J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2022 Sep;24(3):257-262. 10.7461/jcen.2022.E2021.06.005.
Use of covered stent (CGuard) in the treatment of post-traumatic internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India
- KMID: 2533677
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2022.E2021.06.005
Abstract
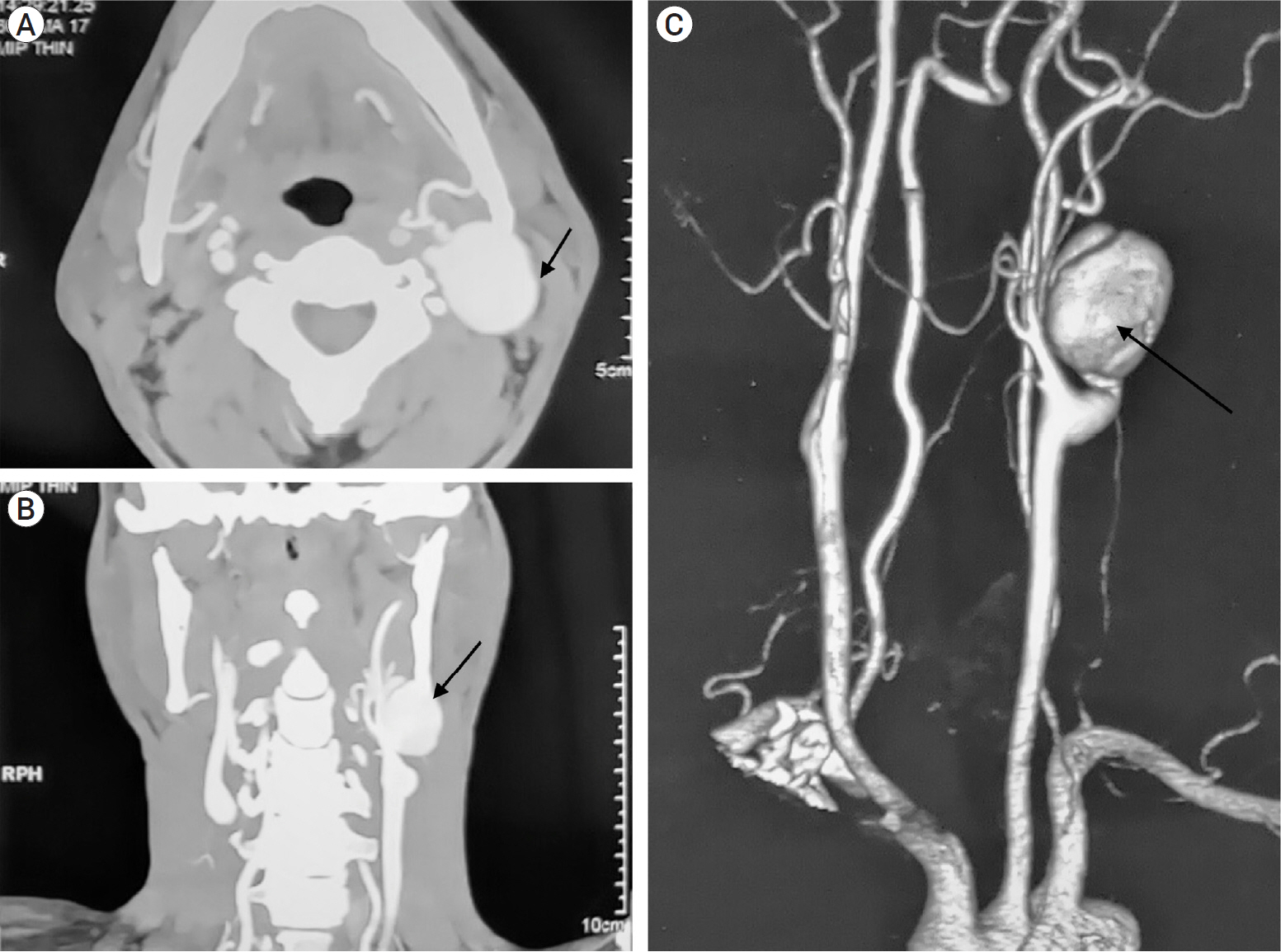
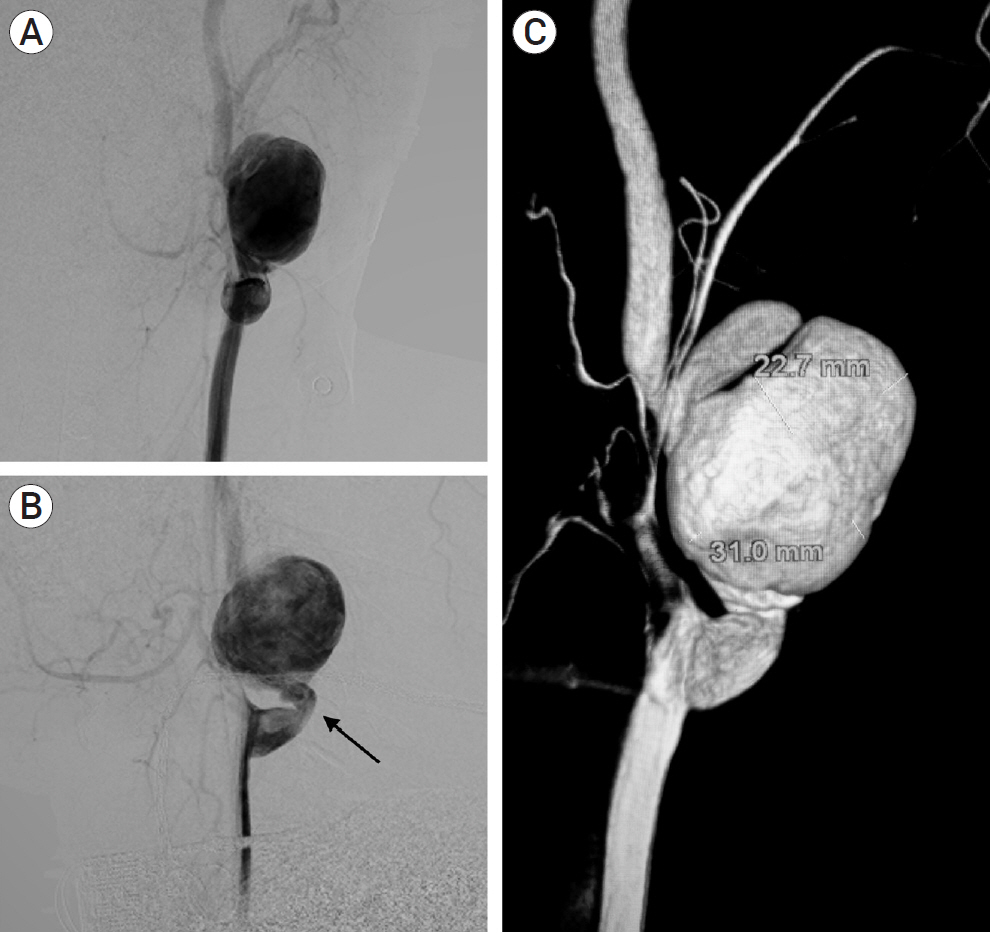
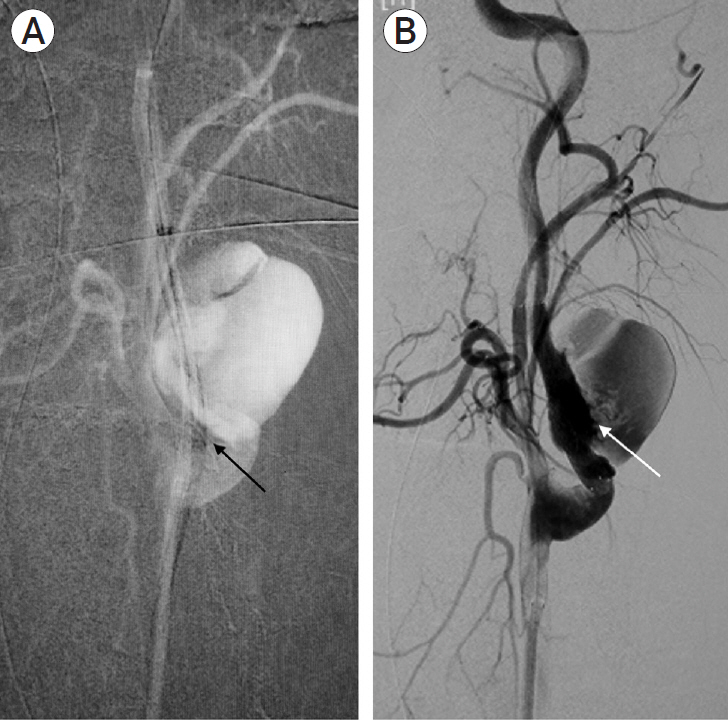
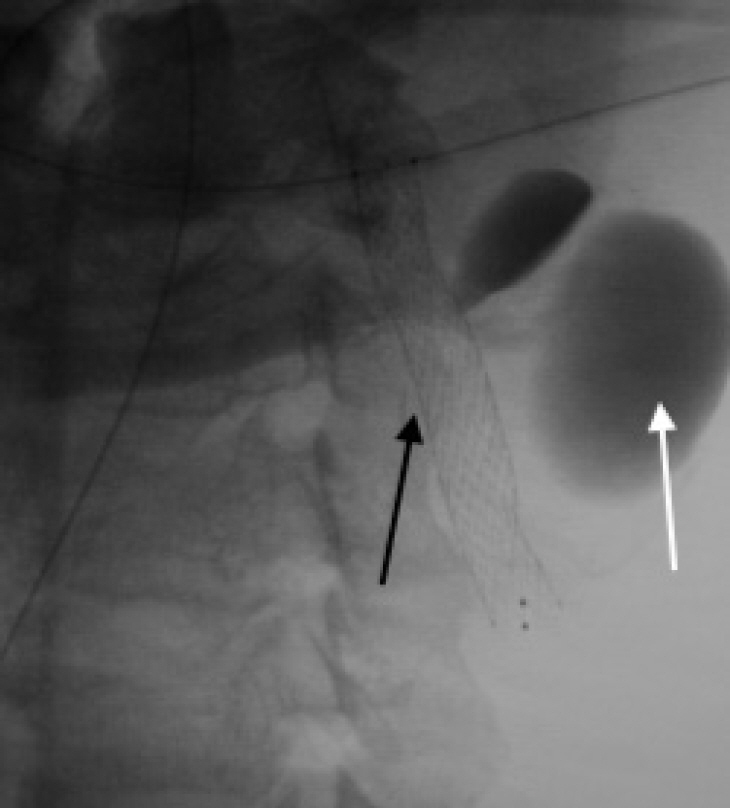
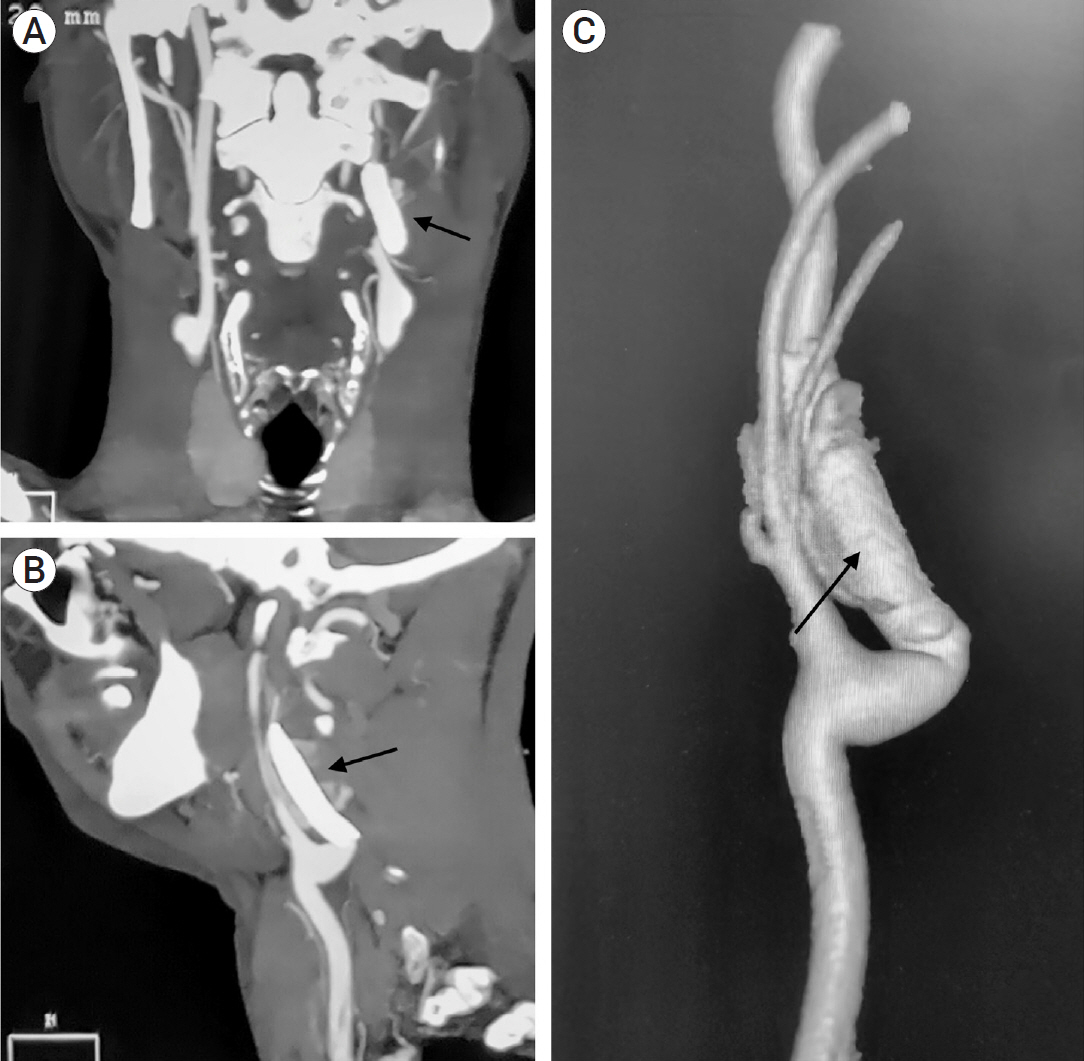
- Post-traumatic internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm (ICA PSA) is a rare occurrence with high mortality rates, and with the advent of endovascular therapy, its treatment has shown drastic improvement in clinical as well as radiological outcomes. Here we are describing our experience with the CGuard embolic protection system (InspireMD, Tel Aviv, Israel) for the treatment of