Diabetes Metab J.
2020 Feb;44(1):158-172. 10.4093/dmj.2018.0235.
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Attenuates Diabetes-Induced Renal Fibrosis by Negatively Regulating TGF-β-p53-Smad2/3-Mediated Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via Activation of AKT
- Affiliations
-
- 1Ruian Center of Chinese-American Research Institute for Diabetic Complications, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China. zhangchi515@126.com, lu89118@medmail.com.cn
- 2Chinese-American Research Institute for Diabetic Complications, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China.
- 3School of Pharmaceutical Science, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China.
- KMID: 2470964
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0235
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is required for renal fibrosis, which is a characteristic of diabetic nephropathy (DN). Our previous study demonstrated that fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) prevented DN associated with the suppressing renal connective tissue growth factor expression, a key marker of renal fibrosis. Therefore, the effects of FGF21 on renal fibrosis in a DN mouse model and the underlying mechanisms were investigated in this study.
METHODS
Type 1 diabetes mellitus was induced in C57BL/6J mice by intraperitoneal injections of multiple low doses of streptozotocin. Then, diabetic and non-diabetic mice were treated with or without FGF21 in the presence of pifithrin-α (p53 inhibitor) or 10-[4"²-(N,N-Diethylamino)butyl]-2-chlorophenoxazine hydrochloride (10-DEBC) hydrochloride (Akt inhibitor) for 4 months.
RESULTS
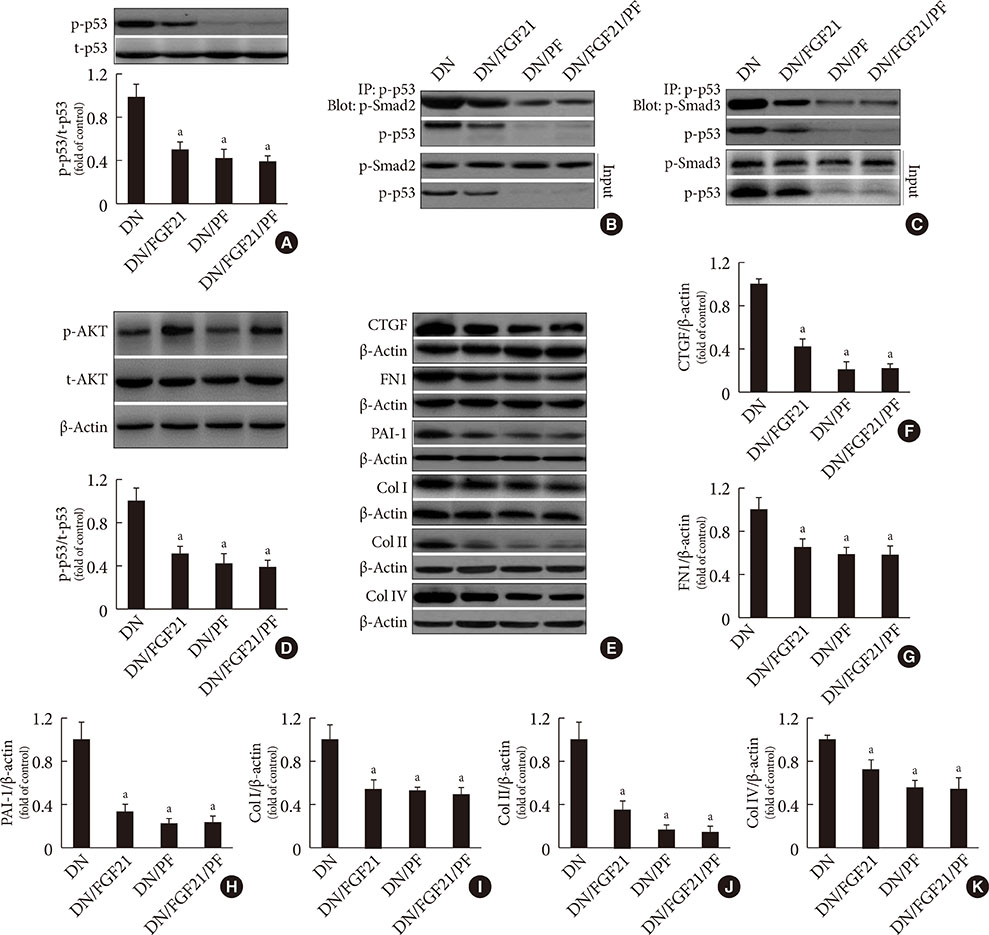
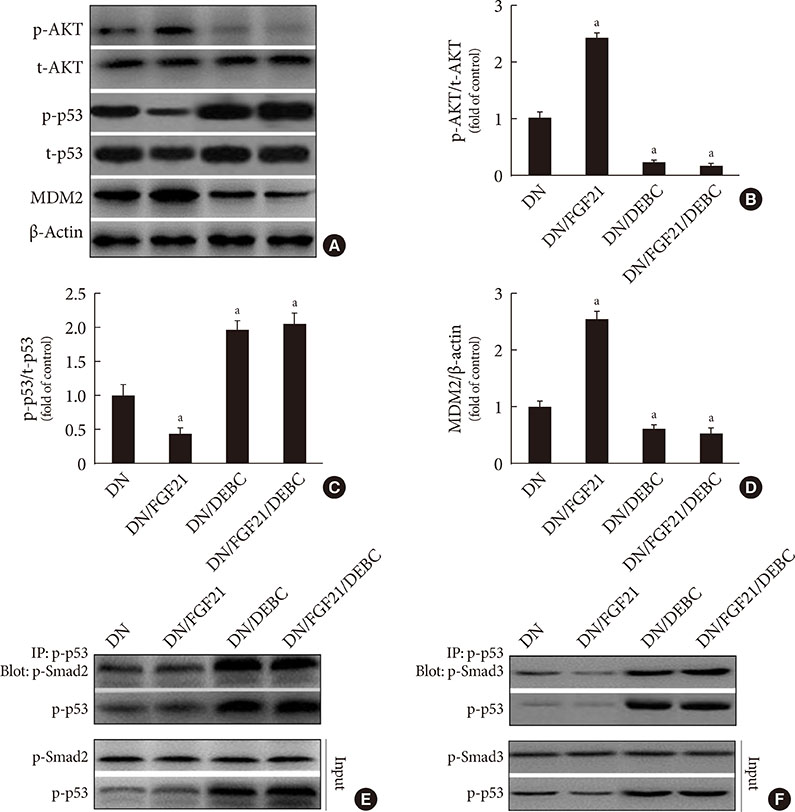
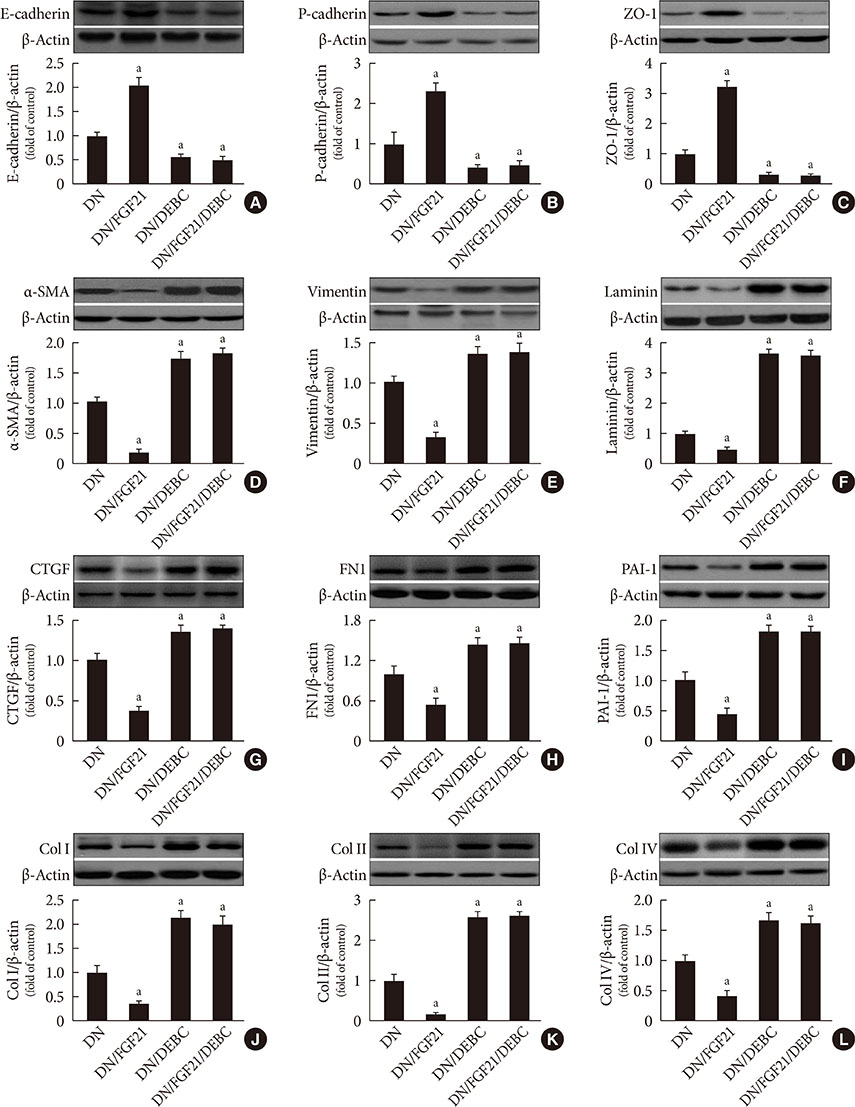
DN was diagnosed by renal dysfunction, hypertrophy, tubulointerstitial lesions, and glomerulosclerosis associated with severe fibrosis, all of which were prevented by FGF21. FGF21 also suppressed the diabetes-induced renal EMT in DN mice by negatively regulating transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β)-induced nuclear translocation of Smad2/3, which is required for the transcription of multiple fibrotic genes. The mechanistic studies showed that FGF21 attenuated nuclear translocation of Smad2/3 by inhibiting renal activity of its conjugated protein p53, which carries Smad2/3 into the nucleus. Moreover pifithrin-α inhibited the FGF21-induced preventive effects on the renal EMT and subsequent renal fibrosis in DN mice. In addition, 10-DEBC also blocked FGF21-induced inhibition of renal p53 activity by phosphorylation of mouse double minute-2 homolog (MDM2).
CONCLUSION
FGF21 prevents renal fibrosis via negative regulation of the TGF-β/Smad2/3-mediated EMT process by activation of the Akt/MDM2/p53 signaling pathway.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Connective Tissue Growth Factor
