Clin Endosc.
2020 Nov;53(6):646-651. 10.5946/ce.2020.262.
Role of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) in the Management of Esophageal Diverticula
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Victor Babeș University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Timișoara, Romania
- 2Department of Medicine, Saint Agnes Hospital, Baltimore, MD, USA
- 3Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, MD, USA
- KMID: 2511223
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2020.262
Abstract
- Esophageal diverticula are uncommon; however, when present, they can cause symptoms of dysphagia, regurgitation, and chest pain. Based on location and pathophysiological characteristics, they are classified as pulsion- and traction-type diverticula. In the past, the open surgical approach was the only treatment available; however, in the past few decades, transoral incisionless approaches in the form of rigid and flexible endoscopy have gained popularity. Diverticular peroral endoscopic myotomy has emerged as an alternative treatment option. In this paper, we reviewed the role of peroral endoscopic myotomy as a treatment option for different types of esophageal diverticula. Although a safe and effective procedure, this novel submucosal tunneling technique for the treatment of esophageal diverticula requires further validation, and head-to-head comparisons between the different approaches for the treatment of esophageal diverticula are warranted.
Keyword
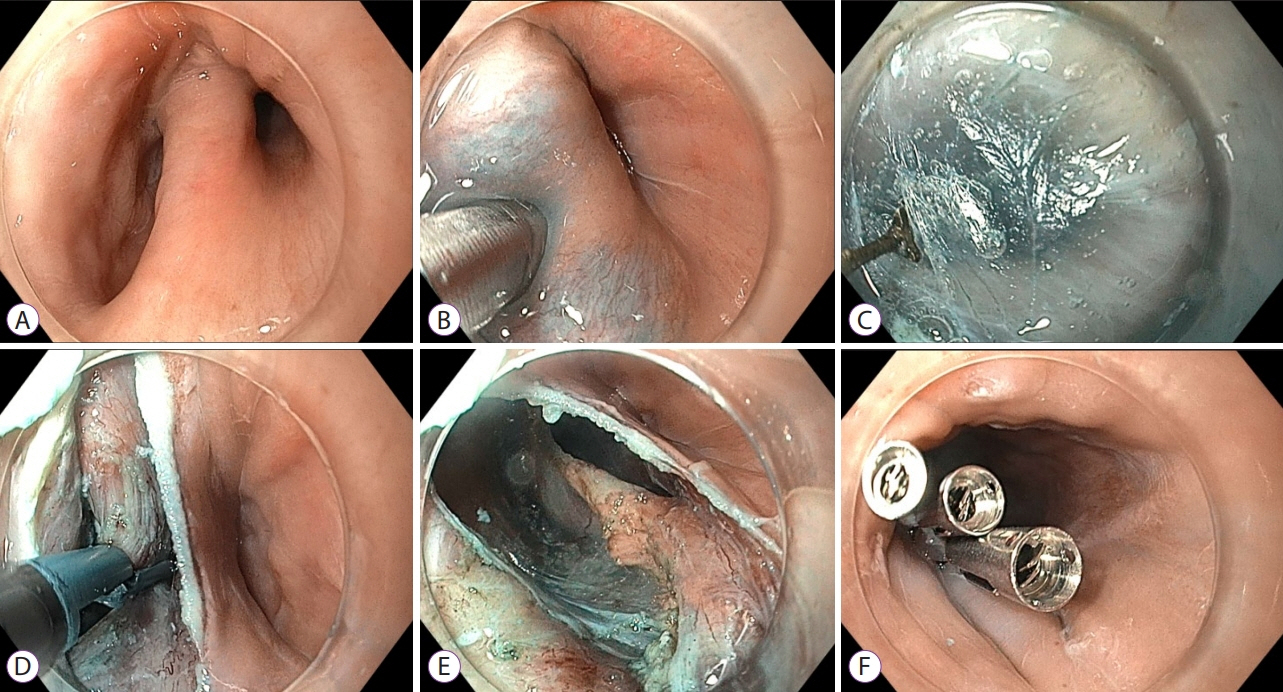
