Clin Endosc.
2021 Sep;54(5):688-693. 10.5946/ce.2021.082.
“Endoshield”: A Physical Protective Box for Pediatric Endoscopy during the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Pediatrics, Srinagarind Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
- 2Department of Clinical Chemistry, Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
- 3Faculty of Architecture, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
- 4Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
- KMID: 2520551
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2021.082
Abstract
- Background/Aims
The coronavirus disease (COVID)-19 pandemic presents challenges for gastrointestinal endoscopy. Although the virus is transmitted through contact and droplets, aerosol-generating procedures produce aerosols that can spread through airborne routes. Several gastrointestinal societies have released statements to protect patients and health care providers (HCPs). This study describes a barrier box that may be used as an adjunctive device in addition to personal protective equipment during endoscopies.
Methods
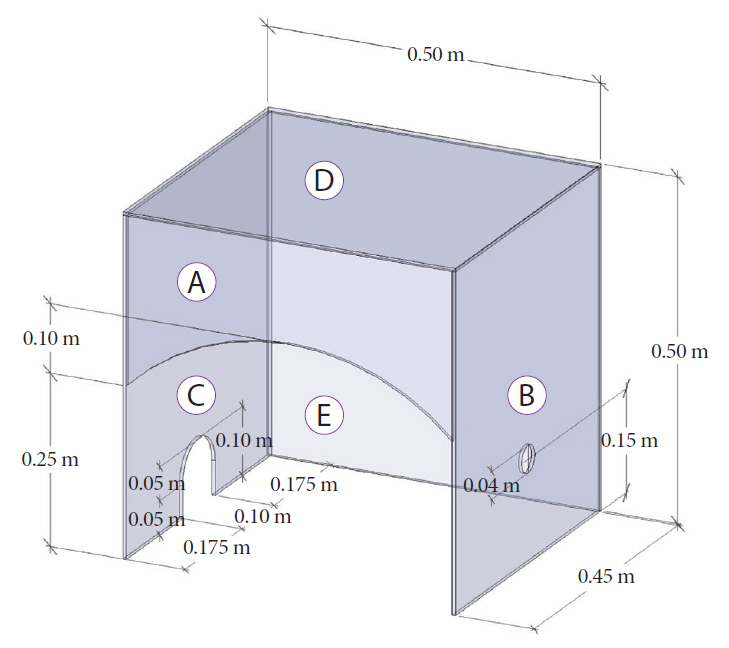
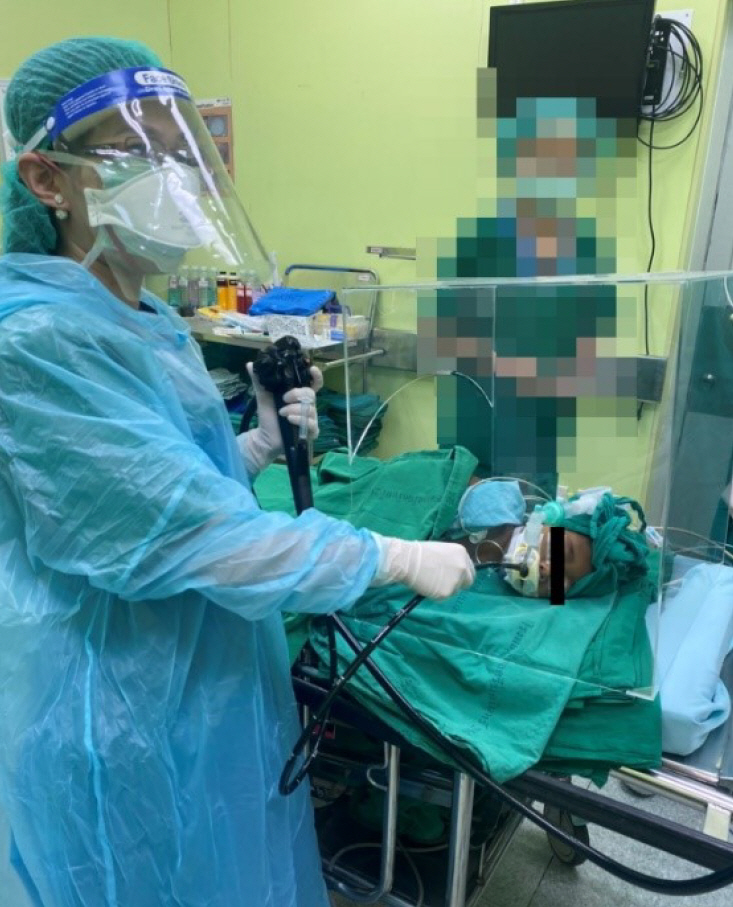
A transparent acrylic box called “Endoshield” was created to place over patient’s head and shoulders and was tested for its ease of use for the endoscopist and suitability for patient size and position.