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1
Diabetic Nephropathies
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
Fibroblast Growth Factors*
Fibroblasts*
Fibrosis*
Hypertrophy
Injections, Intraperitoneal
Kidney
Mice
Phosphorylation
Streptozocin
Transforming Growth Factor beta
Tumor Suppressor Protein p53
Connective Tissue Growth Factor
Fibroblast Growth Factors
Streptozocin
Transforming Growth Factor beta
Tumor Suppressor Protein p53
Figure
Reference
-
1. Reidy K, Kang HM, Hostetter T, Susztak K. Molecular mechanisms of diabetic kidney disease. J Clin Invest. 2014; 124:2333–2340.
Article2. Gallagher H, Suckling RJ. Diabetic nephropathy: where are we on the journey from pathophysiology to treatment? Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016; 18:641–647.3. Jha JC, Banal C, Okabe J, Gray SP, Hettige T, Chow BSM, Thallas-Bonke V, De Vos L, Holterman CE, Coughlan MT, Power DA, Skene A, Ekinci EI, Cooper ME, Touyz RM, Kennedy CR, Jandeleit-Dahm K. NADPH oxidase Nox5 accelerates renal injury in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 2017; 66:2691–2703.
Article4. Pontrelli P, Conserva F, Papale M, Oranger A, Barozzino M, Vocino G, Rocchetti MT, Gigante M, Castellano G, Rossini M, Simone S, Laviola L, Giorgino F, Grandaliano G, Di Paolo S, Gesualdo L. Lysine 63 ubiquitination is involved in the progression of tubular damage in diabetic nephropathy. FASEB J. 2017; 31:308–319.
