Clin Orthop Surg.
2019 Mar;11(1):95-102. 10.4055/cios.2019.11.1.95.
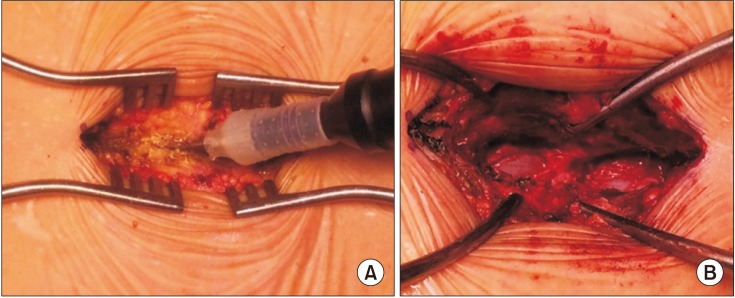
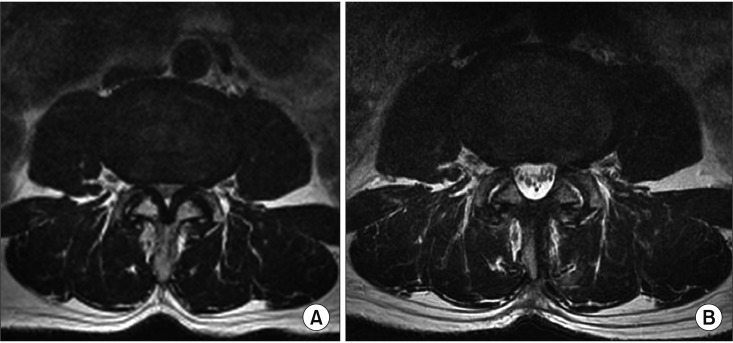
Restoration of the Spinous Process Following Muscle-Preserving Posterior Lumbar Decompression via Sagittal Splitting of the Spinous Process
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hmkim21@gmail.com
- KMID: 2438339
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2019.11.1.95
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
In lumbar spinal stenosis, spinous process-splitting decompression has demonstrated good clinical outcomes with preservation of the posterior ligamentous complex and paraspinal muscles in comparison to conventional laminectomy, but the radiological consequence and clinical impact of the split spinous processes have not been fully understood.
METHODS
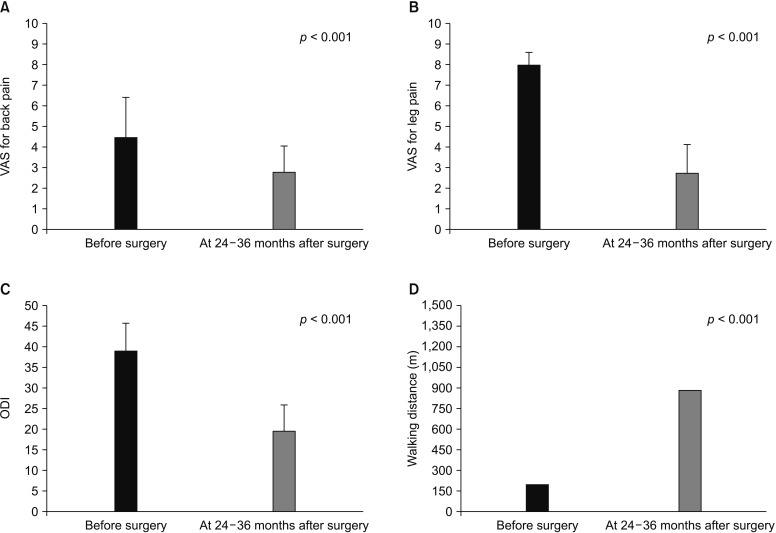
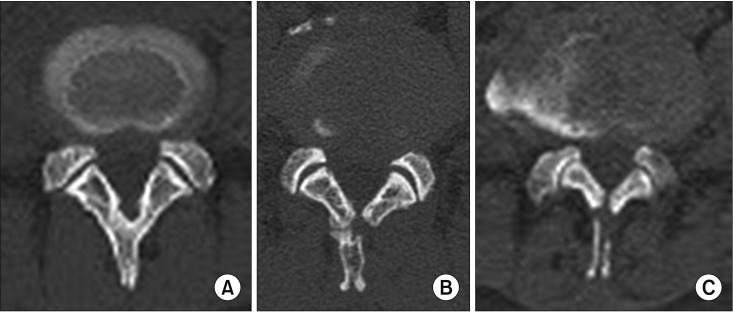
Seventy-three patients who underwent spinous process-splitting decompression were included. The bone union rate and pattern were evaluated by computed tomography performed 6-18 months after surgery and compared among subgroups divided according to the number of levels decompressed and the extent of spinous process splitting. The bone union pattern was classified into three categories: complete union, partial union, and nonunion. The visual analog scale (VAS) score, Oswestry disability index (ODI), and walking distance assessed both before and 24-36 months after surgery were compared among subgroups divided according to the union pattern of the split spinous process.
RESULTS
Overall, the rates of complete union, partial union, and nonunion were 51.7%, 43.2%, and 5.1%, respectively. In the subgroup with partial splitting of the spinous process, the rates were 85.7%, 14.3%, and 0%, respectively; those of the subgroup with total splitting of the spinous process were 32.9%, 59.2%, and 7.9%, respectively. With single-level decompression, a higher rate of union was observed compared with multilevel decompression. The VAS, ODI, and walking distance were significantly improved after surgery and did not differ according to the degree of union of the split spinous process.
CONCLUSIONS
We found that the single-level operation and partial splitting of the spinous process were favourable factors for obtaining complete restoration of the posterior bony structure of the lumbar spine in spinous process-splitting decompression.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Verbiest H. A radicular syndrome from developmental narrowing of the lumbar vertebral canal. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1954; 36(2):230–237. PMID: 13163105.
Article2. Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Gejo R, Tsuji H. Preventive measures of back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery in rats. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998; 23(21):2282–2287. PMID: 9820907.
Article3. Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery. Part 1: histologic and histochemical analyses in rats. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19(22):2590–2597. PMID: 7855686.4. Kawaguchi Y, Yabuki S, Styf J, et al. Back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery: topographic evaluation of intramuscular pressure and blood flow in the porcine back muscle during surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21(22):2683–2688. PMID: 8961456.5. See DH, Kraft GH. Electromyography in paraspinal muscles following surgery for root compression. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1975; 56(2):80–83. PMID: 1124981.6. Sihvonen T, Herno A, Paljarvi L, Airaksinen O, Partanen J, Tapaninaho A. Local denervation atrophy of paraspinal muscles in postoperative failed back syndrome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993; 18(5):575–581. PMID: 8484148.
Article7. Mariconda M, Zanforlino G, Celestino GA, Brancaleone S, Fava R, Milano C. Factors influencing the outcome of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord. 2000; 13(2):131–137. PMID: 10780688.
Article8. Radu AS, Menkes CJ. Update on lumbar spinal stenosis: retrospective study of 62 patients and review of the literature. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1998; 65(5):337–345. PMID: 9636953.9. Silvers HR, Lewis PJ, Asch HL. Decompressive lumbar laminectomy for spinal stenosis. J Neurosurg. 1993; 78(5):695–701. PMID: 8468598.
Article10. Watanabe K, Hosoya T, Shiraishi T, Matsumoto M, Chiba K, Toyama Y. Lumbar spinous process-splitting laminectomy for lumbar canal stenosis: technical note. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005; 3(5):405–408. PMID: 16302638.11. Watanabe K, Matsumoto M, Ikegami T, et al. Reduced post-operative wound pain after lumbar spinous process-splitting laminectomy for lumbar canal stenosis: a randomized controlled study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011; 14(1):51–58. PMID: 21142464.