Results
Twelve children (66.67%, male) with a median age of 9 years (range, 2–11 years) underwent emergency or urgent endoscopy between April and June 2020 during the COVID-19 outbreak. The most common presenting symptom was life-threatening gastrointestinal bleeding (8/12, 66.67%), while the rest had urgent symptoms (4/12, 33.33%). The “Endoshield” was suitable for all patient positions (left lateral position: 9/12, 75% and supine position: 3/12, 25%). The patients and HCPs were followed up for their symptoms on day 14, and none of them had any symptoms of concern.
Conclusions
The “Endoshield” is affordable, reusable, and suitable for both positions.
Figure
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. Pneumonia of unknown cause – China [Internet]. Geneva: WHO;c2020. [updated 2020 Jan 5; cited 2020 Mar 21]. Available from: https://www.who.int/csr/don/05-january-2020-pneumonia-of-unkown-cause-china/en/.2. World Health Organization. WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020 [Internet]. Geneva: WHO;c2020. [updated 2020 Mar 11; cited 2020 Mar 21]. Available from: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020.3. Bedford J, Enria D, Giesecke J, et al. COVID-19: towards controlling of a pandemic. Lancet. 2020; 395:1015–1018.
Article4. Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:727–733.
Article5. Wang C, Horby PW, Hayden FG, Gao GF. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet. 2020; 395:470–473.
Article6. Chiu PWY, Ng SC, Inoue H, et al. Practice of endoscopy during COVID-19 pandemic: position statements of the Asian Pacific Society for Digestive Endoscopy (APSDE-COVID statements). Gut. 2020; 69:991–996.
Article7. Gralnek IM, Hassan C, Beilenhoff U, et al. ESGE and ESGENA position statement on gastrointestinal endoscopy and the COVID-19 pandemic. Endoscopy. 2020; 52:483–490.
Article8. Walsh CM, Fishman DS, Lerner DG. Pediatric endoscopy in the era of coronavirus disease 2019: a North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition position paper. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2020; 70:741–750.
Article9. Kongkam P, Tiankanon K, Ratanalert S, et al. The practice of endoscopy during the COVID-19 pandemic: recommendations from the Thai Association for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (TAGE) in collaboration with the Endoscopy Nurse Society (Thailand). Siriraj Medical Journal. 2020; 72:283–286.10. Lu X, Zhang L, Du H, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in children. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:1663–1665.
Article11. Kelvin AA, Halperin S. COVID-19 in children: the link in the transmission chain. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020; 20:633–634.
Article12. Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, et al. Epidemiology of COVID-19 among children in China. Pediatrics. 2020; 145:e20200702.
Article13. Su L, Ma X, Yu H, et al. The different clinical characteristics of corona virus disease cases between children and their families in China - the character of children with COVID-19. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020; 9:707–713.
Article14. Qiu H, Wu J, Hong L, Luo Y, Song Q, Chen D. Clinical and epidemiological features of 36 children with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Zhejiang, China: an observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020; 20:689–696.
Article15. Cruz AT, Zeichner SL. COVID-19 in children: initial characterization of the pediatric disease. Pediatrics. 2020; 145:e20200834.
Article16. She J, Liu L, Liu W. COVID-19 epidemic: disease characteristics in children. J Med Virol. 2020; 92:747–754.
Article17. Begley JL, Lavery KE, Nickson CP, Brewster DJ. The aerosol box for intubation in coronavirus disease 2019 patients: an in-situ simulation crossover study. Anaesthesia. 2020; 75:1014–1021.
Article18. Canelli R, Connor CW, Gonzalez M, Nozari A, Ortega R. Barrier enclosure during endotracheal intubation. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:1957–1958.
Article19. Campos S, Carreira C, Marques PP, Vieira A. Endoprotector: protective box for safe endoscopy use during COVID-19 outbreak. Endosc Int Open. 2020; 8:E817–E821.
Article20. Ljubicic N, Stojsavljevic-Shapeski S, Virovic-Jukic L, Nikolic M. Plexiglas barrier box to improve ERCP safety during the COVID-19 pandemic. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020; 92:428–429.
Article21. Lui RN, Wong SH, Sánchez-Luna SA, et al. Overview of guidance for endoscopy during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020; 35:749–759.
Article22. Edwards C, Penman ID, Coleman M. Gastrointestinal endoscopy during COVID-19: when less is more. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2020; 11:256–257.
Article23. Kramer RE, Lerner DG, Lin T, et al. Management of ingested foreign bodies in children: a clinical report of the NASPGHAN Endoscopy Committee. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015; 60:562–574.24. Bianco F, Incollingo P, Grossi U, Gallo G. Preventing transmission among operating room staff during COVID-19 pandemic: the role of the Aerosol Box and other personal protective equipment. Updates Surg. 2020; 72:907–910.
Article25. Sagami R, Nishikiori H, Sato T, Murakami K. Endoscopic shield: barrier enclosure during the endoscopy to prevent aerosol droplets during the COVID-19 pandemic. VideoGIE. 2020; 5:445–448.
Article