Article5. Zhao Y, Yin Z, Li H, Fan J, Yang S, Chen C, Wang DW. MiR-30c protects diabetic nephropathy by suppressing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in db/db mice. Aging Cell. 2017; 16:387–400.
Article6. Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009; 139:871–890.
Article7. Higgins SP, Tang Y, Higgins CE, Mian B, Zhang W, Czekay RP, Samarakoon R, Conti DJ, Higgins PJ. TGF-β1/p53 signaling in renal fibrogenesis. Cell Signal. 2018; 43:1–10.
Article8. Ma J, Zhang L, Hao J, Li N, Tang J, Hao L. Up-regulation of microRNA-93 inhibits TGF-β1-induced EMT and renal fibrogenesis by down-regulation of Orai1. J Pharmacol Sci. 2018; 136:218–227.
Article9. Piccolo S. P53 regulation orchestrates the TGF-beta response. Cell. 2008; 133:767–769.10. Yang H, Feng A, Lin S, Yu L, Lin X, Yan X, Lu X, Zhang C. Fibroblast growth factor-21 prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy via AMPK-mediated antioxidation and lipid-lowering effects in the heart. Cell Death Dis. 2018; 9:227.
Article11. Zhang C, Shao M, Yang H, Chen L, Yu L, Cong W, Tian H, Zhang F, Cheng P, Jin L, Tan Y, Li X, Cai L, Lu X. Attenuation of hyperlipidemia- and diabetes-induced early-stage apoptosis and late-stage renal dysfunction via administration of fibroblast growth factor-21 is associated with suppression of renal inflammation. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e82275.
Article12. Li F, Liu Z, Tang C, Cai J, Dong Z. FGF21 is induced in cisplatin nephrotoxicity to protect against kidney tubular cell injury. FASEB J. 2018; 32:3423–3433.
Article13. Wang XM, Xiao H, Liu LL, Cheng D, Li XJ, Si LY. FGF21 represses cerebrovascular aging via improving mitochondrial biogenesis and inhibiting p53 signaling pathway in an AMPK-dependent manner. Exp Cell Res. 2016; 346:147–156.
Article14. Zhang Q, Li Y, Liang T, Lu X, Liu X, Zhang C, Jiang X, Martin RC, Cheng M, Cai L. Loss of FGF21 in diabetic mouse during hepatocellular carcinogenetic transformation. Am J Cancer Res. 2015; 5:1762–1774.15. Guo D, Xiao L, Hu H, Liu M, Yang L, Lin X. FGF21 protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells against high glucose-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt/Fox3a signaling pathway. J Diabetes Complications. 2018; 32:729–736.
Article16. Zhang C, Zhang L, Chen S, Feng B, Lu X, Bai Y, Liang G, Tan Y, Shao M, Skibba M, Jin L, Li X, Chakrabarti S, Cai L. The prevention of diabetic cardiomyopathy by non-mitogenic acidic fibroblast growth factor is probably mediated by the suppression of oxidative stress and damage. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e82287.
Article17. Shao M, Yu L, Zhang F, Lu X, Li X, Cheng P, Lin X, He L, Jin S, Tan Y, Yang H, Zhang C, Cai L. Additive protection by LDR and FGF21 treatment against diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes model. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 309:E45–E54.
Article18. Shao M, Lu X, Cong W, Xing X, Tan Y, Li Y, Li X, Jin L, Wang X, Dong J, Jin S, Zhang C, Cai L. Multiple low-dose radiation prevents type 2 diabetes-induced renal damage through attenuation of dyslipidemia and insulin resistance and subsequent renal inflammation and oxidative stress. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e92574.
Article19. Zhang C, Lu X, Tan Y, Li B, Miao X, Jin L, Shi X, Zhang X, Miao L, Li X, Cai L. Diabetes-induced hepatic pathogenic damage, inflammation, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance was exacerbated in zinc deficient mouse model. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e49257.
Article20. Gu J, Wang B, Liu Y, Zhong L, Tang Y, Guo H, Jiang T, Wang L, Li Y, Cai L. Murine double minute 2 siRNA and wild-type p53 gene therapy interact positively with zinc on prostate tumours in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Cancer. 2014; 50:1184–1194.
