Korean J Orthod.
2022 Jan;52(1):3-19. 10.4041/kjod.2022.52.1.3.
Accuracy of one-step automated orthodontic diagnosis model using a convolutional neural network and lateral cephalogram images with different qualities obtained from nationwide multi-hospitals
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, Asan Medical Institute of Convergence Science and Technology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Private Practice, Incheon, Korea
- 4Department of Orthodontics, Chonnam National University School of Dentistry, Gwangju, Korea
- 5Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- 6Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea
- 7Department of Orthodontics, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
- 8Department of Orthodontics, Kyung Hee University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea
- 9Department of Orthodontics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 10Department of Orthodontics, Institute of Oral Health Science, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- 11Department of Orthodontics, College of Dentistry, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea
- 12Department of Convergence Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 13Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Dental Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2524898
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2022.52.1.3
Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study was to investigate the accuracy of one-step automated orthodontic diagnosis of skeletodental discrepancies using a convolutional neural network (CNN) and lateral cephalogram images with different qualities from nationwide multi-hospitals.
Methods
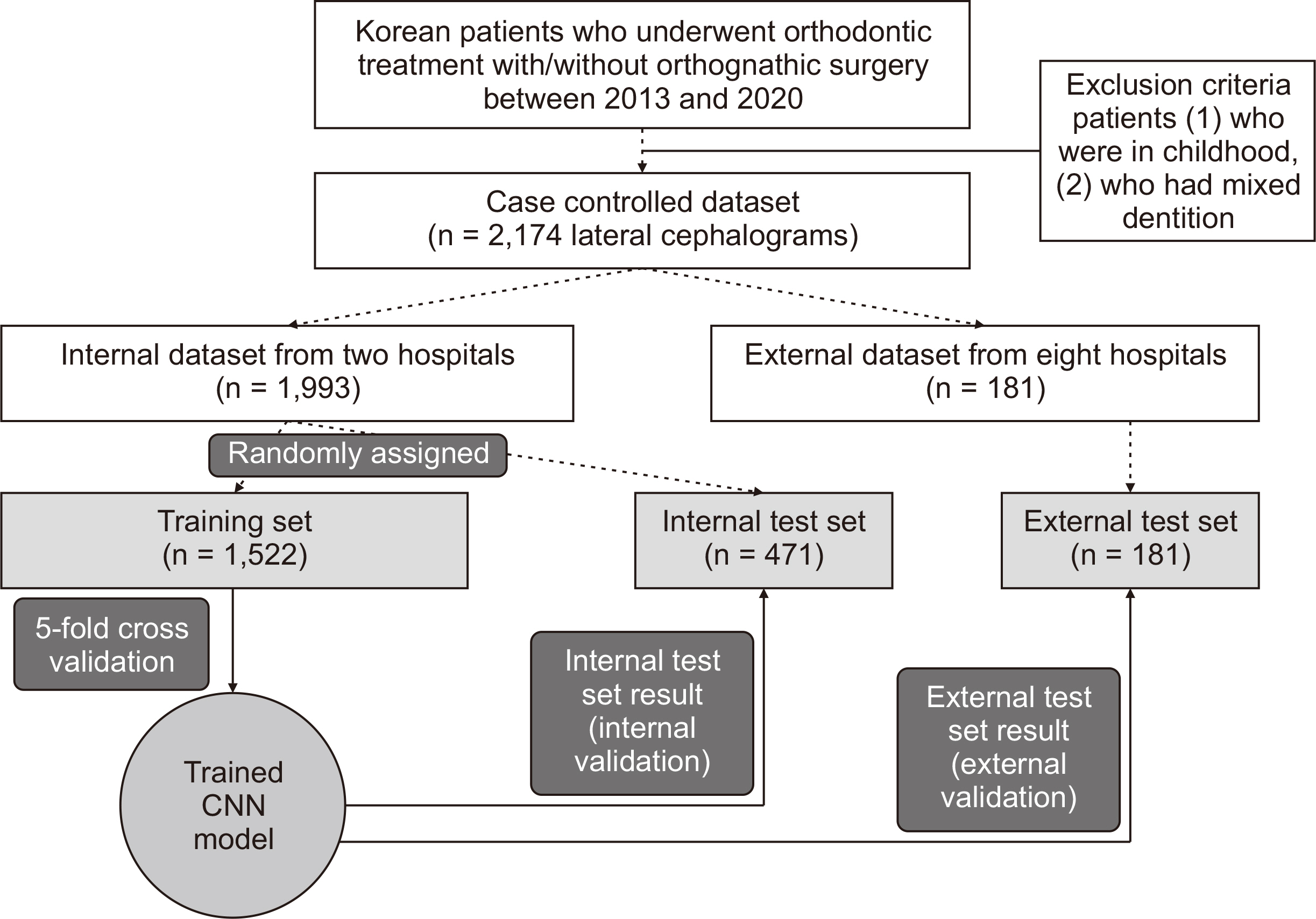
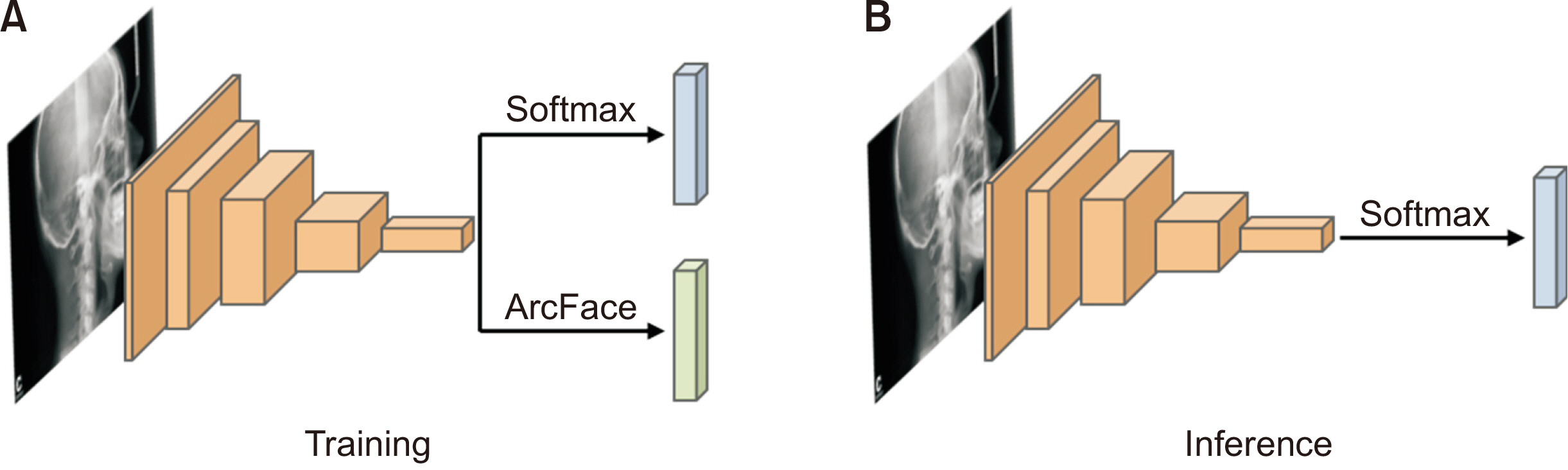
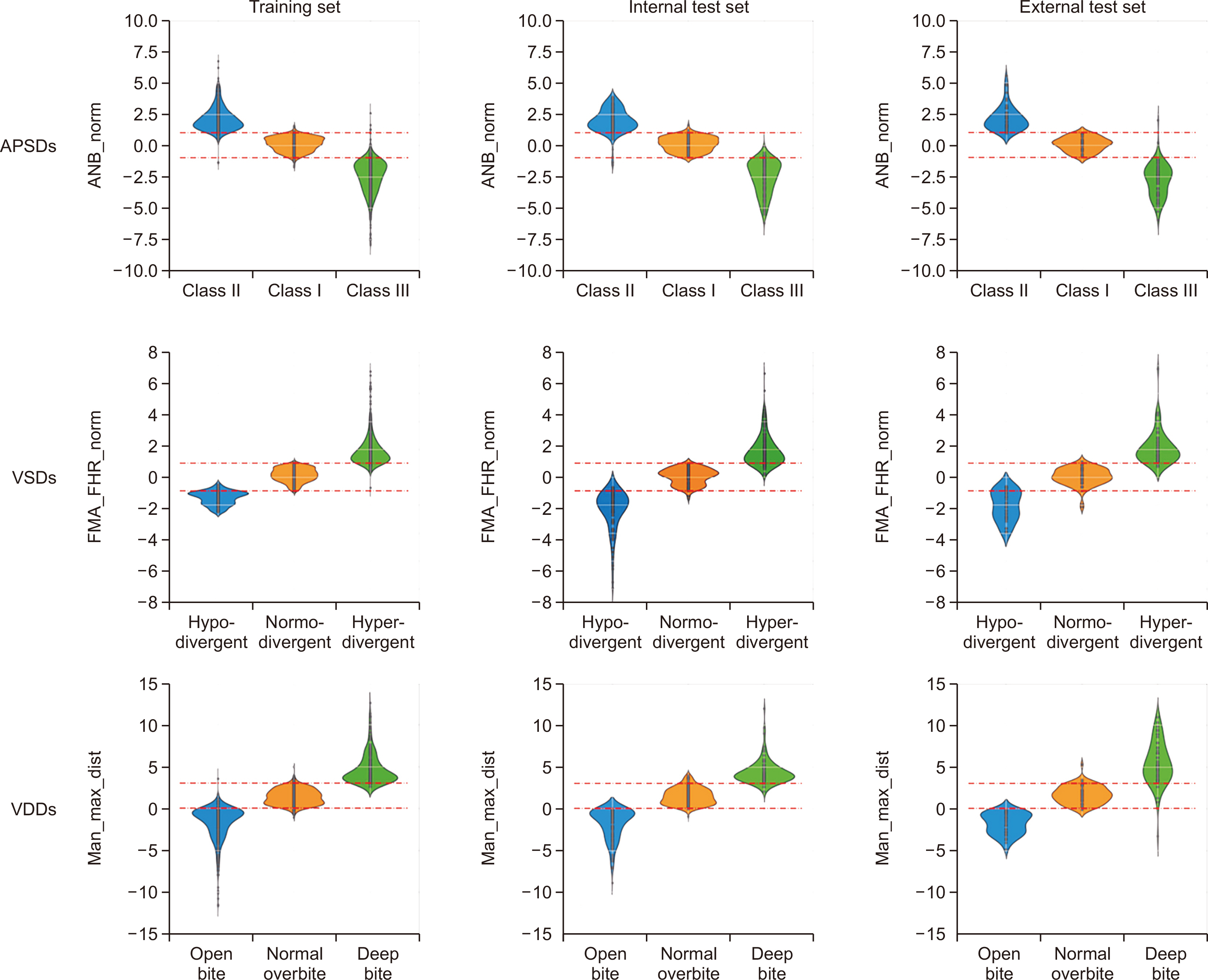
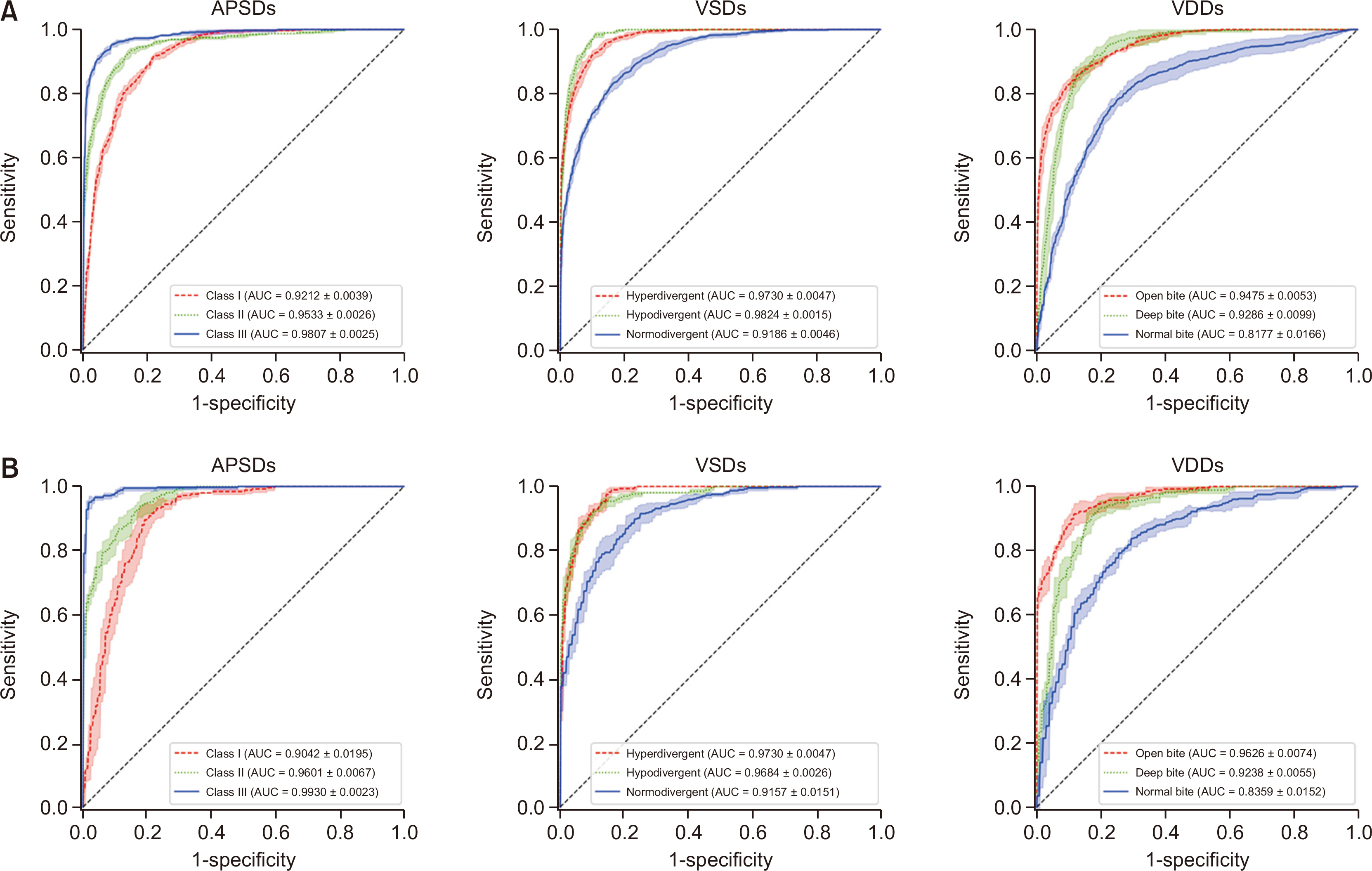
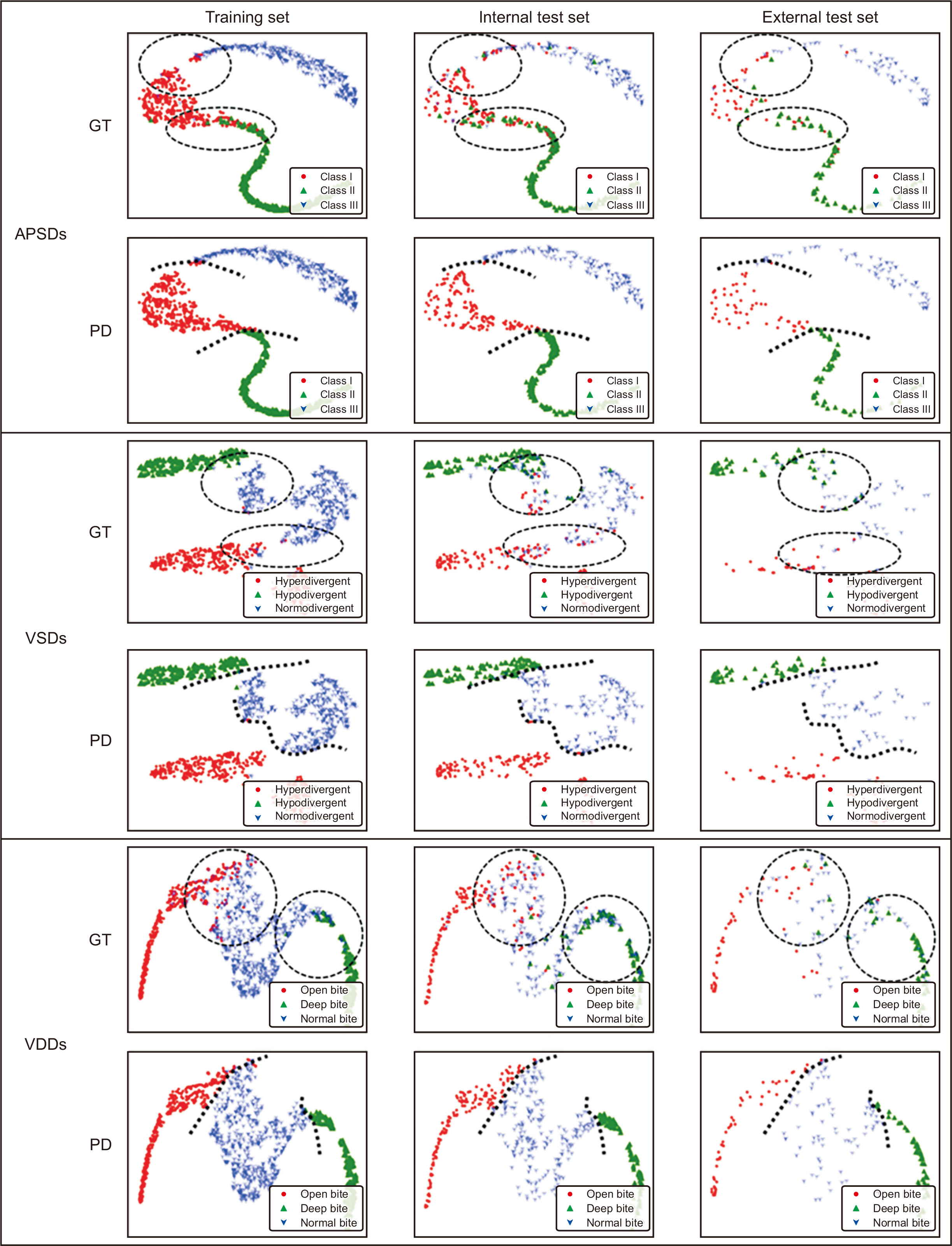
Among 2,174 lateral cephalograms, 1,993 cephalograms from two hospitals were used for training and internal test sets and 181 cephalograms from eight other hospitals were used for an external test set. They were divided into three