J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2022 Sep;24(3):281-290. 10.7461/jcen.2022.E2021.09.004.
Anatomical safety and precaution of transarterial embolization of a falcotentorial dural arteriovenous fistula fed by the artery of Davidoff and Schechter: Case report and review of the literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2533681
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2022.E2021.09.004
Abstract
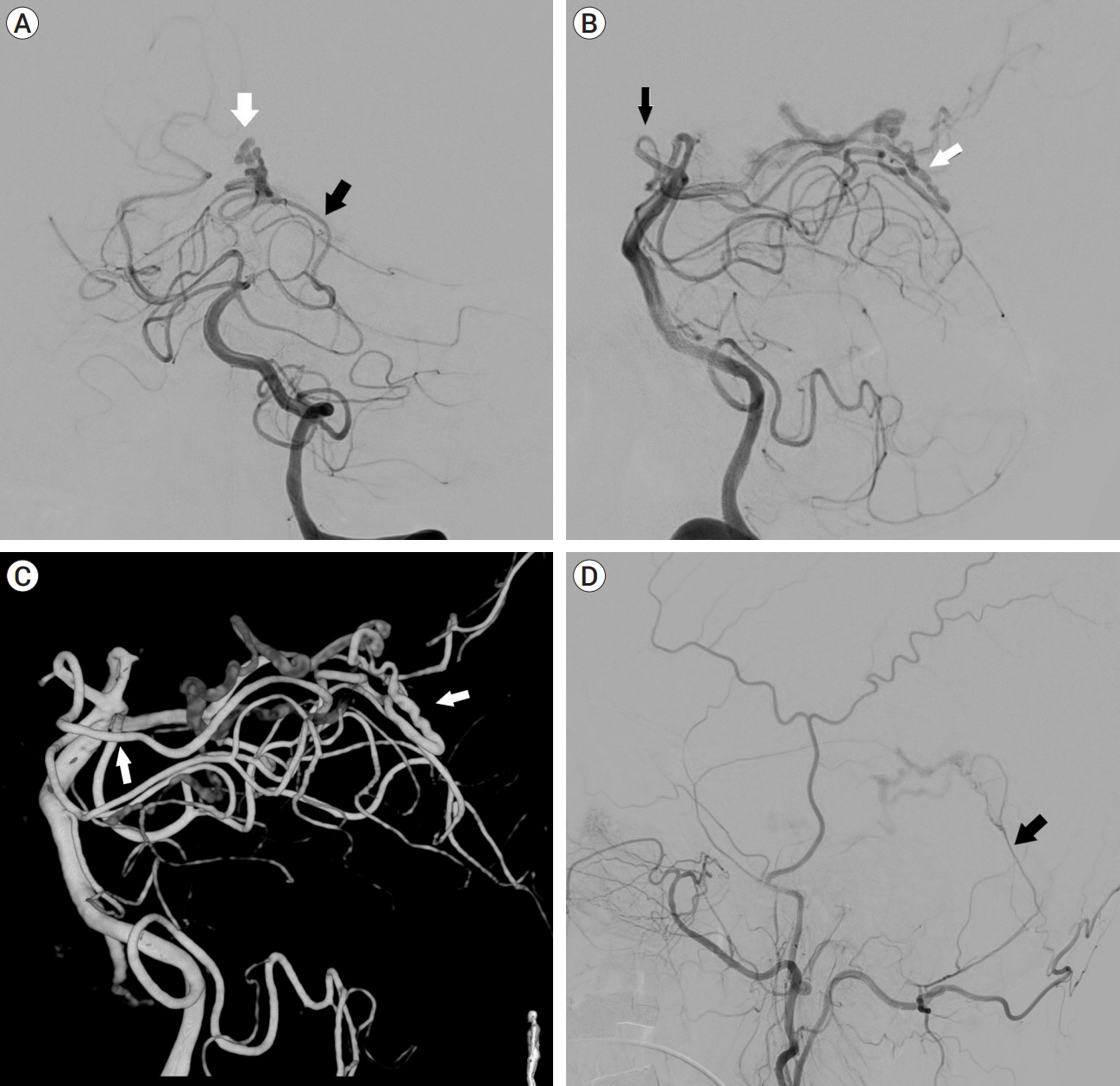
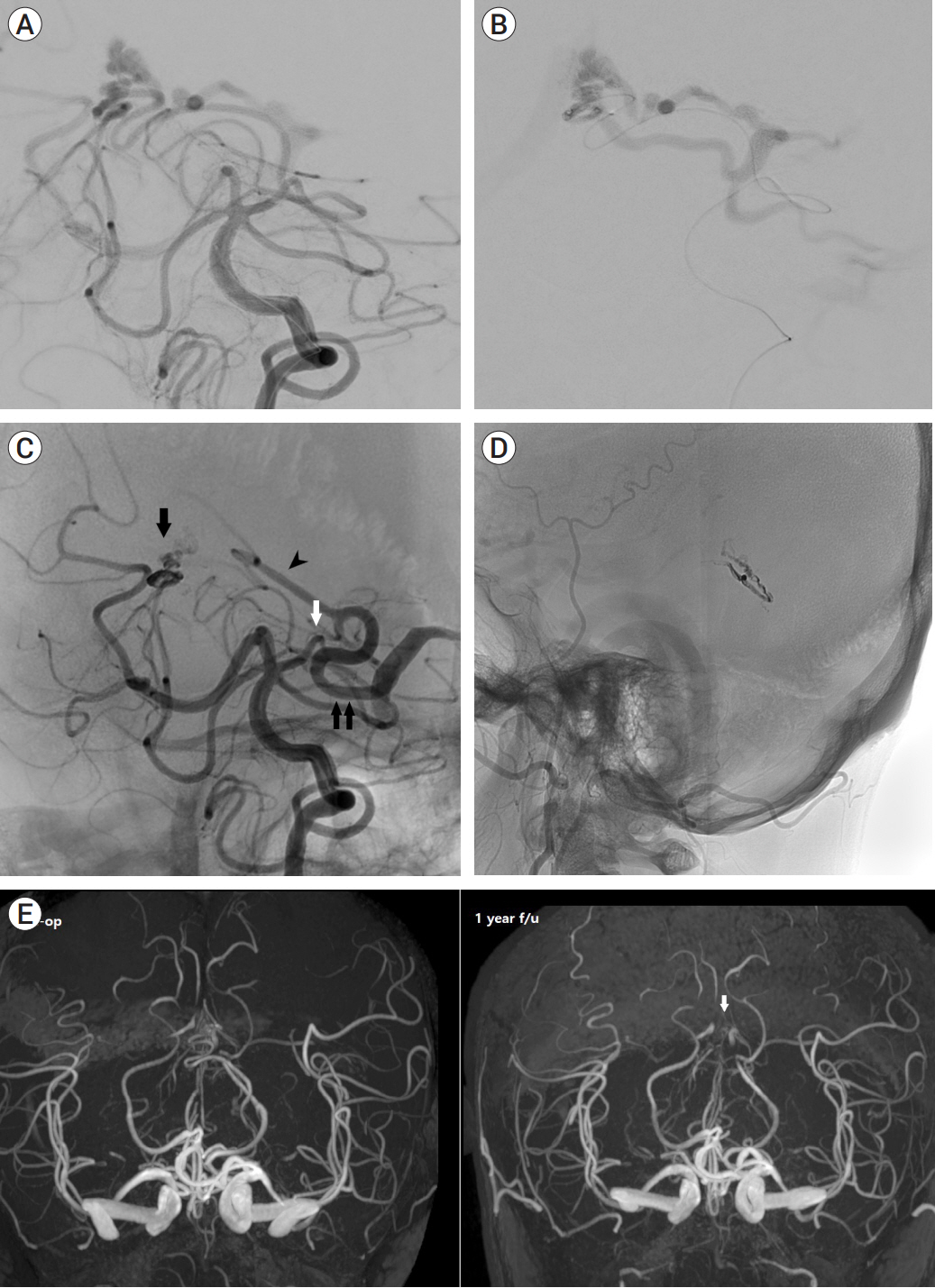
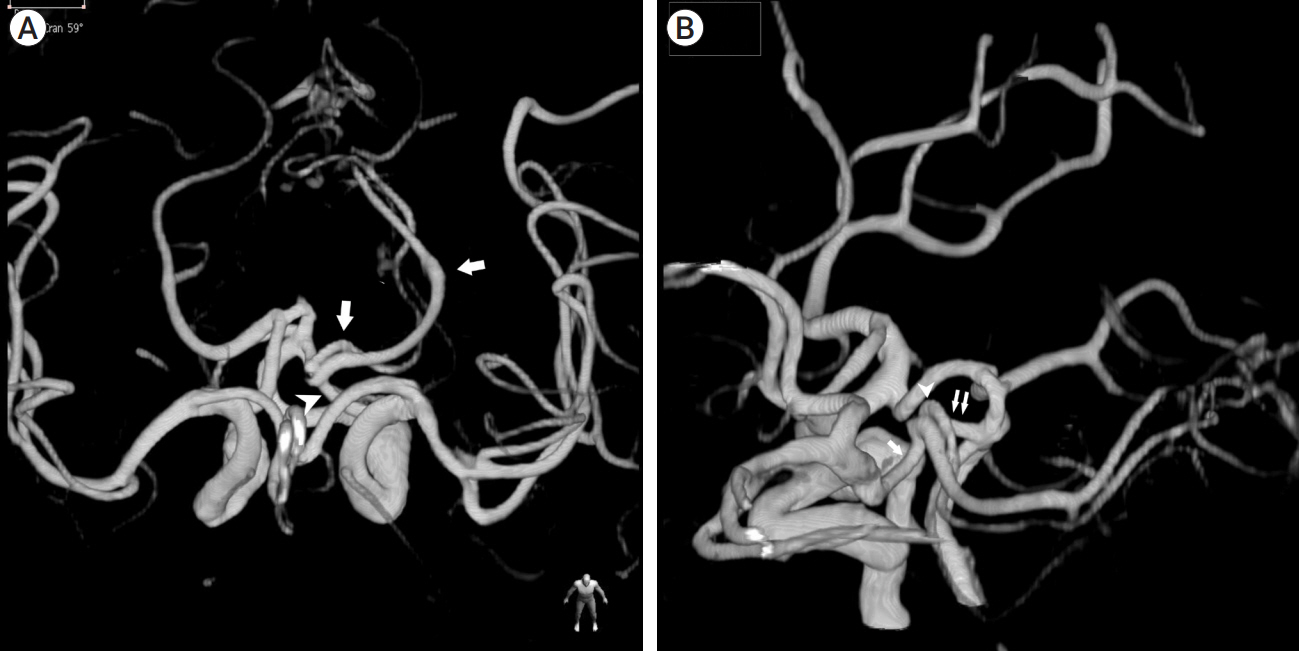
- The artery of Davidoff and Schechter (ADS), a pure meningeal branch of the posterior cerebral artery (PCA), is often reported as a feeder of the tentorial dural arteriovenous fistula (TDAVF). However, there are few reported cases of embolization via this artery. We present an interesting case of a patient with incidentally found TDAVF fed by the ADS and with fetal type posterior communicating artery, in which the feeder was confused with the PCA due to the similar pathways around the brain stem. It was successfully treated with transarterial embolization through the ADS. We reviewed related published articles to determine the safety of embolization via the ADS.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bhatia KD, Kortman H, Walchli T, Radovanovic I, Pereira VM, Krings T. Artery of Davidoff and Schechter supply in dural arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020; Feb. 41(2):300–4.
