Yeungnam Univ J Med.
2021 Oct;38(4):374-380. 10.12701/yujm.2021.01284.
Anesthetic management during whole-lung lavage using lung ultrasound in a patient with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan, Korea
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- KMID: 2521720
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2021.01284
Abstract
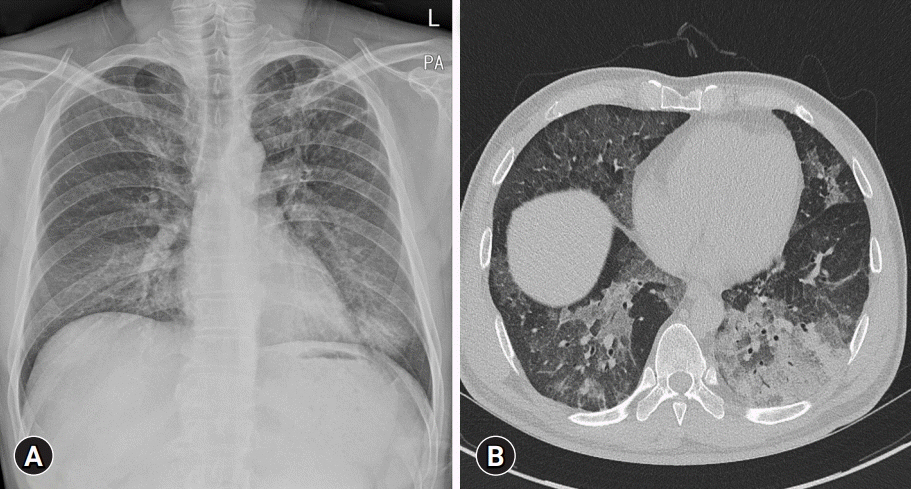
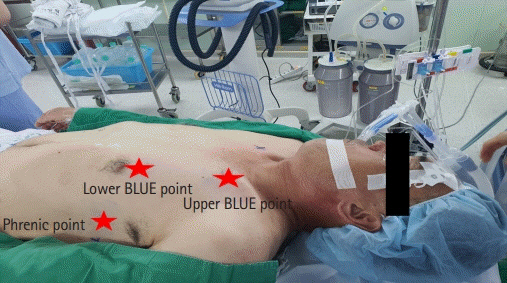
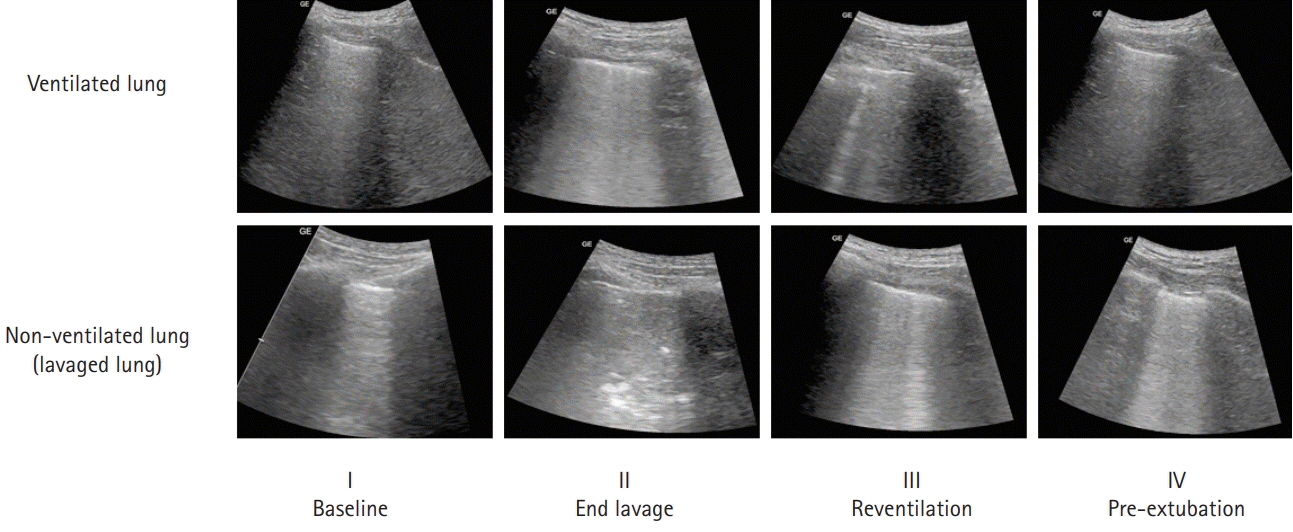
- Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is an uncommon disease characterized by progressive accumulation of lipoprotein material in the lungs due to impaired surfactant clearance. Whole-lung lavage (WLL) is the current standard treatment and consists of sequential lavage of each lung to mechanically remove the residual material from the alveoli. Although WLL is considered safe, unexpected complications can occur. Moreover, due to the rarity of the disease itself, this procedure is unknown to many physicians, and management of intraoperative complications can be challenging for anesthesiologists. Lung ultrasound (LUS) provides reliable and valuable information for detecting perioperative pulmonary complications and, in particular, quantitation of lung water content. There have been reports on monitoring the different stages of controlled deaeration of the non-ventilated lung during WLL using LUS. However, it has been limited to non-ventilated lungs. Therefore, we report the use of LUS in WLL to proactively detect pulmonary edema in the ventilated lung and implement a safe and effective anesthesia strategy. Given the limited diagnostic tools available to anesthesiologists in the operating room, LUS is a reliable, fast, and noninvasive method for identifying perioperative pulmonary complications in patients with PAP undergoing WLL.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ra SW, Park SE, Lee HK, Han IS, Park SH. Whole lung lavage using a rapid infusion system to treat a patient with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020; 37:67–72.