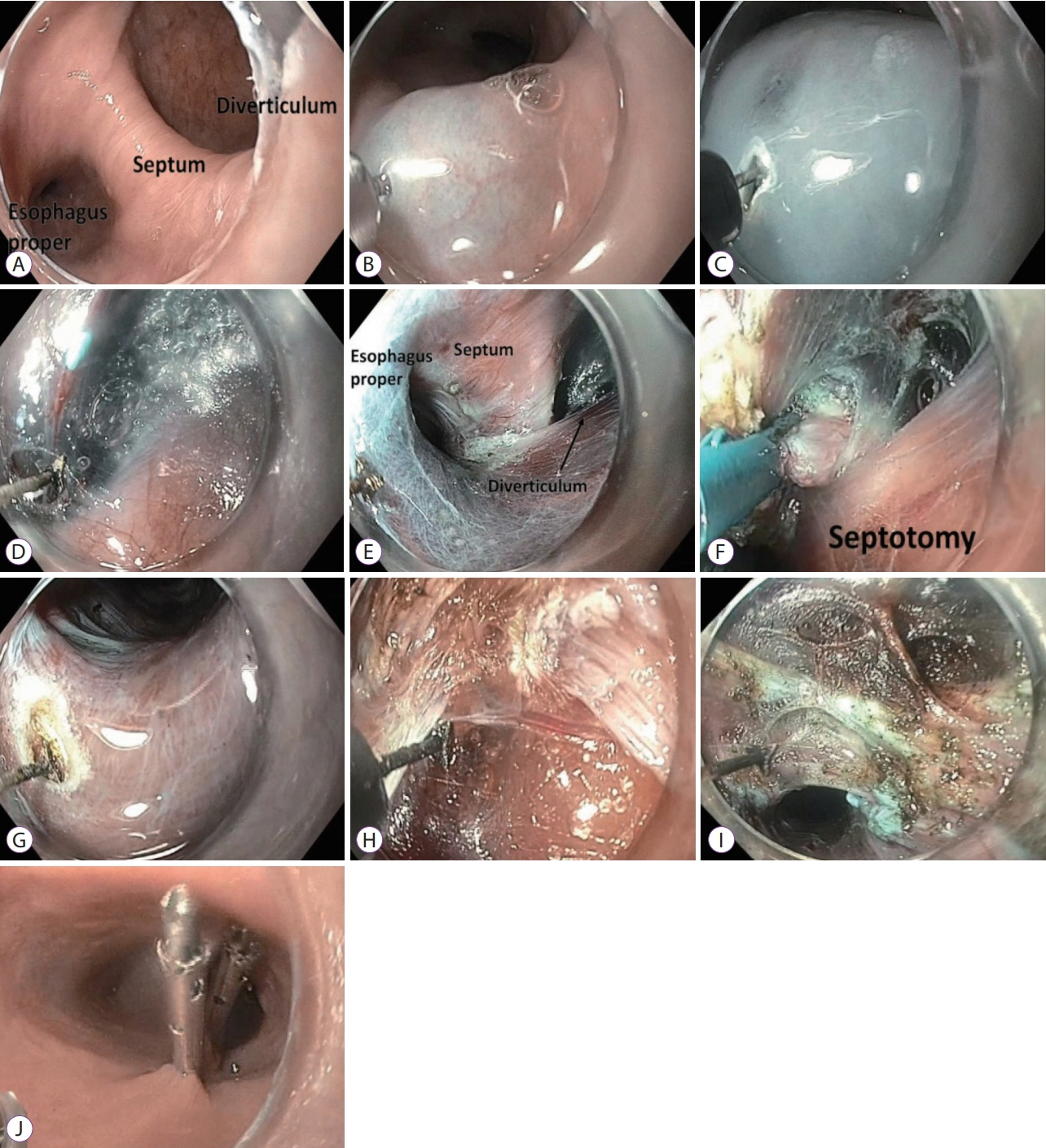
Figure
Reference
-
1. Herbella FA, Patti MG. Modern pathophysiology and treatment of esophageal diverticula. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2012; 397:29–35.
Article2. Aiolfi A, Scolari F, Saino G, Bonavina L. Current status of minimally invasive endoscopic management for Zenker diverticulum. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 7:87–93.
Article3. Inoue H, Minami H, Kobayashi Y, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:265–271.
Article4. Nabi Z, Nageshwar Reddy D, Ramchandani M. Recent advances in third-space endoscopy. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2018; 14:224–232.5. Li QL, Chen WF, Zhang XC, et al. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic septum division: a novel technique for treating Zenker’s diverticulum. Gastroenterology. 2016; 151:1071–1074.6. Smith CD. Esophageal strictures and diverticula. Surg Clin North Am. 2015; 95:669–681.
Article7. Sonbare DJ. Pulsion diverticulum of the oesophagus: more than just an out pouch. Indian J Surg. 2015; 77:44–48.
Article8. Bizzotto A, Iacopini F, Landi R, Costamagna G. Zenker’s diverticulum: exploring treatment options. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2013; 33:219–229.9. Yuan Y, Zhao YF, Hu Y, Chen LQ. Surgical treatment of Zenker’s diverticulum. Dig Surg. 2013; 30:207–218.
Article10. Ferreira LE, Simmons DT, Baron TH. Zenker’s diverticula: pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and flexible endoscopic management. Dis Esophagus. 2008; 21:1–8.