Article2. Borden JA, Wu JK, Shucart WA. A proposed classification for spinal and cranial dural arteriovenous fistulous malformations and implications for treatment. J Neurosurg. 1995; Feb. 82(2):166–79.
Article3. Brinjikji W, Cloft HJ, Lanzino G. Clinical, angiographic, and treatment characteristics of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with pial arterial supply. J Neurointerv Surg. 2021; Apr. 13(4):331–5.
Article4. Byrne JV, Garcia M. Tentorial dural fistulas: endovascular management and description of the medial dural-tentorial branch of the superior cerebellar artery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; Sep. 34(9):1798–804.
Article5. Gioppo A, Farago G, Caldiera V, Caputi L, Cusin A, Ciceri E. Medial tentorial dural arteriovenous fistula embolization: single experience with embolic liquid polymer SQUID and review of the literature. World Neurosurg. 2017; Nov. 107:1050.
Article6. Griessenauer CJ, Loukas M, Scott JA, Tubbs RS, Cohen-Gadol AA. The artery of Davidoff and Schechter: an anatomical study with neurosurgical case correlates. Br J Neurosurg. 2013; Dec. 27(6):815–8.
Article7. Hart JL, Davagnanam I, Chandrashekar HS, Brew S. Angiography and selective microcatheter embolization of a falcine meningioma supplied by the artery of Davidoff and Schechter. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2011; Mar. 114(3):710–3.8. Islak C, Bagcilar O, Nacar Dogan S, Korkmazer B, Arslan S, Kizilkilic O, et al. Endovascular management of anterior falcotentorial dural arteriovenous fistulas: importance of functionality of deep venous system and existence of accompanying choroidal arteriovenous malformation. J Neurointerv Surg. 2021; Jul. neurintsurg-2021-017730.
Article9. Lawton MT, Sanchez-Mejia RO, Pham D, Tan J, Halbach VV. Tentorial dural arteriovenous fistulae: operative strategies and microsurgical results for six types. Neurosurgery. 2008; Mar. 62(3 Suppl 1):110–24. discussion 124-5.10. Martins C, Yasuda A, Campero A, Ulm AJ, Tanriover N, Rhoton A Jr. Microsurgical anatomy of the dural arteries. Neurosurgery. 2005; Apr. 56(2 Suppl):211–51. discussion 211-51.
Article11. Puri AS. Dural arteriovenous fistula supplied by the artery of Davidoff and Schechter. Radiol Case Rep. 2015; Nov. 5(2):375.
Article12. Roman NIS, Rodriguez P, Nasser H, Cox M, Ramchand P, Choudhri O, et al. Artery of Davidoff and Schechter: A large angiographic case series of dural AV fistulas. Neurohospitalist. 2022; Jan. 12(1):155–61.
Article13. Sato K, Matsumoto Y, Endo H, Tominaga T. A hemorrhagic complication after Onyx embolization of a tentorial dural arteriovenous fistula: A caution about subdural extension with pial arterial supply. Interv Neuroradiol. 2017; Jun. 23(3):307–12.
Article14. Wollschlaeger PB, Wollschlaeger G. An infratentorial meningeal artery. Radiologe. 1965; Nov. 5(11):451–2.15. Wu Q, Zhang XS, Wang HD, Zhang QR, Wen LL, Hang CH, et al. Onyx embolization for tentorial dural arteriovenous fistula with pial arterial supply: Case series and analysis of complications. World Neurosurg. 2016; Aug. 92:58–64.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Involving Transverse Sinus: Successful Embolization Using Onyx(R)
- Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of Jugular Foramen with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage : Selective Transarterial Embolization
- Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistula with Supply from the Lateral Sacral Artery: Case Report and Review of Literature
- Embolization through the Ophthalmic Artery with Onyx in Bilateral Ethmoidal Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report
- Infantile Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Transverse Sinus Presenting with Ocular Symptoms, Case Reports and Review of Literature