Chonnam Med J.
2018 Jan;54(1):63-71. 10.4068/cmj.2018.54.1.63.
Effects of ATP on Pacemaker Activity of Interstitial Cells of Cajal from the Mouse Small Intestine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. jyjun@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 2458587
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2018.54.1.63
Abstract
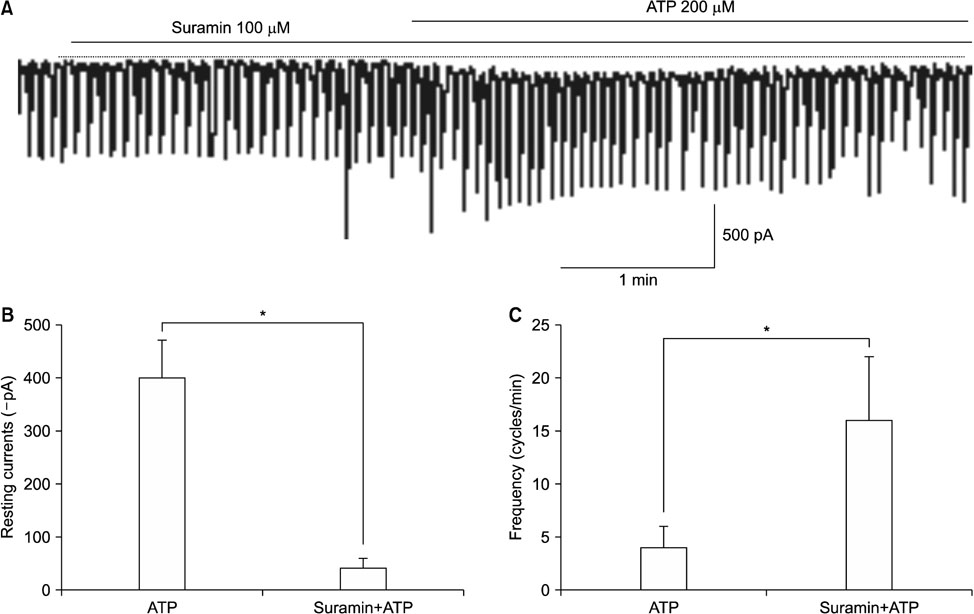
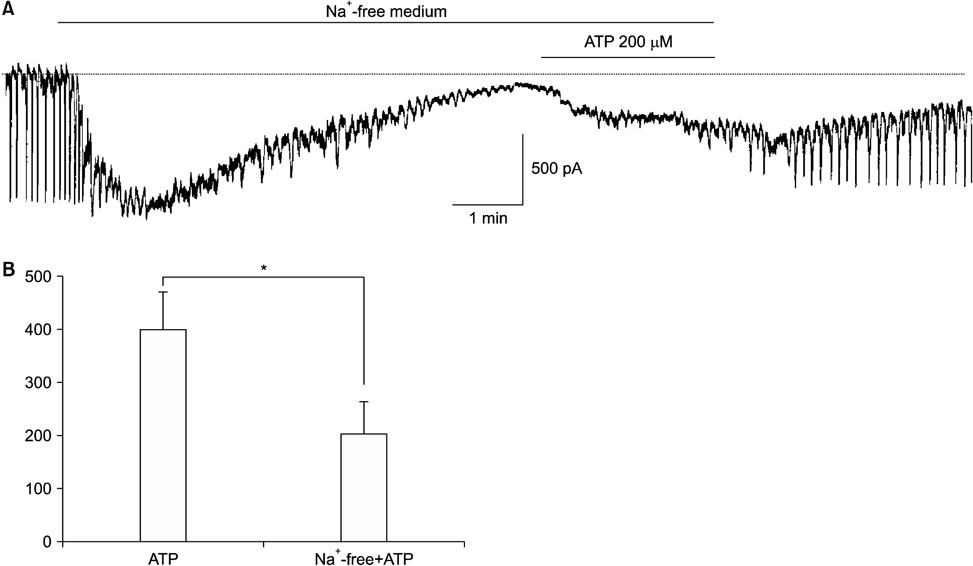
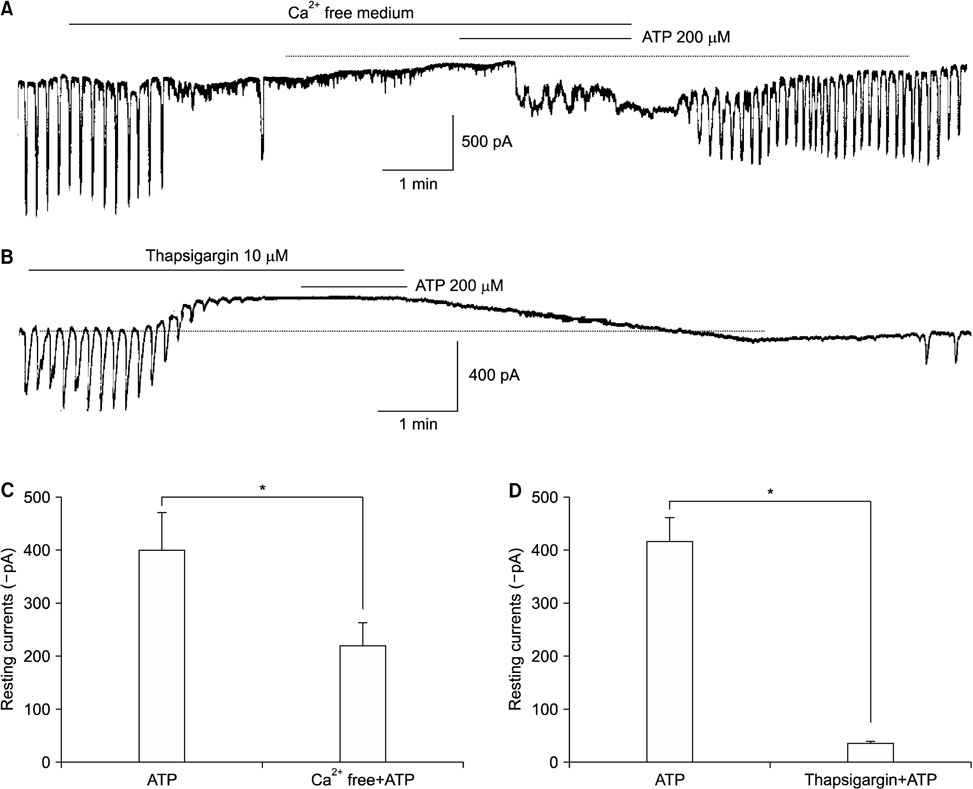
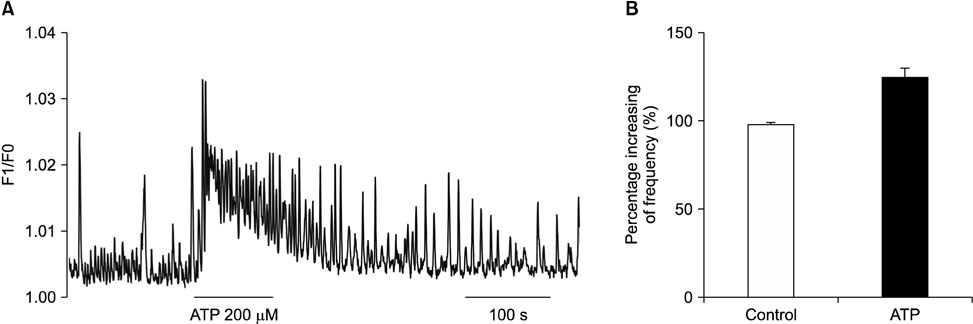
- Purinergic receptors play an important role in regulating gastrointestinal (GI) motility. Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) are pacemaker cells that regulate GI smooth muscle activity. We studied the functional roles of external adenosine 5"²-triphosphate (ATP) on pacemaker activity in cultured ICCs from mouse small intestines by using the whole-cell patch clamp technique and intracellular Ca²âº ([Ca²âº]áµ¢) imaging. External ATP dose-dependently depolarized the resting membrane and produced tonic inward pacemaker currents, and these effects were antagonized by suramin, a purinergic P2 receptor antagonist. ATP-induced effects on pacemaker currents were suppressed by an external Naâº-free solution and inhibited by the nonselective cation channel blockers, flufenamic acid and niflumic acid. The removal of external