post-traumatic left ICA PSA in a 49-year-old male. New improved biomechanics and navigability have proven it to be a safe and efficient treatment modality for ICA PSA. However, a multicentric large-scale randomized trial is recommended to support this modality.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Biffl WL, Moore EE, Offner PJ, Brega KE, Franciose RJ, Burch JM. Blunt carotid arterial injuries: Implications of a new grading scale. J Trauma. 1999; Nov. 47(5):845–53.
Article2. Ducrocq X, Lacour JC, Debouverie M, Bracard S, Girard F, Weber M. Cerebral ischemic accidents in young subjects: A prospective study of 296 patients aged 16 to 45 years [in French]. Rev Neurol (Paris). 1999; Sep. 155(8):575–82.3. El-Sabrout R, Cooley DA. Extracranial carotid artery aneurysms: Texas Heart Institute experience. J Vasc Surg. 2000; Apr. 31(4):702–12.
Article4. Hoppe H, Barnwell SL, Nesbit GM, Petersen BD. Stent-grafts in the treatment of emergent or urgent carotid artery disease: Review of 25 Cases. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008; Jan. 19(1):31–41.
Article5. Kumar A, Prabhakar A, Gupta V, Khandelwal N, Ahuja CK, Singhal M, et al. Endovascular management of internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysms: A single-centre experience of 20 patients. Neurol India. 2018; 66(4):1067–74.
Article6. Bracken ME. Evaluation and management of neck trauma. Emerg Med Clin N Am. 2007; Aug. 25(3):679–94.
Article7. Sliker CW, Lui FY, Scalea TM. Blunt cerebrovascular injuries: Does treatment always matter? J Trauma. 2009; Jan. 66(1):132–43.
Article8. Tseng YY, Yang ST, Yeh YS, Yang TC, Wong HF. Traumatic internal carotid pseudoaneurysm mimicking sphenoid sinus tumor. Rhinology. 2007; Dec. 45(4):332–4.9. Wang W, Li MH, Li YD, Gu BX, Wang J, Zhang PL, et al. Treatment of traumatic internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysms with the Willis covered stent: A prospective study. J Trauma. 2011; Apr. 70(4):816–22.
Article10. Wissgott C, Schmidt W, Brandt-Wunderlich C, Behrens P, Andresen R. Clinical results and mechanical properties of the carotid CGUARD double-layered embolic prevention stent. Journal of Endovascular Therapy. 2017; Feb. 24(1):130–137.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm of the External and Internal Carotid Artery Presenting as Epistaxis: Case Report
- Covered Stenting Is an Effective Option for Traumatic Carotid Pseudoaneurysm with Promising Long-Term Outcome
- Internal Carotid Artery Pseudoaneurysm in a Patient Presenting With Recurrent Epistaxis: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Conjoined Stent Technique for Radiation Induced Long Segment Carotid Stenosis and Pseudoaneurysm
- Symptomatic Post Endarterectomy Common Carotid Artery Pseudoaneurysm Treated with Combination of Flow Diverter Implantation and Carotid Stenting