classification groups according to anteroposterior skeletal discrepancies (Class I, II, and III), vertical skeletal discrepancies (normodivergent, hypodivergent, and hyperdivergent patterns), and vertical dental discrepancies (normal overbite, deep bite, and open bite) as a gold standard. Pre-trained DenseNet-169 was used as a CNN classifier model. Diagnostic performance was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis, t-stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE), and gradientweighted class activation mapping (Grad-CAM).
Results
In the ROC analysis, the mean area under the curve and the mean accuracy of all classifications were high with both internal and external test sets (all, > 0.89 and > 0.80). In the t-SNE analysis, our model succeeded in creating good separation between three classification groups. Grad-CAM figures showed differences in the location and size of the focus areas between three classification groups in each diagnosis.
Conclusions
Since the accuracy of our model was validated with both internal and external test sets, it shows the possible usefulness of a one-step automated orthodontic diagnosis tool using a CNN model. However, it still needs technical improvement in terms of classifying vertical dental discrepancies.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arık SÖ, Ibragimov B, Xing L. 2017; Fully automated quantitative cephalometry using convolutional neural networks. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 4:014501. DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.4.1.014501. PMID: 28097213. PMCID: PMC5220585.2. Kim H, Shim E, Park J, Kim YJ, Lee U, Kim Y. 2020; Web-based fully automated cephalometric analysis by deep learning. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 194:105513. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105513. PMID: 32403052.
Article3. Nishimoto S, Sotsuka Y, Kawai K, Ishise H, Kakibuchi M. 2019; Personal computer-based cephalometric landmark detection with deep learning, using cephalograms on the internet. J Craniofac Surg. 30:91–5. DOI: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000004901. PMID: 30439733.
Article4. Erkan M, Gurel HG, Nur M, Demirel B. 2012; Reliability of four different computerized cephalometric analysis programs. Eur J Orthod. 34:318–21. DOI: 10.1093/ejo/cjr008. PMID: 21502380.
Article5. Wen J, Liu S, Ye X, Xie X, Li J, Li H, et al. 2017; Comparative study of cephalometric measurements using 3 imaging modalities. J Am Dent Assoc. 148:913–21. DOI: 10.1016/j.adaj.2017.07.030. PMID: 29042006.
Article6. Rudolph DJ, Sinclair PM, Coggins JM. 1998; Automatic computerized radiographic identification of cephalometric landmarks. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 113:173–9. DOI: 10.1016/S0889-5406(98)70289-6. PMID: 9484208.
Article7. Mosleh MA, Baba MS, Malek S, Almaktari RA. 2016; Ceph-X: development and evaluation of 2D cephalometric system. BMC Bioinformatics. 17(Suppl 19):499. DOI: 10.1186/s12859-016-1370-5. PMID: 28155649. PMCID: PMC5259857.
Article8. Yu HJ, Cho SR, Kim MJ, Kim WH, Kim JW, Choi J. 2020; Automated skeletal classification with lateral cephalometry based on artificial intelligence. J Dent Res. 99:249–56. DOI: 10.1177/0022034520901715. PMID: 31977286.
Article9. Park JH, Hwang HW, Moon JH, Yu Y, Kim H, Her SB, et al. 2019; Automated identification of cephalometric landmarks: part 1-comparisons between the latest deep-learning methods YOLOV3 and SSD. Angle Orthod. 89:903–9. DOI: 10.2319/022019-127.1. PMID: 31282738. PMCID: PMC8109157.
Article10. Hwang HW, Park JH, Moon JH, Yu Y, Kim H, Her SB, et al. 2020; Automated identification of cephalometric landmarks: part 2-might it be better than human? Angle Orthod. 90:69–76. DOI: 10.2319/022019-129.1. PMID: 31335162. PMCID: PMC8087057.
Article11. Kunz F, Stellzig-Eisenhauer A, Zeman F, Boldt J. 2020; Artificial intelligence in orthodontics: evaluation of a fully automated cephalometric analysis using a customized convolutional neural network. J Orofac Orthop. 81:52–68. DOI: 10.1007/s00056-019-00203-8. PMID: 31853586.12. Korean Association of Orthodontics Malocclusion White Paper Publication Committee. 1997. Cephalometric analysis of normal occlusion in Korean adults. Korean Association of Orthodontists;Seoul:13. Bujang MA, Baharum N. 2017; Guidelines of the minimum sample size requirements for Cohen's Kappa. Epidemiol Biostat Public Health. 14:e12267.14. McHugh ML. 2012; Interrater reliability: the Kappa statistic. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 22:276–82. DOI: 10.11613/BM.2012.031. PMID: 23092060. PMCID: PMC3900052.
Article15. Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, et al. 2015; ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis. 115:211–52. DOI: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y. PMID: 31222375.
Article16. Huang G, Liu Z, van Der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ. 2017. Densely connected convolutional networks. Paper presented at: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Jul 21-26; Honolulu, USA. IEEE;Piscataway: p. 2261–9. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.243. PMCID: PMC5598342.
Article17. Goyal P, Dollár P, Girshick R, Noordhuis P, Wesolowski L, Kyrola A, et al. 2017. Jun. 8. Accurate, large minibatch SGD: training ImageNet in 1 hour [Internet]. arxiv. Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02677. updated 2018 Apr 30; cited 2020 Aug 7.18. Jia X, Song S, He W, Wang Y, Rong H, Zhou F, et al. 2018. Jul. 30. Highly scalable deep learning training system with mixed-precision: training ImageNet in four minutes [Internet]. arxiv. Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.11205. cited 2020 Aug 7.19. Ioffe S, Szegedy C. 2015. Feb. 11. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift [Internet]. arxiv. Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167. updated 2015 Mar 2; cited 2020 Sep 8.20. Wu Y, He K. Ferrari V, Hebert M, Sminchisescu C, Weiss Y, editors. 2018. Group normalization. ECCV 2018: Computer vision - ECCV 2018. Springer;Cham: p. 3–19. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-01261-8_1.21. Deng J, Guo J, Xue N, Zafeiriou S. 2019. ArcFace: additive angular margin loss for deep face recognition. Paper presented at: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2019 Jun 15-20; Long Beach, USA. IEEE;Piscataway: p. 4690–9. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00482. PMID: 30957192. PMCID: PMC6522832.22. Dreiseitl S, Ohno-Machado L, Binder M. 2000; Comparing three-class diagnostic tests by three-way ROC analysis. Med Decis Making. 20:323–31. DOI: 10.1177/0272989X0002000309. PMID: 10929855.
Article23. Li J, Fine JP. 2008; ROC analysis with multiple classes and multiple tests: methodology and its application in microarray studies. Biostatistics. 9:566–76. DOI: 10.1093/biostatistics/kxm050. PMID: 18304996.
Article24. van der Maaten L, Hinton G. 2008; Visualizing data using t-SNE. J Mach Learn Res. 9:2579–605.25. Selvaraju RR, Cogswell M, Das A, Vedantam R, Parikh D, Batra D. 2017. Grad-CAM: visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. Paper presented at: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). 2017 Oct 22-29; Venice, Italy. IEEE;Piscataway: p. 618–26. DOI: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.74.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Implementation of Pattern Classifier for Karyotype Classification
- Evaluation of a multi-stage convolutional neural network-based fully automated landmark identification system using cone-beam computed tomographysynthesized posteroanterior cephalometric images
- Lesion-Based Convolutional Neural Network in Diagnosis of Early Gastric Cancer
- Classification of dental implant systems using cloud-based deep learning algorithm: an experimental study
- Artificial Intelligence Detection of Cervical Spine Fractures Using Convolutional Neural Network Models