions of anterior cingulate cortex to behaviour. Brain. 1995; 118(Pt 1):279–306.
Article37. Chen WT, Chou KH, Liu LK, Lee PL, Lee WJ, Chen LK, et al. Reduced cerebellar gray matter is a neural signature of physical frailty. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015; 36:3666–76.
Article38. Buchman AS, Yu L, Wilson RS, Schneider JA, Bennett DA. Association of brain pathology with the progression of frailty in older adults. Neurology. 2013; 80:2055–61.
Article39. Murray AM, Tupper DE, Knopman DS, Gilbertson DT, Pederson SL, Li S, et al. Cognitive impairment in hemodialysis patients is common. Neurology. 2006; 67:216–23.
Article40. Cherng YG, Lin CS, Shih CC, Hsu YH, Yeh CC, Hu CJ, et al. Stroke risk and outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease or end-stage renal disease: two nationwide studies. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0191155.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Phenomenology on the Hemodialysis Experience of Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease
- A Studyof Dermal Mast Cells Number in End Stage of Renal Failure
- Acquired Cystic Kidney Disease in Patients Undergoing Long-term Hemodialysis Treatment
- Alterations of Cortical Folding Patterns in Patients with Bipolar I Disorder: Analysis of Local Gyrification Index
- Valacyclovir-Induced Neurotoxicity in a Maintenance Hemodialysis Patient