J Rheum Dis.
2023 Apr;30(2):106-115. 10.4078/jrd.2023.0002.
Acute coronary syndrome in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: a Korean single-centre cohort study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Institute for Immunology and Immunological Diseases, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2541054
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2023.0002
Abstract
Objective
This study investigated the incidence and patterns of the acute coronary syndrome (ACS) after AAV diagnosis and searched for the predictors of ACS in a single-centre cohort of Korean patients diagnosed with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV).
Methods
A total of 262 patients with AAV were included in this study. ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), non-STEMI (NSTEMI), and unstable angina (UA) were defined as ACS in this study. Only ACS that occurred during or after AAV diagnosis was counted.
Results
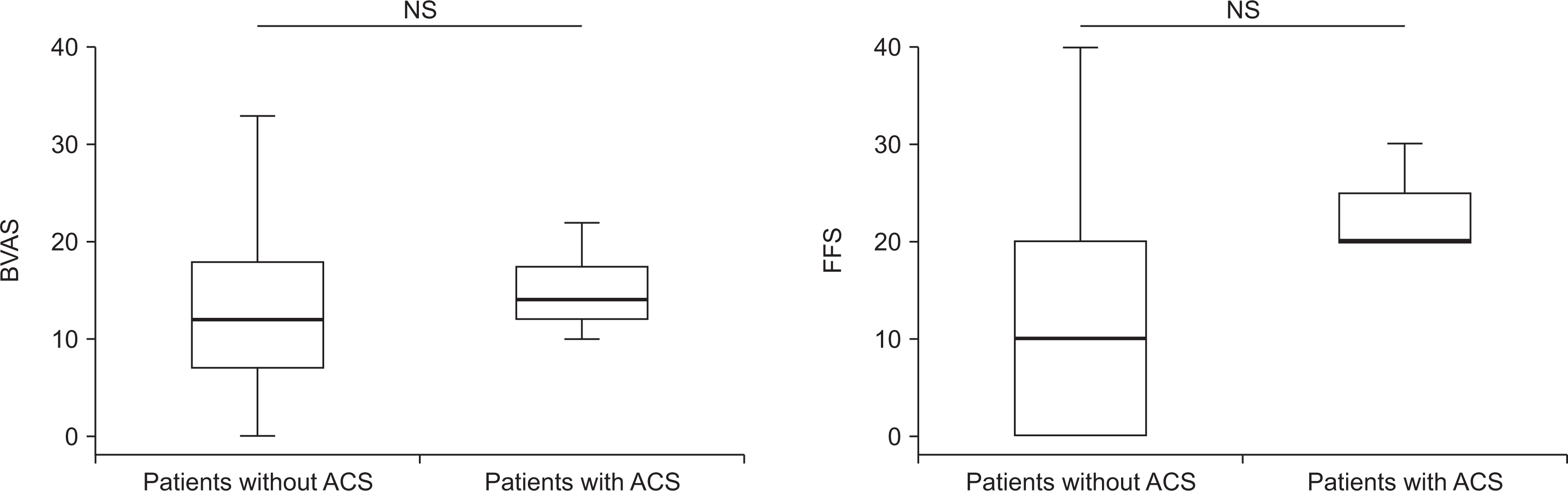
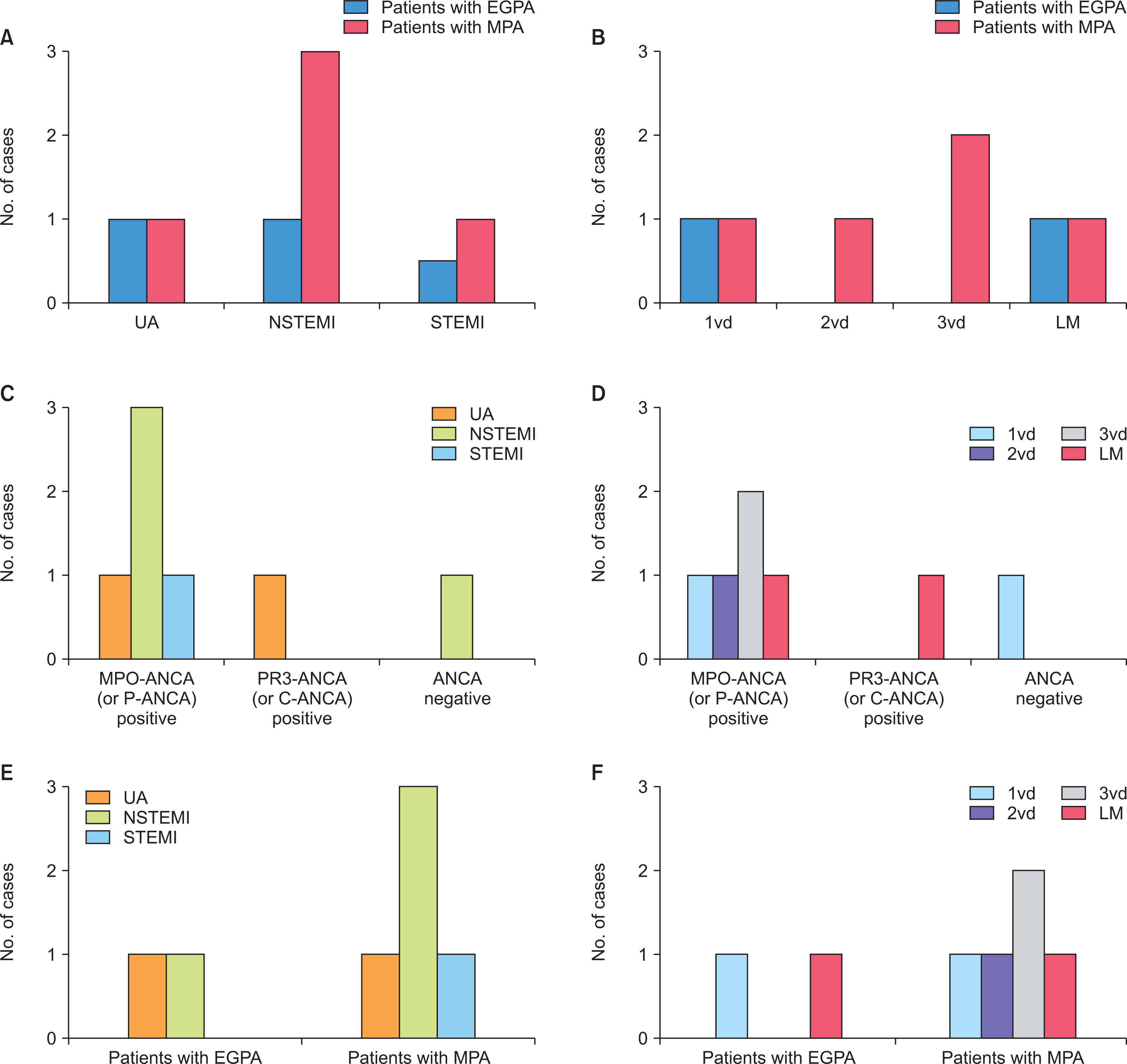
The incidence of ACS in patients with AAV was 2.7% (7 patients), and the most common type of ACS was NSTEMI regardless of the affected site or the number of coronary arteries. Five patients with ACS were diagnosed with microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) and all of them had myeloperoxidase (MPO)-ANCA (or perinuclear [P]-ANCA), whereas the remaining two patients were diagnosed with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA). Of the seven patients, 2 patients experienced ACS within the first year after AAV diagnosis, and 2 experienced ACS 5 years after AAV diagnosis. Among clinical variables, only the male sex was a predictor of ACS during the follow-up period in patients diagnosed with AAV.