Article21. Zhang Z, Wang S, Zhou S, Yan X, Wang Y, Chen J, Mellen N, Kong M, Gu J, Tan Y, Zheng Y, Cai L. Sulforaphane prevents the development of cardiomyopathy in type 2 diabetic mice probably by reversing oxidative stress-induced inhibition of LKB1/AMPK pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014; 77:42–52.
Article22. Zhang F, Yu L, Lin X, Cheng P, He L, Li X, Lu X, Tan Y, Yang H, Cai L, Zhang C. Minireview: roles of fibroblast growth factors 19 and 21 in metabolic regulation and chronic diseases. Mol Endocrinol. 2015; 29:1400–1413.
Article23. Anuwatmatee S, Tang S, Wu BJ, Rye KA, Ong KL. Fibroblast growth factor 21 in chronic kidney disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2019; 489:196–202.
Article24. Lee CH, Hui EY, Woo YC, Yeung CY, Chow WS, Yuen MM, Fong CH, Xu A, Lam KS. Circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 levels predict progressive kidney disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and normoalbuminuria. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 100:1368–1375.
Article25. Trakarnvanich T, Prommool S, Kurathong S, Teepprasan T, Wang Y. Associations among cardio-ankle vascular index, carotid intima-media thickness, and fibroblast growth factor-21 levels in kidney transplant patients. Transplant Proc. 2017; 49:1791–1796.
Article26. Bagheri L, Hami M, Mojahedi MJ, Ghorban Sabbagh M, Ayatollahi H. Association of metabolic syndrome with serum fibroblast growth factor 21 in kidney transplanted patients. J Renal Inj Prev. 2016; 5:79–84.
Article27. Kohara M, Masuda T, Shiizaki K, Akimoto T, Watanabe Y, Honma S, Sekiguchi C, Miyazawa Y, Kusano E, Kanda Y, Asano Y, Kuro-O M, Nagata D. Association between circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 and mortality in end-stage renal disease. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0178971.
Article28. Esteghamati A, Khandan A, Momeni A, Behdadnia A, Ghajar A, Nikdad MS, Noshad S, Nakhjavani M, Afarideh M. Circulating levels of fibroblast growth factor 21 in early-stage diabetic kidney disease. Ir J Med Sci. 2017; 186:785–794.
Article29. Hindricks J, Ebert T, Bachmann A, Kralisch S, Lossner U, Kratzsch J, Stolzenburg JU, Dietel A, Beige J, Anders M, Bast I, Bluher M, Stumvoll M, Fasshauer M. Serum levels of fibroblast growth factor-21 are increased in chronic and acute renal dysfunction. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014; 80:918–924.
Article30. Han SH, Choi SH, Cho BJ, Lee Y, Lim S, Park YJ, Moon MK, Lee HK, Kang SW, Han DS, Kim YB, Jang HC, Park KS. Serum fibroblast growth factor-21 concentration is associated with residual renal function and insulin resistance in end-stage renal disease patients receiving long-term peritoneal dialysis. Metabolism. 2010; 59:1656–1662.
Article31. Shi YC, Lu WW, Hou YL, Fu K, Gan F, Cheng SJ, Wang SP, Qi YF, Liu JH. Protection effect of exogenous fibroblast growth factor 21 on the kidney injury in vascular calcification rats. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018; 131:532–538.
Article32. Kim HW, Lee JE, Cha JJ, Hyun YY, Kim JE, Lee MH, Song HK, Nam DH, Han JY, Han SY, Han KH, Kang YS, Cha DR. Fibroblast growth factor 21 improves insulin resistance and ameliorates renal injury in db/db mice. Endocrinology. 2013; 154:3366–3376.
Article33. Wente W, Efanov AM, Brenner M, Kharitonenkov A, Koster A, Sandusky GE, Sewing S, Treinies I, Zitzer H, Gromada J. Fibroblast growth factor-21 improves pancreatic beta-cell function and survival by activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and Akt signaling pathways. Diabetes. 2006; 55:2470–2478.34. Kalluri R, Weinberg RA. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 2009; 119:1420–1428.
Article35. Kalluri R. EMT: when epithelial cells decide to become mesenchymal-like cells. J Clin Invest. 2009; 119:1417–1419.