Article11. Gonzalez-Calatayud M, Targarona EM, Balague C, Rodriguez-Luppi C, Martin AB, Trias M. Minimally invasive therapy for epiphrenic diverticula: systematic review of literature and report of six cases. J Minim Access Surg. 2014; 10:169–174.12. Brandeis AE, Singhal S, Lee TH, Mittal SK. Surgical management of epiphrenic diverticulum: a single-center experience and brief review of literature. Am J Surg. 2018; 216:280–285.
Article13. Ballehaninna UK, Shaw JP, Brichkov I. Traction esophageal diverticulum: a rare cause of gastro-intestinal bleeding. Springerplus. 2012; 1:50.
Article14. Brewer Gutierrez OI, Ichkhanian Y, Spadaccini M, Vosoughi K, Repici A, Khashab MA. Zenker’s diverticulum per-oral endoscopic myotomy techniques: changing paradigms. Gastroenterology. 2019; 156:2134–2135.
Article15. Katzka DA, Baron TH. Transoral flexible endoscopic therapy of Zenker’s diverticulum: is it time for gastroenterologists to stick their necks out? Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77:708–710.
Article16. Wilmsen J, Baumbach R, Stüker D, et al. New flexible endoscopic controlled stapler technique for the treatment of Zenker’s diverticulum: a case series. World J Gastroenterol. 2017; 23:3084–3091.
Article17. Brieau B, Leblanc S, Bordacahar B, et al. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic septum division for Zenker’s diverticulum: a reproducible procedure for endoscopists who perform peroral endoscopic myotomy. Endoscopy. 2017; 49:613–614.
Article18. Hernández Mondragón OV, Solórzano Pineda MO, Blancas Valencia JM. Zenker’s diverticulum: submucosal tunneling endoscopic septum division (Z-POEM). Dig Endosc. 2018; 30:124.
Article19. Sato H, Takeuchi M, Hashimoto S, et al. Esophageal diverticulum: new perspectives in the era of minimally invasive endoscopic treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 2019; 25:1457–1464.
Article20. Yang J, Novak S, Ujiki M, et al. An international study on the use of peroral endoscopic myotomy in the management of Zenker’s diverticulum. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020; 91:163–168.
Article21. Repici A, Spadaccini M, Belletrutti PJ, et al. Peroral endoscopic septotomy for short-septum Zenker’s diverticulum. Endoscopy. 2020; 52:563–568.
Article22. Yang J, Zeng X, Yuan X, et al. An international study on the use of peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) in the management of esophageal diverticula: the first multicenter D-POEM experience. Endoscopy. 2019; 51:346–349.
Article23. Maydeo A, Patil GK, Dalal A. Operative technical tricks and 12-month outcomes of diverticular peroral endoscopic myotomy (D-POEM) in patients with symptomatic esophageal diverticula. Endoscopy. 2019; 51:1136–1140.
Article24. Li X, Zhang W, Yang J, et al. Safety and efficacy of submucosal tunneling endoscopic septum division for epiphrenic diverticula. Endoscopy. 2019; 51:1141–1145.
Article25. Basile P, Gonzalez JM, Le Mouel JP, Irarrazaval R, Caillo L, Barthet M. Per-oral endoscopic myotomy with septotomy for the treatment of distal esophageal diverticula (D-POEM). Surg Endosc. 2020; 34:2321–2325.
Article26. Kinoshita M, Tanaka S, Kawara F, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy alone is effective for esophageal motility disorders and esophageal epiphrenic diverticulum: a retrospective single-center study. Surg Endosc. 2020; 34:5447–5454.
Article27. Ghamdi SSA, Farha J, Meybodi MA, et al. International multicenter study comparing Z-POEM and flexible/rigid endoscopic Zenker’s diverticulotomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020; 91(6 Suppl):AB3–AB4.28. Aslan F, Yilmaz O, Sengun B, Unlukaplan A, Karahan SN, Kocak E. A new technique in treatment of Zenker diverticulum: submucosal tunneling endoscopic septum division (Z-POEM) versus classic endoscopic septomyotomy techniques. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019; 89(6 Suppl):AB629.29. Desai PN, Kabrawala MV. Submucosal tunnelling endoscopic septum division for Zenker’s diverticulum (Z POEM): a new emerging technique compared to conventional flexible endoscopic septotomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019; 89(6 Suppl):AB450.30. Cerchione R, Parise P, Olivari G, et al. Endoscopic management of Zenker’s diverticulum: stapling vs . Z-POEM. Shanghai Chest. 2020; 4:43.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Esophageal Diverticulum
- Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Esophageal Motility Disorders
- Double-Scope Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) for Esophageal Achalasia: The First Trial of a New Double-Scope POEM
- Current Status of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy
- Perspective on Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia: Zhongshan Experience