Conclusion
The incidence of ACS was 2.7%, and the most common type of ACS was NSTEMI in Korean patients with AAV.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F, et al. 2013; 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 65:1–11. DOI: 10.1002/art.37715. PMID: 23045170.2. Watts R, Lane S, Hanslik T, Hauser T, Hellmich B, Koldingsnes W, et al. 2007; Development and validation of a consensus methodology for the classification of the ANCA-associated vasculitides and polyarteritis nodosa for epidemiological studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 66:222–7. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.054593. PMID: 16901958. PMCID: PMC1798520.
Article3. Lee SW, Park YB. 2019; Classification of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. J Rheum Dis. 26:156–64. DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2019.26.3.156.
Article4. Englund M, Merkel PA, Tomasson G, Segelmark M, Mohammad AJ. 2016; Comorbidities in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis versus the general population. J Rheumatol. 43:1553–8. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.151151. PMID: 27252425.
Article5. Faurschou M, Mellemkjaer L, Sorensen IJ, Svalgaard Thomsen B, Dreyer L, Baslund B. 2009; Increased morbidity from ischemic heart disease in patients with Wegener's granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 60:1187–92. DOI: 10.1002/art.24386. PMID: 19333952.
Article6. Morgan MD, Turnbull J, Selamet U, Kaur-Hayer M, Nightingale P, Ferro CJ, et al. 2009; Increased incidence of cardiovascular events in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides: a matched-pair cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 60:3493–500. DOI: 10.1002/art.24957. PMID: 19877070.