Ca²âº or treatment with thapsigargin (inhibitor of Ca²âº uptake into endoplasmic reticulum) inhibited the ATP-induced effects on pacemaker currents. Spontaneous [Ca²âº]áµ¢ oscillations were enhanced by external ATP. These results suggest that external ATP modulates pacemaker activity by activating nonselective cation channels via external Ca²âº influx and [Ca²âº]áµ¢ release from the endoplasmic reticulum. Thus, it seems that activating the purinergic P2 receptor may modulate GI motility by acting on ICCs in the small intestine.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenosine
Adenosine Triphosphate*
Animals
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Flufenamic Acid
Interstitial Cells of Cajal*
Intestine, Small*
Membranes
Mice*
Muscle, Smooth
Niflumic Acid
Pacemaker, Artificial
Receptors, Purinergic
Receptors, Purinergic P2
Suramin
Thapsigargin
Adenosine
Adenosine Triphosphate
Flufenamic Acid
Niflumic Acid
Receptors, Purinergic
Receptors, Purinergic P2
Suramin
Thapsigargin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Szurszewski JH. Electrical basis for gastrointestinal motility. In : Johnson LR, editor. Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. 2nd ed. New York: Ravin Press;1987. p. 384–422.2. Olsson C, Holmgren S. The control of gut motility. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2001; 128:481–503.