Article12. Cho DY, Lin HL, Lee WY, Lee HC. Split-spinous process laminotomy and discectomy for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: a preliminary report. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007; 6(3):229–239. PMID: 17355022.
Article13. Kim K, Isu T, Sugawara A, Matsumoto R, Isobe M. Comparison of the effect of 3 different approaches to the lumbar spinal canal on postoperative paraspinal muscle damage. Surg Neurol. 2008; 69(2):109–113. PMID: 18261638.
Article14. Nomura H, Yanagisawa Y, Arima J, Oga M. Clinical outcome of microscopic lumbar spinous process-splitting laminectomy: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014; 21(2):187–194. PMID: 24878270.15. Uehara M, Takahashi J, Hashidate H, et al. Comparison of spinous process-splitting laminectomy versus conventional laminectomy for lumbar spinal stenosis. Asian Spine J. 2014; 8(6):768–776. PMID: 25558319.
Article16. Kanbara S, Yukawa Y, Ito K, Machino M, Kato F. Surgical outcomes of modified lumbar spinous process-splitting laminectomy for lumbar spinal stenosis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015; 22(4):353–357. PMID: 25594729.
Article17. Lee S, Srikantha U. Spinous process splitting laminectomy: clinical outcome and radiological analysis of extent of decompression. Int J Spine Surg. 2015; 9:20. PMID: 26114089.
Article18. Baghdadi YM, Moussallem CD, Shuaib MA, Clarke MJ, Dekutoski MB, Nassr AN. Lumbar spinous process-splitting laminoplasty: a novel technique for minimally invasive lumbar decompression. Orthopedics. 2016; 39(5):e950–e956. PMID: 27337665.
Article19. Maruo K, Tachibana T, Inoue S, Arizumi F, Yoshiya S. Prognostic factors of surgical outcome after spinous process-splitting laminectomy for lumbar spinal stenosis. Asian Spine J. 2015; 9(5):705–712. PMID: 26435788.
Article20. Kakiuchi M, Fukushima W. Impact of spinous process integrity on ten to twelve-year outcomes after posterior decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: study of open-door laminoplasty using a spinous process-splitting approach. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015; 97(20):1667–1677. PMID: 26491131.21. Lee DY, Lee SH. Spinous process splitting laminectomy for lumbar canal stenosis: a critical appraisal. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2008; 51(4):204–207. PMID: 18683110.
Article22. Rajasekaran S, Thomas A, Kanna RM, Prasad Shetty A. Lumbar spinous process splitting decompression provides equivalent outcomes to conventional midline decompression in degenerative lumbar canal stenosis: a prospective, randomized controlled study of 51 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38(20):1737–1743. PMID: 23797498.23. Hatta Y, Shiraishi T, Sakamoto A, et al. Muscle-preserving interlaminar decompression for the lumbar spine: a minimally invasive new procedure for lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34(8):E276–E280. PMID: 19365236.24. Cammisa FP Jr, Girardi FP, Sangani PK, Parvataneni HK, Cadag S, Sandhu HS. Incidental durotomy in spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25(20):2663–2667. PMID: 11034653.
Article25. Wang JC, Bohlman HH, Riew KD. Dural tears secondary to operations on the lumbar spine: management and results after a two-year-minimum follow-up of eighty-eight patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80(12):1728–1732. PMID: 9875930.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Spinous Process-Splitting Laminectomy versus Conventional Laminectomy for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Posterior Dural Shifts Following Spinous Process-Splitting Multi-Level Intervertebral Lumbar Laminectomies
- Spinous Process-Splitting Hemilaminoplasty for Intradural and Extradural Lesions
- Midterm Outcomes of Muscle-Preserving Posterior Lumbar Decompression via Sagittal Splitting of the Spinous Process: Minimum 5-Year Follow-up
- Twelve Contiguous Spinous Process Fracture of Cervico-Thoracic Spine