Article7. Gori T. 2021; Coronary vasculitis. Biomedicines. 9:622. DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9060622. PMID: 34072772. PMCID: PMC8226826.8. Mukhtyar C, Lee R, Brown D, Carruthers D, Dasgupta B, Dubey S, et al. 2009; Modification and validation of the Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (version 3). Ann Rheum Dis. 68:1827–32. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2008.101279. PMID: 19054820.
Article9. Park PG, Pyo JY, Ahn SS, Song JJ, Park YB, Huh JH, et al. 2021; Metabolic syndrome severity score, comparable to serum creatinine, could predict the occurrence of end-stage kidney disease in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. J Clin Med. 10:5744. DOI: 10.3390/jcm10245744. PMID: 34945043. PMCID: PMC8708376.
Article10. Kim MK, Pyo JY, Ahn SS, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. 2022; A retrospective analysis of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis aiming for an equation prediction end-stage renal disease. Clin Rheumatol. 41:773–81. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-021-05972-5. PMID: 34750691.11. Guillevin L, Pagnoux C, Seror R, Mahr A, Mouthon L, Toumelin PL. French Vasculitis Study Group (FVSG). 2011; The Five-Factor Score revisited: assessment of prognoses of systemic necrotizing vasculitides based on the French Vasculitis Study Group (FVSG) cohort. Medicine (Baltimore). 90:19–27. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0b013e318205a4c6. PMID: 21200183.12. Stone JH, Hoffman GS, Merkel PA, Min YI, Uhlfelder ML, Hellmann DB, et al. 2001; A disease-specific activity index for Wegener's granulomatosis: modification of the Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score. International Network for the Study of the Systemic Vasculitides (INSSYS). Arthritis Rheum. 44:912–20. DOI: 10.1002/1529-0131(200104)44:4<912::AID-ANR148>3.0.CO;2-5. PMID: 11318006.13. McAdoo SP, Medjeral-Thomas N, Gopaluni S, Tanna A, Mansfield N, Galliford J, et al. 2019; Long-term follow-up of a combined rituximab and cyclophosphamide regimen in renal anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 34:63–73. Erratum. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfx378. PMID: 29462348. PMCID: PMC6322443.
Article14. Murray CJ, Atkinson C, Bhalla K, Birbeck G, Burstein R, Chou D, et al. 2013; The state of US health, 1990-2010: burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. JAMA. 310:591–608. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2013.13805. PMID: 23842577. PMCID: PMC5436627.15. Kim J, Lee E, Lee T, Sohn A. 2013; Economic burden of acute coronary syndrome in South Korea: a national survey. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 13:55. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2261-13-55. PMID: 23924508. PMCID: PMC3751132.
Article16. Kitching AR, Anders HJ, Basu N, Brouwer E, Gordon J, Jayne DR, et al. 2020; ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 6:71. DOI: 10.1038/s41572-020-0204-y. PMID: 32855422.
Article17. Jennette JC, Falk RJ. 2014; Pathogenesis of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-mediated disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:463–73. DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.103. PMID: 25003769.
Article18. Wang H, Liu Z, Shao J, Lin L, Jiang M, Wang L, et al. 2020; Immune and inflammation in acute coronary syndrome: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. J Immunol Res. 2020:4904217. DOI: 10.1155/2020/4904217. PMID: 32908939. PMCID: PMC7450309.
Article19. Lee JK, Kim H, Hong JB, Sheen SH, Han IB, Sohn S. 2020; Association of acute myocardial infarction with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis in Korea: a nationwide longitudinal cohort study. J Clin Neurosci. 78:97–101. DOI: 10.1016/j.jocn.2020.06.002. PMID: 32620475.
Article20. Jeong H, Baek SY, Kim SW, Eun YH, Kim IY, Kim H, et al. 2017; Comorbidities of rheumatoid arthritis: results from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. PLoS One. 12:e0176260. Erratum. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178309. PMID: 28542532. PMCID: PMC5436868.
Article21. Kook HY, Jeong MH, Oh S, Yoo SH, Kim EJ, Ahn Y, et al. 2014; Current trend of acute myocardial infarction in Korea (from the Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry from 2006 to 2013). Am J Cardiol. 114:1817–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.09.019. PMID: 25438907.
Article22. Schiefermueller J, Alaour B, Calver A, Curzen N. 2017; Lesson of the month 1: beware the atypical presentation: eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis presenting as acute coronary syndrome. Clin Med (Lond). 17:180–2. DOI: 10.7861/clinmedicine.17-2-180. PMID: 28365634. PMCID: PMC6297632.
