Clin Endosc.
2020 Nov;53(6):754-756. 10.5946/ce.2020.111.
Multidisciplinary Approach to Diagnose and Treat Diffuse Esophageal Leiomyomatosis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Hospital Professor Doutor Fernando Fonseca, Amadora, Portugal
- 2Department of Pathology, Hospital Professor Doutor Fernando Fonseca, Amadora, Portugal
- KMID: 2511238
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2020.111
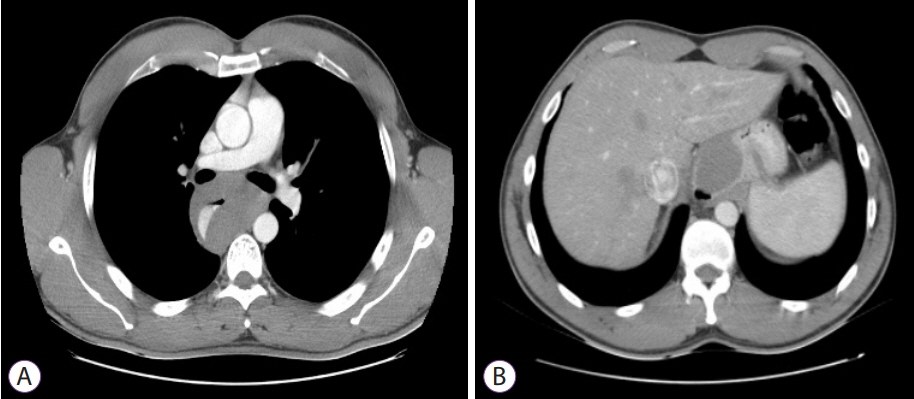
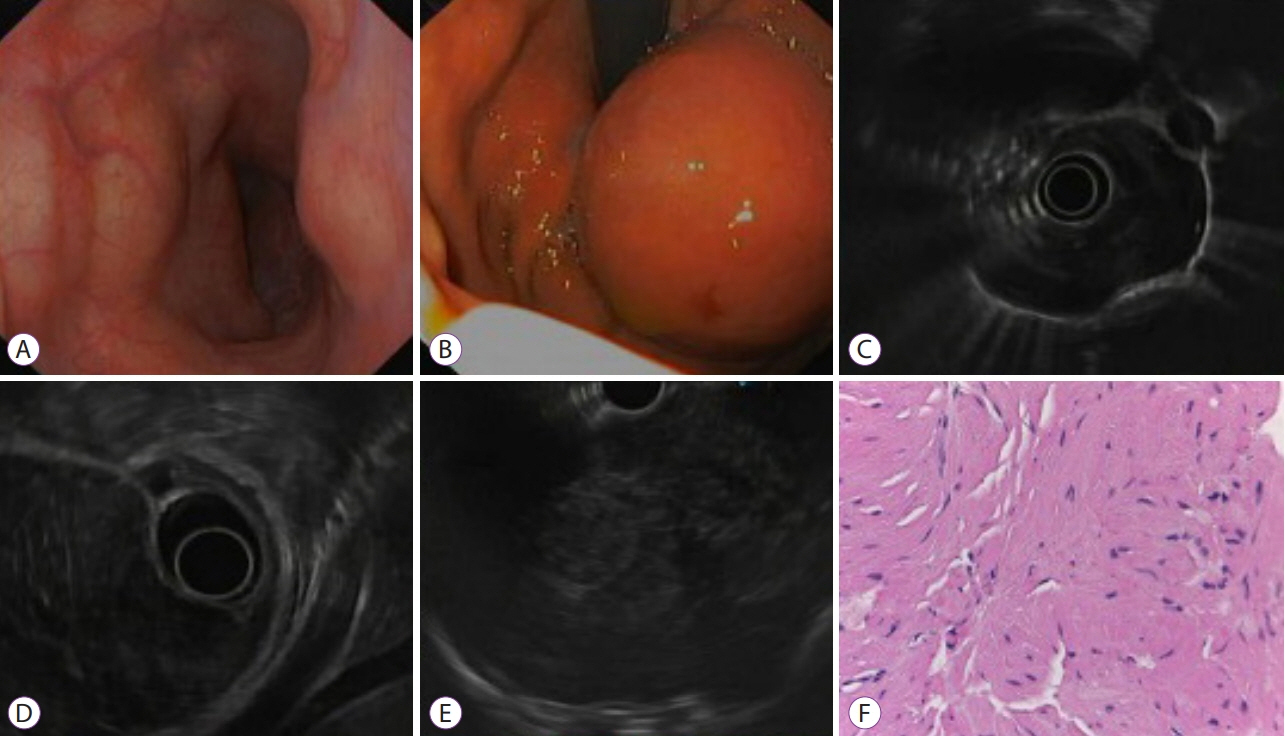
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rapp JB, Ciullo S, Mallon MG. Diffuse esophageal leiomyomatosis: a case report with surgical correlation. Clin Imaging. 2019; 58:161–165.
Article2. Berenguer Francés M, Onrubia Pintado JA, Vázquez Pérez G. [Diffuse esophageal leiomyomatosis as a differential diagnosis of dysphagia]. Med Clin (Barc). 2016; 147:377–378.
Article3. Ray S, Saluja SS, Gupta R, Chattopadhyay TK. Esophageal leiomyomatosis -- an unusual cause of pseudoachalasia. Can J Gastroenterol. 2008; 22:187–189.
Article4. Milito P, Asti E, Aiolfi A, Zanghi S, Siboni S, Bonavina L. Clinical outcomes of minimally invasive enucleation of leiomyoma of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction. J Gastrointest Surg. 2020; 24:499–504.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diffuse Leiomyomatosis of The Esophagus: A Case Report
- Diffuse Esophageal Leiomyomatosis in a Child with Alport Syndrome: Case Report
- Diffuse Leiomyomatosis of the Esophagus: A case report
- A Case of Alport Syndrome Associated with Diffuse Esophageal Leiomyomatosis
- Diffuse Esophageal Leiomyomatosis: A Case Report