Article3. Sanders KM. A case for interstitial cells of Cajal as pacemakers and mediators of neurotransmission in the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1996; 111:492–515.
Article4. Thomsen L, Robinson TL, Lee JC, Farraway LA, Hughes MJ, Andrews DW, et al. Interstitial cells of Cajal generate a rhythmic pacemaker current. Nat Med. 1998; 4:848–851.
Article5. Koh SD, Sanders KM, Ward SM. Spontaneous electrical rhythmicity in cultured interstitial cells of cajal from the murine small intestine. J Physiol. 1998; 513:203–213.
Article6. Hanani M, Farrugia G, Komuro T. Intercellular coupling of interstitial cells of cajal in the digestive tract. Int Rev Cytol. 2005; 242:249–282.
Article7. Sanders KM, Hwang SJ, Ward SM. Neuroeffector apparatus in gastrointestinal smooth muscle organs. J Physiol. 2010; 588:4621–4639.
Article8. Won KJ, Sanders KM, Ward SM. Interstitial cells of Cajal mediate mechanosensitive responses in the stomach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:14913–14918.
Article9. Vanderwinden JM, Rumessen JJ. Interstitial cells of Cajal in human gut and gastrointestinal disease. Microsc Res Tech. 1999; 47:344–360.
Article10. Jain D, Moussa K, Tandon M, Culpepper-Morgan J, Proctor DD. Role of interstitial cells of Cajal in motility disorders of the bowel. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003; 98:618–624.
Article11. Burnstock G, Kennedy C. P2X receptors in health and disease. Adv Pharmacol. 2011; 61:333–372.
Article12. Ralevic V, Burnstock G. Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol Rev. 1998; 50:413–492.13. Giaroni C, Knight GE, Ruan HZ, Glass R, Bardini M, Lecchini S, et al. P2 receptors in the murine gastrointestinal tract. Neuropharmacology. 2002; 43:1313–1323.
Article14. Bornstein JC. Purinergic mechanisms in the control of gastrointestinal motility. Purinergic Signal. 2008; 4:197–212.
Article15. Christofi FL. Purinergic receptors and gastrointestinal secretomotor function. Purinergic Signal. 2008; 4:213–236.
Article16. Burnstock G. The journey to establish purinergic signalling in the gut. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2008; 20:Suppl 1. 8–19.
Article17. Burnstock G, Lavin S. Interstitial cells of Cajal and purinergic signalling. Auton Neurosci. 2002; 97:68–72.
Article18. Vanderwinden JM, Timmermans JP, Schiffmann SN. Glial cells, but not interstitial cells, express P2X7, an ionotropic purinergic receptor, in rat gastrointestinal musculature. Cell Tissue Res. 2003; 312:149–154.
Article19. Van Nassauw L, Costagliola A, Van Op den Bosch J, Cecio A, Vanderwinden JM, Burnstock G, et al. Region-specific distribution of the P2Y4 receptor in enteric glial cells and interstitial cells of Cajal within the guinea-pig gastrointestinal tract. Auton Neurosci. 2006; 126-127:299–306.
Article20. Chen H, Redelman D, Ro S, Ward SM, Ordög T, Sanders KM. Selective labeling and isolation of functional classes of interstitial cells of Cajal of human and murine small intestine. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007; 292:C497–C507.
Article21. Jiang R, Taly A, Grutter T. Moving through the gate in ATP-activated P2X receptors. Trends Biochem Sci. 2013; 38:20–29.
Article22. Ward SM, Ordog T, Koh SD, Baker SA, Jun JY, Amberg G, et al. Pacemaking in interstitial cells of Cajal depends upon calcium handling by endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. J Physiol. 2000; 525:355–361.
Article23. Gallego D, Vanden Berghe P, Farré R, Tack J, Jiménez M. P2Y1 receptors mediate inhibitory neuromuscular transmission and enteric neuronal activation in small intestine. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2008; 20:159–168.24. Hwang SJ, Blair PJ, Durnin L, Mutafova-Yambolieva V, Sanders KM, Ward SM. P2Y1 purinoreceptors are fundamental to inhibitory motor control of murine colonic excitability and transit. J Physiol. 2012; 590:1957–1972.