Article23. Wagner AD, Meyer GP, Rihl M, Rathmann A, Wittkop U, Zeidler H, et al. 2007; Acute coronary syndrome associated with Churg-Strauss syndrome. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 3:775–9.24. Correia AS, Gonçalves A, Araújo V, Pereira JM, Rodrigues Pereira P, et al. Almeida e Silva J. 2013; Churg-Strauss syndrome presenting with eosinophilic myocarditis: a diagnostic challenge. Rev Port Cardiol. 32:707–11. DOI: 10.1016/j.repc.2012.10.017. PMID: 23890465.
Article25. Buckley CD, Rainger GE, Nash GB, Raza K. 2005; Endothelial cells, fibroblasts and vasculitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 44:860–3. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh542. PMID: 15644388. PMCID: PMC3119433.
Article26. Pagnoux C, Chironi G, Simon A, Guillevin L. 2007; Atherosclerosis in ANCA-associated vasculitides. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1107:11–21. DOI: 10.1196/annals.1381.002. PMID: 17804528.
Article27. Frustaci A, Alfarano M, Verardo R, Agrati C, Casetti R, Miraldi F, et al. 2021; Myocarditis-associated necrotizing coronary vasculitis: incidence, cause, and outcome. Eur Heart J. 42:1609–17. DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa973. PMID: 33355356. PMCID: PMC8088814.
Article28. Meier LA, Binstadt BA. 2018; The contribution of autoantibodies to inflammatory cardiovascular pathology. Front Immunol. 9:911. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00911. PMID: 29755478. PMCID: PMC5934424.
Article29. Wick G, Jakic B, Buszko M, Wick MC, Grundtman C. 2014; The role of heat shock proteins in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 11:516–29. DOI: 10.1038/nrcardio.2014.91. PMID: 25027488.
Article30. Mandal K, Jahangiri M, Xu Q. 2004; Autoimmunity to heat shock proteins in atherosclerosis. Autoimmun Rev. 3:31–7. DOI: 10.1016/S1568-9972(03)00088-0. PMID: 15003185.
Article31. Bijl M. 2003; Endothelial activation, endothelial dysfunction and premature atherosclerosis in systemic autoimmune diseases. Neth J Med. 61:273–7.32. Millet A, Pederzoli-Ribeil M, Guillevin L, Witko-Sarsat V, Mouthon L. 2013; Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides: is it time to split up the group? Ann Rheum Dis. 72:1273–9. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203255. PMID: 23606701.
Article33. Mavrogeni S, Karabela G, Gialafos E, Stavropoulos E, Spiliotis G, Katsifis G, et al. 2013; Cardiac involvement in ANCA (+) and ANCA (-) Churg-Strauss syndrome evaluated by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 12:322–7. DOI: 10.2174/18715281113129990054. PMID: 23909889.
Article34. Cheung CC, Constantine M, Ahmadi A, Shiau C, Chen LYC. 2017; Eosinophilic myocarditis. Am J Med Sci. 354:486–92. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjms.2017.04.002. PMID: 29173361.
Article35. Kim Y, Ahn Y, Cho MC, Kim CJ, Kim YJ, Jeong MH. 2019; Current status of acute myocardial infarction in Korea. Korean J Intern Med. 34:1–10. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2018.381. PMID: 30612415. PMCID: PMC6325441.
Article36. Mourguet M, Chauveau D, Faguer S, Ruidavets JB, Béjot Y, Ribes D, et al. 2019; Increased ischemic stroke, acute coronary artery disease and mortality in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis. J Autoimmun. 96:134–41. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.09.004. PMID: 30236485.
Article37. Ahn SS, Yoon T, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW. 2020; Lipid profiles in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: a cross-sectional analysis. J Rheum Dis. 27:261–9. DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2020.27.4.261.
Article38. Zhuang Q, Shen C, Chen Y, Zhao X, Wei P, Sun J, et al. 2019; Association of high sensitive C-reactive protein with coronary heart disease: a Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med Genet. 20:170. DOI: 10.1186/s12881-019-0910-z. PMID: 31694563. PMCID: PMC6836320.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- ANCA : The Marker Antibody of Vasculitis
- ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Presenting with Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis
- ANCA-Associated Vasculitic Neuropathy with Concurrent Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- A Case of Propylthiouracil-induced Lupus Erythematosus Accompanied by Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-positive Vasculitis
- A Case of Sub-acute Bacterial Endocarditis associated with a Positive ANCA Serology