Ann Surg Treat Res.
2020 Apr;98(4):190-198. 10.4174/astr.2020.98.4.190.
Drainage procedure for pancreatolithiasis: re-examination of the pancreatic duct diameter standard
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou University, People’s Hospital of Henan University, Zhengzhou, China
- 2Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- KMID: 2500819
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2020.98.4.190
Abstract
- Purpose
Pancreatic duct decompression relieves pancreatic duct stone (PDS)-associated abdominal pain, though a consensus indication for the drainage procedure of the main pancreatic duct (MPD) is lacking. Moreover, major prognostic factors for postsurgical long-term pain relief and recurrence are largely unknown.
Methods
The clinical outcomes of 65 consecutive PDS patients undergoing surgery from 2008–2012 with 3+ years of follow-up were assessed.
Results
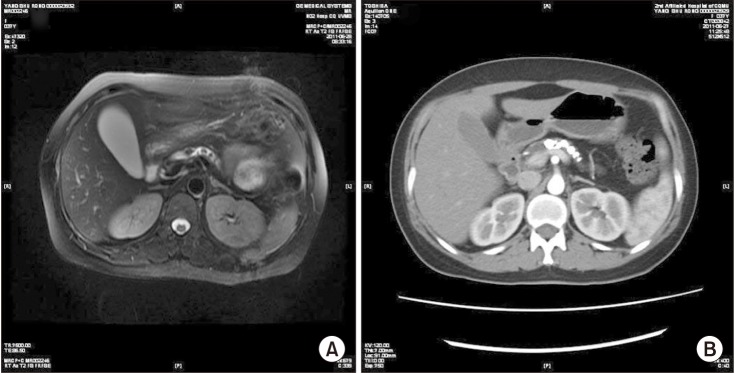
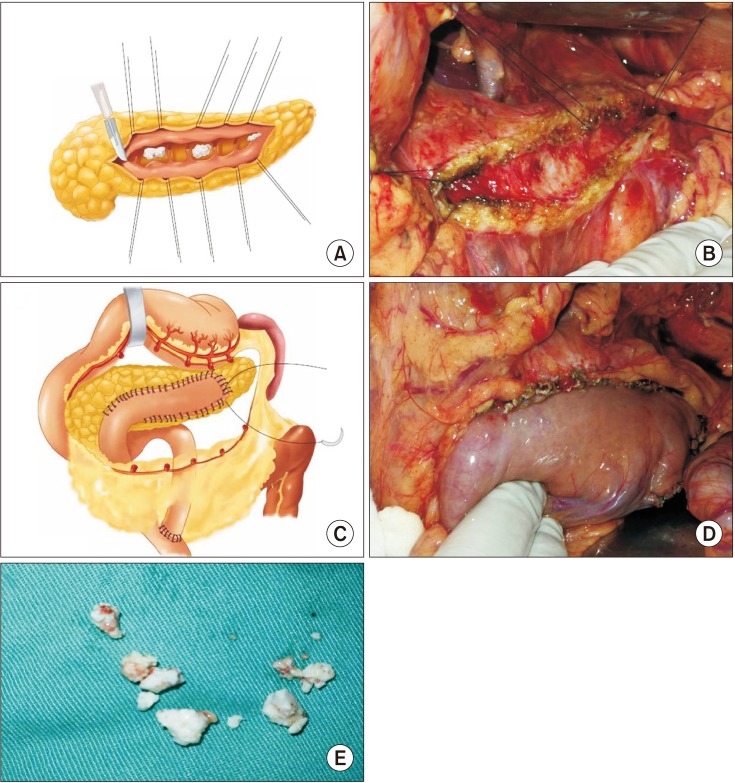
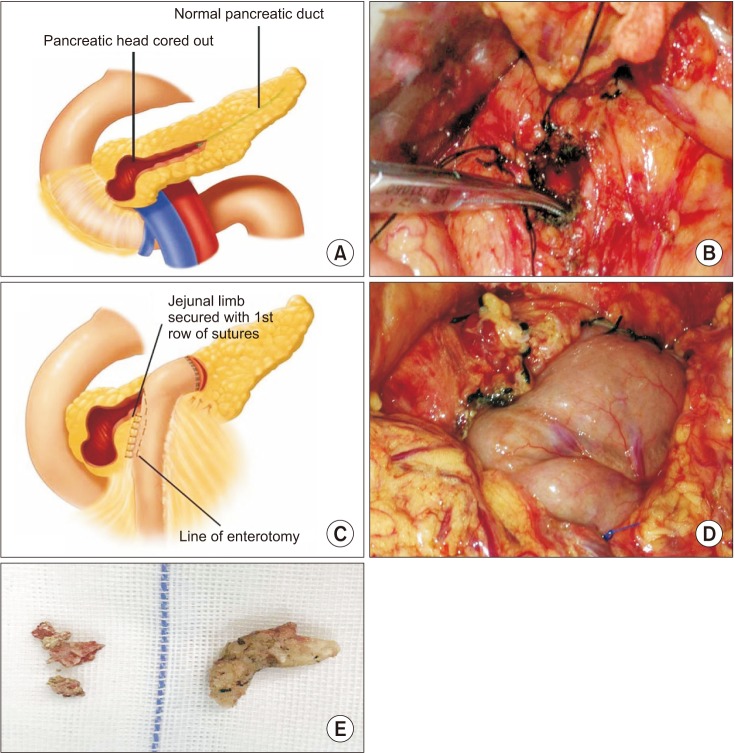
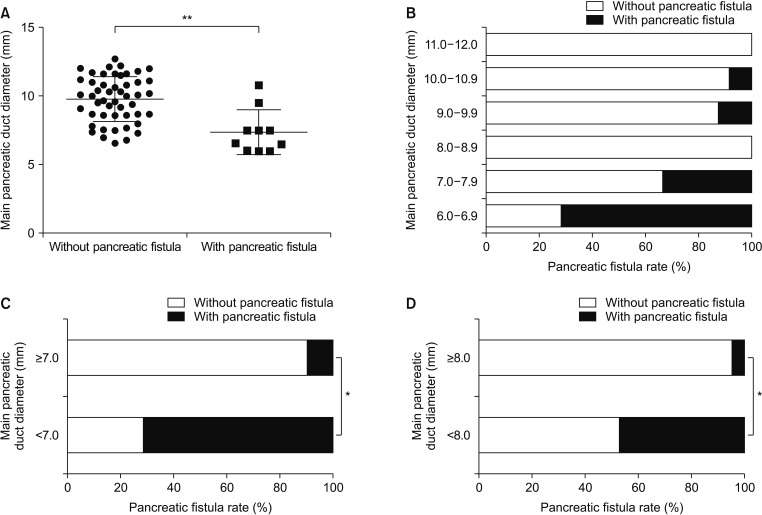
At postsurgical follow-up (median, 4.5 years; range, 3–7 years; procedure: Partington, n = 32; Frey, n = 27; pancreatoduodenectomy, n = 3; distal pancreatectomy, n = 3), the early complication and complete stone clearance rates were 29.2% and 97%, respectively. Long-term, complete and partial pain relief were 93.9%, 83.1%, and 10.8%, respectively. The risk of pancreatic fistula was higher in the <8 mm group than in the >8 mm group (P < 0.05), and 80% of the pancreatic fistula cases occurred in the <8 mm group. A shorter pain duration (P = 0.007), smaller MPD diameter (P = 0.04), and lower Izbicki pain score (P < 0.001) predicted long-term pain relief. Pain recurrence after initial remission occurred in 5 patients and was only related to pain duration (P = 0.02). Stone recurrence and pancreatic exocrine functional and endocrine functional deterioration occurred in 2, 5, and 11 patients, respectively.
Conclusion
Surgery provides excellent stone clearance, long-term pain relief, and acceptable postoperative morbidity. Using 8 mm as the criterion for drainage surgery can minimize the postoperative pancreatic fistula risk. Individualized and timely surgical treatment may improve the effect of surgery.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yadav D, Timmons L, Benson JT, Dierkhising RA, Chari ST. Incidence, prevalence, and survival of chronic pancreatitis: a population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011; 106:2192–2199. PMID: 21946280.
Article2. Garg PK, Tandon RK. Survey on chronic pancreatitis in the Asia-Pacific region. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 19:998–1004. PMID: 15304116.
Article3. Ketwaroo GA, Freedman SD, Sheth SG. Approach to patients with suspected chronic pancreatitis: a comprehensive review. Pancreas. 2015; 44:173–180. PMID: 25675419.4. Talukdar R, Murthy HV, Reddy DN. Role of methionine containing antioxidant combination in the management of pain in chronic pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pancreatology. 2015; 15:136–144. PMID: 25648074.
Article5. Isaji S. Has the Partington procedure for chronic pancreatitis become a thing of the past? A review of the evidence. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010; 17:763–769. PMID: 19779664.
Article6. Dumonceau JM, Delhaye M, Tringali A, Dominguez-Munoz JE, Poley JW, Arvanitaki M, et al. Endoscopic treatment of chronic pancreatitis: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) clinical guideline. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:784–800. PMID: 22752888.
Article7. Inui K, Masamune A, Igarashi Y, Ohara H, Tazuma S, Sugiyama M, et al. Management of pancreatolithiasis: a nationwide survey in Japan. Pancreas. 2018; 47:708–714. PMID: 29851750.8. Choi EK, McHenry L, Watkins JL, Sherman S, Fogel EL, Cote GA, et al. Use of intravenous secretin during extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy to facilitate endoscopic clearance of pancreatic duct stones. Pancreatology. 2012; 12:272–275. PMID: 22687384.
Article9. Zheng Z, Xiang G, Tan C, Zhang H, Liu B, Gong J, et al. Pancreaticoduodenectomy versus duodenum-preserving pancreatic head resection for the treatment of chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2012; 41:147–152. PMID: 21775913.
Article10. Bachmann K, Tomkoetter L, Erbes J, Hofmann B, Reeh M, Perez D, et al. Beger and Frey procedures for treatment of chronic pancreatitis: comparison of outcomes at 16-year follow-up. J Am Coll Surg. 2014; 219:208–216. PMID: 24880955.
Article11. D'Haese JG, Ceyhan GO, Demir IE, Tieftrunk E, Friess H. Treatment options in painful chronic pancreatitis: a systematic review. HPB (Oxford). 2014; 16:512–521. PMID: 24033614.12. Ceyhan GO, Demir IE, Maak M, Friess H. Fate of nerves in chronic pancreatitis: neural remodeling and pancreatic neuropathy. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; 24:311–322. PMID: 20510831.
Article13. Keck T, Wellner UF, Riediger H, Adam U, Sick O, Hopt UT, et al. Long-term outcome after 92 duodenum-preserving pancreatic head resections for chronic pancreatitis: comparison of Beger and Frey procedures. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010; 14:549–556. PMID: 20033344.
Article14. Bachmann K, Tomkoetter L, Kutup A, Erbes J, Vashist Y, Mann O, et al. Is the Whipple procedure harmful for long-term outcome in treatment of chronic pancreatitis? 15-years follow-up comparing the outcome after pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy and Frey procedure in chronic pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 2013; 258:815–820. discussion 820-1. PMID: 24096767.
Article15. Ahmed Ali U, Issa Y, Bruno MJ, van Goor H, van Santvoort H, Busch OR, et al. Early surgery versus optimal current step-up practice for chronic pancreatitis (ESCAPE): design and rationale of a randomized trial. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013; 13:49. PMID: 23506415.
Article16. Del Chiaro M, Segersvard R, Lohr M, Verbeke C. Early detection and prevention of pancreat ic cancer: is it real ly possible today? World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:12118–12131. PMID: 25232247.17. Wilson GC, Sutton JM, Abbott DE, Smith MT, Lowy AM, Matthews JB, et al. Long-term outcomes after total pancreatectomy and islet cell autotransplantation: is it a durable operation? Ann Surg. 2014; 260:659–665. discussion 665-7. PMID: 25203883.18. Suzuki Y, Sugiyama M, Inui K, Igarashi Y, Ohara H, Tazuma S, et al. Management for pancreatolithiasis: a Japanese multicenter study. Pancreas. 2013; 42:584–588. PMID: 23558239.19. Nguyen-Tang T, Dumonceau JM. Endoscopic t reatment in chronic pancreatitis, timing, duration and type of intervention. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; 24:281–298. PMID: 20510829.20. Tandan M, Reddy DN, Santosh D, Vinod K, Ramchandani M, Rajesh G, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy and endotherapy for pancreatic calculi-a large single center experience. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2010; 29:143–148. PMID: 20717860.
Article21. Milovic V, Wehrmann T, Dietrich CF, Bailey AA, Caspary WF, Braden B. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy with a transportable mini-lithotripter and subsequent endoscopic treatment improves clinical outcome in obstructive calcific chronic pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:1294–1299. PMID: 21981815.
Article22. Tandan M, Talukdar R, Reddy DN. Management of pancreatic calculi: an update. Gut Liver. 2016; 10:873–880. PMID: 27784844.
Article23. Panek-Jeziorna M, Wierzbicki J, Annabhani A, Paradowski L, Mulak A. Pancreatic duct stones: a report on 16 cases. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017; 26:609–613. PMID: 28691427.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Technical tips for endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct access and drainage
- A Case of Pancreatic Pseudocyst Resolved by Transpapillary Drainage via the Main Pancreatic Duct
- Are Newer Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Models Truly Improving Pancreatolithiasis Lithotripsy Performance? A Japanese Single-Center Study Using Endoscopic Adjunctive Treatment
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Drainage of Pancreatic Fluid Collections (with Video)
- Anomalous Drainage of the Common Bile Duct and Pancreatic Duct into the Duodenal Bulb