Article2. Via G, Lichtenstein D, Mojoli F, Rodi G, Neri L, Storti E, et al. Whole lung lavage: a unique model for ultrasound assessment of lung aeration changes. Intensive Care Med. 2010; 36:999–1007.
Article3. Mata-Suarez SM, Castro-Lalín A, Mc Loughlin S, De Domini J, Bianco JC. Whole-lung lavage-a narrative review of anesthetic management. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2020; Dec. 5. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2020.12.002.
Article4. Picano E, Pellikka PA. Ultrasound of extravascular lung water: a new standard for pulmonary congestion. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37:2097–104.
Article5. Misra S, Das PK, Bal SK, Elayat A, Sahoo S, Dahl AB, et al. Therapeutic whole lung lavage for alveolar proteinosis. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2020; 34:250–7.
Article6. Ramachandran P, Chaudhury A, Devaraj U, Maheshwari KU, D’Souza G. Monitoring whole-lung lavage using lung ultrasound: the changing phases of the lung. Lung India. 2018; 35:350–3.
Article7. Lichtenstein DA. BLUE-protocol and FALLS-protocol: two applications of lung ultrasound in the critically ill. Chest. 2015; 147:1659–70.8. Kumar A, Abdelmalak B, Inoue Y, Culver DA. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in adults: pathophysiology and clinical approach. Lancet Respir Med. 2018; 6:554–65.
Article9. Campo I, Luisetti M, Griese M, Trapnell BC, Bonella F, Grutters J, et al. Whole lung lavage therapy for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: a global survey of current practices and procedures. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2016; 11:115.
Article10. Seymour JF, Presneill JJ. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: progress in the first 44 years. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 166:215–35.11. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 34-1974. N Engl J Med. 1974; 291:464–9.12. Huber GL, Edmunds LH Jr, Finley TN. Effect of experimental saline lavage on pulmonary mechanics and morphology. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971; 104:337–47.
Article13. McClenahan JB. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Arch Intern Med. 1974; 133:284–7.
Article14. Rupp GH, Wasserman K, Ogawa M, Heiner DC. Bronchopulmonary fluids in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1973; 51:227–37.
Article15. Rogers RM, Szidon JP, Shelburne J, Neigh JL, Shuman JF, Tantum KR. Hemodynamic response of the pulmonary circulation to bronchopulmonary lavage in man. N Engl J Med. 1972; 286:1230–3.
Article16. Anile A, Russo J, Castiglione G, Volpicelli G. A simplified lung ultrasound approach to detect increased extravascular lung water in critically ill patients. Crit Ultrasound J. 2017; 9:13.
Article17. Agricola E, Bove T, Oppizzi M, Marino G, Zangrillo A, Margonato A, et al. “Ultrasound comet-tail images”: a marker of pulmonary edema: a comparative study with wedge pressure and extravascular lung water. Chest. 2005; 127:1690–5.
Article18. Enghard P, Rademacher S, Nee J, Hasper D, Engert U, Jörres A, et al. Simplified lung ultrasound protocol shows excellent prediction of extravascular lung water in ventilated intensive care patients. Crit Care. 2015; 19:36.
Article19. Leblanc D, Bouvet C, Degiovanni F, Nedelcu C, Bouhours G, Rineau E, et al. Early lung ultrasonography predicts the occurrence of acute respiratory distress syndrome in blunt trauma patients. Intensive Care Med. 2014; 40:1468–74.
Article20. Goldstein LS, Kavuru MS, Curtis-McCarthy P, Christie HA, Farver C, Stoller JK. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: clinical features and outcomes. Chest. 1998; 114:1357–62.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anesthetic Management of Lung Lavage in Patient with Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Related to Pneumoconiosis: A case report
- Anesthetic Management for Whole-Lung Lavage in a Patient with Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis
- Bilateral Sequential Bronchopulmonary Lavage in One Stage for Recurred Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis: A case report
- Whole Lung Lavage and Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in a Patient with Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis and Lung Cancer
- Anesthetic Management of Whole-Lung Lavage Using Propofol-Remifentanil in a Patient with Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis