Clin Orthop Surg.
2019 Mar;11(1):73-81. 10.4055/cios.2019.11.1.73.
Role of Suction Drain after Knee Arthroplasty in the Tranexamic Acid Era: A Randomized Controlled Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedics, Lilavati Hospital and Research Centre, Mumbai, India. drmaniar@jointspeciality.com
- 2Department of Orthopaedics, Siddharth Municipal Hospital, Mumbai, India.
- 3Department of Orthopaedics, Dr. Vasantrao Pawar Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Nashik, India.
- 4Centre for Hip Surgery, Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, UK.
- KMID: 2438336
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2019.11.1.73
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Postoperative suction drains are used after total knee arthroplasty to avoid intra-articular hematoma formation although they can increase blood loss due to a negative suction effect. The use of tranexamic acid to reduce blood loss may nullify this. The aim of this study was to compare outcomes in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty with or without drains and to analyze whether the drain's diameter also has an impact.
METHODS
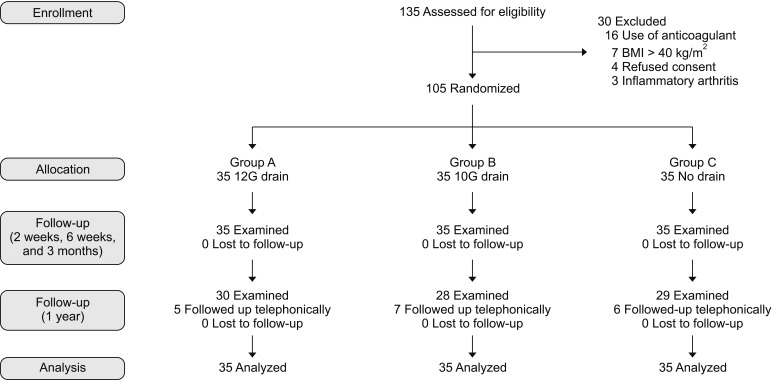
This is a prospective randomized study of patients undergoing unilateral total knee arthroplasty performed by a single surgeon. The study population was divided into three groups (A, 10G drain; B, 12G drain; and C, no drain). Pain, blood loss, swelling, wound-related complications, functional outcomes and questionnaire-based outcomes were assessed postoperatively.
RESULTS
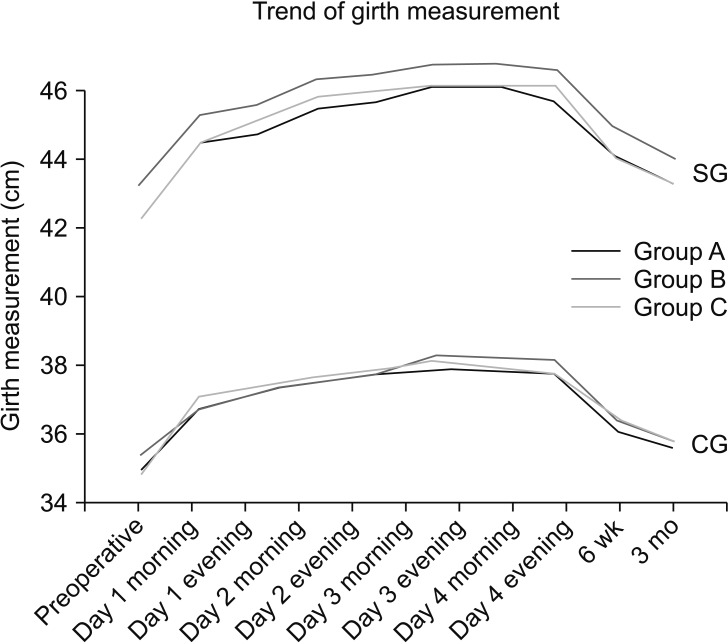
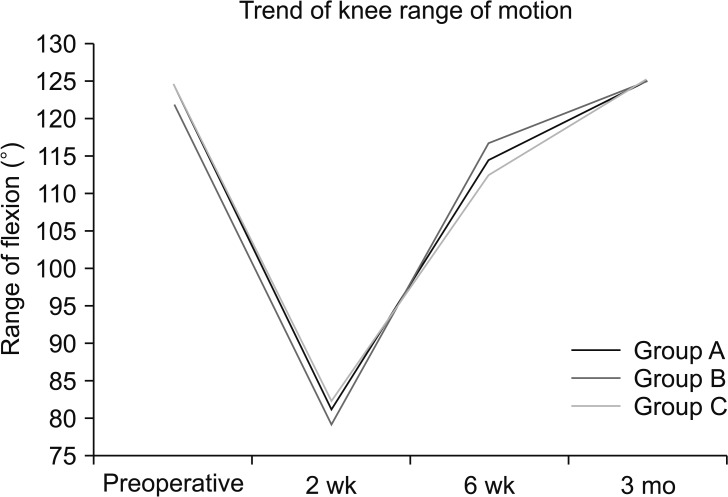
Each group had 35 patients comparable in most demographic and pre- and intraoperative characteristics. During the first 6 hours postoperatively, opioid consumption was significantly higher when the drain was not used (p = 0.036). At 3 months postoperatively, new Knee Society Score (NKSS) was highest with the use of 12G drain (p = 0.018). However, NKSS at 1 year was comparable across the three groups. With the use of tranexamic acid, blood loss and incidence of soakage of dressing were unaffected by the presence or absence of a drain. The calf girth, suprapatellar girth, soakage of dressing and range of motion were comparable in all three groups. There was no incidence of surgical site infection or deep vein thrombosis.
CONCLUSIONS
Presence of a suction drain significantly reduces opioid consumption during the first 6 hours after total knee arthroplasty. Use of a drain made no difference to the functional outcome at 1 year postoperatively. With the use of tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty, the total blood loss and the requirement of blood transfusion were unaffected by the presence or absence of closed suction drainage or by the bore of the drain used. The clinical parameters such as swelling, range of motion, infection and deep vein thrombosis also remained the same.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mirzatolooei F, Tabrizi A, Gargari MM. A comparison of the postoperative complications between two drainage methods after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2018; 6(1):47–51. PMID: 29430495.2. Raja A, Manzoor H, Jan WM, Assad S. Comparison between closed suction drainage and no drainage following total knee arthroplasty in a tertiary care setting in Pakistan. Cureus. 2016; 8(10):e842. PMID: 27909630.
Article3. Cox JS, Friess D. Retained surgical drains in orthopedics: two case reports and a review of the literature. Case Rep Orthop. 2017; 2017:8194571. PMID: 28503334.
Article4. Chen JY, Lee WC, Chan HY, Chang PC, Lo NN, Yeo SJ. Drain use in total knee arthroplasty is neither associated with a greater transfusion rate nor a longer hospital stay. Int Orthop. 2016; 40(12):2505–2509. PMID: 27290896.
Article5. de Andrade MA, de Oliveira Campos TV, Silva BF, et al. Six month follow-up of patients submitted to total knee arthroplasty with and without placement of suction drainage devices. Rev Bras Ortop. 2015; 45(6):549–553. PMID: 27026962.
Article6. Zhang Q, Liu L, Sun W, et al. Are closed suction drains necessary for primary total knee arthroplasty? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(30):e11290. PMID: 30045254.7. Si HB, Yang TM, Zeng Y, Shen B. No clear benefit or drawback to the use of closed drainage after primary total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016; 17:183. PMID: 27118129.
Article8. Leao MG, Neta GM, Silva TM, Ferreira YM, Dias WR. Does the suction drain diameter matter? Bleeding analysis after total knee replacement comparing different suction drain gauges. Rev Bras Ortop. 2016; 51(5):547–554. PMID: 27818976.
Article9. Maniar RN, Kumar G, Singhi T, Nayak RM, Maniar PR. Most effective regimen of tranexamic acid in knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled study in 240 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470(9):2605–2612. PMID: 22419350.
Article10. Ishida K, Tsumura N, Kitagawa A, et al. Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid reduces not only blood loss but also knee joint swelling after total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2011; 35(11):1639–1645. PMID: 21253725.
Article11. Kelsey JL, Whittemore AS, Evans AS, Thompson WD. Methods of sampling and estimation of sample size. In : Kelsey JL, Whittemore AS, Evans AS, Thompson WD, editors. Methods in observational epidemiology. 2nd ed. New York: Oxford University Press;1996. p. 311–340.12. Nadler SB, Hidalgo JH, Bloch T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962; 51(2):224–232. PMID: 21936146.13. Fahmy NR, Patel DG. Hemostatic changes and postoperative deep-vein thrombosis associated with use of a pneumatic tourniquet. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981; 63(3):461–465. PMID: 7204448.
Article14. Langdown AJ, Field J, Grote J, Himayat H. Aprotinin (Trasylol) does not reduce bleeding in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000; 15(8):1009–1012. PMID: 11112196.
Article15. Good L, Peterson E, Lisander B. Tranexamic acid decreases external blood loss but not hidden blood loss in total knee replacement. Br J Anaesth. 2003; 90(5):596–599. PMID: 12697586.
Article16. Lisander B, Ivarsson I, Jacobsson SA. Intraoperative autotransfusion is associated with modest reduction of allogeneic transfusion in prosthetic hip surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1998; 42(6):707–712. PMID: 9689278.
Article17. Boutsiadis A, Reynolds RJ, Saffarini M, Panisset JC. Factors that influence blood loss and need for transfusion following total knee arthroplasty. Ann Transl Med. 2017; 5(21):418. PMID: 29201870.
Article18. Pope D, El-Othmani MM, Manning BT, Sepula M, Markwell SJ, Saleh KJ. Impact of age, gender and anesthesia modality on post-operative pain in total knee arthroplasty patients. Iowa Orthop J. 2015; 35:92–98. PMID: 26361449.19. Watanabe T, Muneta T, Yagishita K, Hara K, Koga H, Sekiya I. Closed suction drainage is not necessary for total knee arthroplasty: a prospective study on simultaneous bilateral surgeries of a mean follow-up of 5.5 years. J Arthroplasty. 2016; 31(3):641–645. PMID: 26631284.20. Wang D, Xu J, Zeng WN, et al. Closed suction drainage is not associated with faster recovery after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled study of 80 patients. Orthop Surg. 2016; 8(2):226–233. PMID: 27384732.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Blood Sparing Efficacy of Oral Tranexamic Acid in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Efficacy of Tranexamic Acid during Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: Comparative Study between Intravenous Use and Topical Use
- Effect of Tranexamic Acid on Blood Loss and Blood Transfusion Reduction after Total Knee Arthroplasty
- A Comparative Study of Subcutaneous versus Intra-Articular Indwelling Closed Suction Drainage after Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Effect of Closed Suction Drain on Blood Loss and Transfusion Rates in Simultaneous Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Randomized Study