Article25. Hedlund H, Fändriks L, Delbro D, Fasth S. Effect of alpha, beta-methylene ATP on distal colonic and rectal motility--a possible involvement of P2-purinoceptors in pelvic nerve mediated non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic contraction. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986; 127:425–432.
Article26. Martínez-Cutillas M, Gil V, Gallego D, Mañé N, Clavé P, Martín MT, et al. α,β-meATP mimics the effects of the purinergic neurotransmitter in the human and rat colon. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014; 740:442–454.
Article27. Bian X, Ren J, DeVries M, Schnegelsberg B, Cockayne DA, Ford AP, et al. Peristalsis is impaired in the small intestine of mice lacking the P2X3 subunit. J Physiol. 2003; 551:309–322.
Article28. Matsuo K, Katsuragi T, Fujiki S, Sato C, Furukawa T. ATP release and contraction mediated by different P2-receptor subtypes in guinea-pig ileal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1997; 121:1744–1748.
Article29. Furuzono S, Nakayama S, Imaizumi Y. Purinergic modulation of pacemaker Ca2+ activity in interstitial cells of Cajal. Neuropharmacology. 2005; 48:264–273.
Article30. Kurahashi M, Mutafova-Yambolieva V, Koh SD, Sanders KM. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α-positive cells and not smooth muscle cells mediate purinergic hyperpolarization in murine colonic muscles. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014; 307:C561–C570.
Article31. Peri LE, Sanders KM, Mutafova-Yambolieva VN. Differential expression of genes related to purinergic signaling in smooth muscle cells, PDGFRα-positive cells, and interstitial cells of Cajal in the murine colon. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013; 25:e609–e620.
Article32. Bradley E, Kadima S, Kyle B, Hollywood MA, Thornbury KD, McHale NG, et al. P2X receptor currents in smooth muscle cells contribute to nerve mediated contractions of rabbit urethral smooth muscle. J Urol. 2011; 186:745–752.
Article33. Kim BJ, Lim HH, Yang DK, Jun JY, Chang IY, Park CS, et al. Melastatin-type transient receptor potential channel 7 is required for intestinal pacemaking activity. Gastroenterology. 2005; 129:1504–1517.
Article34. Nakayama S, Kajioka S, Goto K, Takaki M, Liu HN. Calcium-associated mechanisms in gut pacemaker activity. J Cell Mol Med. 2007; 11:958–968.
Article35. Hwang SJ, Blair PJ, Britton FC, O'Driscoll KE, Hennig G, Bayguinov YR, et al. Expression of anoctamin 1/TMEM16A by interstitial cells of Cajal is fundamental for slow wave activity in gastrointestinal muscles. J Physiol. 2009; 587:4887–4904.
Article36. Alvarez J, Coulombe A, Cazorla O, Ugur M, Rauzier JM, Magyar J, et al. ATP/UTP activate cation-permeable channels with TRPC3/7 properties in rat cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008; 295:H21–H28.
Article37. Koshimizu TA, Van Goor F, Tomić M, Wong AO, Tanoue A, Tsujimoto G, et al. Characterization of calcium signaling by purinergic receptor-channels expressed in excitable cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2000; 58:936–945.
Article38. Monaghan KP, Koh SD, Ro S, Yeom J, Horowitz B, Sanders KM. Nucleotide regulation of the voltage-dependent nonselective cation conductance in murine colonic myocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006; 291:C985–C994.
Article39. So KY, Kim SH, Sohn HM, Choi SJ, Parajuli SP, Choi S, et al. Carbachol regulates pacemaker activities in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from the mouse small intestine. Mol Cells. 2009; 27:525–531.
Article40. Povstyan OV, Harhun MI, Gordienko DV. Ca2+ entry following P2X receptor activation induces IP3 receptor-mediated Ca2+ release in myocytes from small renal arteries. Br J Pharmacol. 2011; 162:1618–1638.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Inhibition of Pacemaker Activity of Interstitial Cells of Cajal by Hydrogen Peroxide via Activating ATP-sensitive K(+) Channels
- Capsaicin Inhibits the Spontaneous Pacemaker Activity in Interstitial Cells of Cajal From the Small Intestine of Mouse
- Interplay of Hydrogen Sulfide and Nitric Oxide on the Pacemaker Activity of Interstitial Cells of Cajal from Mouse Small Intestine
- (-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate Inhibits the Pacemaker Activity of Interstitial Cells of Cajal of Mouse Small Intestine
- Modulation of Pacemaker Ca2+ Activity by Serotonin in the Cultured Interstitial Cells of the Cajal Clusters Isolated from Mouse Small Intestine