Article36. Tennakoon AH, Izawa T, Kuwamura M, Yamate J. Pathogenesis of type 2 epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in renal and hepatic fibrosis. J Clin Med. 2015; 5:E4.
Article37. Burns WC, Thomas MC. The molecular mediators of type 2 epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and their role in renal pathophysiology. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2010; 12:e17.
Article38. Ling L, Tan Z, Zhang C, Gui S, Hu Y, Chen L. Long noncoding RNA ENSRNOG00000037522 is involved in the podocyte epithelial-mesenchymal transition in diabetic rats. Int J Mol Med. 2018; 41:2704–2714.
Article39. Ying Q, Wu G. Molecular mechanisms involved in podocyte EMT and concomitant diabetic kidney diseases: an update. Ren Fail. 2017; 39:474–483.
Article40. Hills CE, Squires PE. The role of TGF-β and epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011; 22:131–139.
Article41. Wang B, Koh P, Winbanks C, Coughlan MT, McClelland A, Watson A, Jandeleit-Dahm K, Burns WC, Thomas MC, Cooper ME, Kantharidis P. miR-200a Prevents renal fibrogenesis through repression of TGF-β2 expression. Diabetes. 2011; 60:280–287.
Article42. Kalo E, Buganim Y, Shapira KE, Besserglick H, Goldfinger N, Weisz L, Stambolsky P, Henis YI, Rotter V. Mutant p53 attenuates the SMAD-dependent transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) signaling pathway by repressing the expression of TGF-beta receptor type II. Mol Cell Biol. 2007; 27:8228–8242.43. Kawarada Y, Inoue Y, Kawasaki F, Fukuura K, Sato K, Tanaka T, Itoh Y, Hayashi H. TGF-beta induces p53/Smads complex formation in the PAI-1 promoter to activate transcription. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:35483.
Article44. Yan J, Wang J, Huang H, Huang Y, Mi T, Zhang C, Zhang L. Fibroblast growth factor 21 delayed endothelial replicative senescence and protected cells from H(2)O(2)-induced premature senescence through SIRT1. Am J Transl Res. 2017; 9:4492–4501.45. Jiang X, Chen J, Zhang C, Zhang Z, Tan Y, Feng W, Skibba M, Xin Y, Cai L. The protective effect of FGF21 on diabetes-induced male germ cell apoptosis is associated with up-regulated testicular AKT and AMPK/Sirt1/PGC-1α signaling. Endocrinology. 2015; 156:1156–1170.
Article46. Purvis GSD, Chiazza F, Chen J, Azevedo-Loiola R, Martin L, Kusters DHM, Reutelingsperger C, Fountoulakis N, Gnudi L, Yaqoob MM, Collino M, Thiemermann C, Solito E. Annexin A1 attenuates microvascular complications through restoration of Akt signalling in a murine model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2018; 61:482–495.
Article47. Li B, Cui W, Tan Y, Luo P, Chen Q, Zhang C, Qu W, Miao L, Cai L. Zinc is essential for the transcription function of Nrf2 in human renal tubule cells in vitro and mouse kidney in vivo under the diabetic condition. J Cell Mol Med. 2014; 18:895–906.48. Mayo LD, Donner DB. The PTEN, Mdm2, p53 tumor suppressor-oncoprotein network. Trends Biochem Sci. 2002; 27:462–467.
Article49. Chi SW, Lee SH, Kim DH, Ahn MJ, Kim JS, Woo JY, Torizawa T, Kainosho M, Han KH. Structural details on mdm2-p53 interaction. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:38795–38802.
Article50. Moll UM, Petrenko O. The MDM2-p53 interaction. Mol Cancer Res. 2003; 1:1001–1008.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Renal fibrosis
- Tumor-Associated Macrophages Derived TGF-β‒Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer Cells through Smad2,3-4/Snail Signaling Pathway
- Trefoil Factor 1 Suppresses Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition through Inhibition of TGF-beta Signaling in Gastric Cancer Cells
- Smads as therapeutic targets for chronic kidney disease
- Apolipoprotein A1 Inhibits TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Alveolar Epithelial Cells