Prog Med Phys.
2018 Dec;29(4):106-114. 10.14316/pmp.2018.29.4.106.
Dosimetric and Radiobiological Evaluation of Dose Volume Optimizer (DVO) and Progressive Resolution Optimizer (PRO) Algorithm against Photon Optimizer on IMRT and VMAT Plan for Prostate Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiologic Technology, Choonhae College of Health Sciences, Ulsan, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Bungdang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. jbchung1213@gmail.com
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Konkuk University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2434644
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2018.29.4.106
Abstract
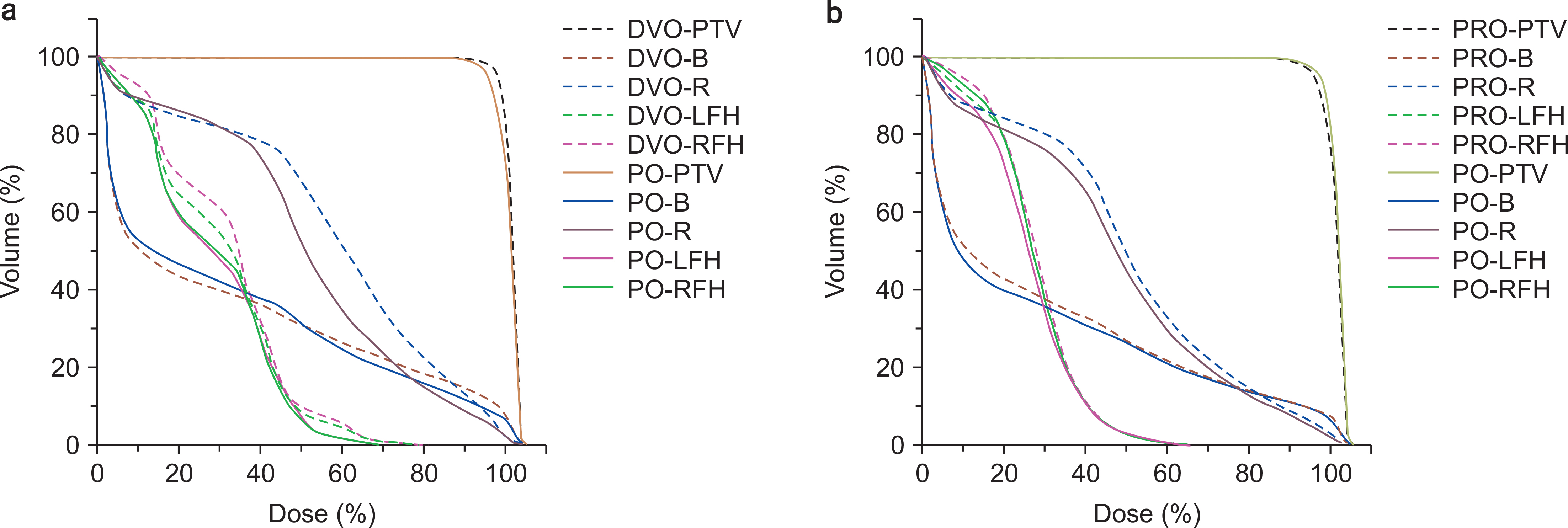
- This study aimed to compare the performance of previous optimization algorithms against new a photon optimizer (PO) algorithm for intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) plans for prostate cancer. Eighteen patients with prostate cancer were retrospectively selected and planned to receive 78 Gy in 39 fractions of the planning target volume (PTV). All plans for each patient optimized with the dose volume optimizer (DVO) and progressive resolution optimizer (PRO) algorithms for IMRT and VMAT were compared against plans optimized with the PO within Eclipse version 13.7. No interactive action was performed during optimization. Dosimetric and radiobiological indices for the PTV and organs at risk were analyzed. The monitor units (MU) per plan were recorded. Based on the plan quality for the target coverage, prostate IMRT and VMAT plans using the PO showed an improvement over DVO and PRO. In addition, the PO generally showed improvement in the tumor control probability for the PTV and normal tissue control probability for the rectum. From a technical perspective, the PO generated IMRT treatment plans with fewer MUs than DVO, whereas it produced slightly more MUs in the VMAT plan, compared with PRO. The PO showed over potentiality of DVO and PRO whenever available, although it led to more MUs in VMAT than PRO. Therefore, the PO has become the preferred choice for planning prostate IMRT and VMAT at our institution.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Cho B. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy: a review with a physics perspective. Radiat Oncol J. 2018. 36(1):1–10.
Article2.Censor Y., Palta JR., Mackie TR. Mathematical optimization for the inverse problem of intensity modulated radiation therapy the state of the art. Madison: AAPM Med Phys Publishing;2003. p. 25–49.3.Cassioli A., Unkelbach J. Aperture shape optimization for IMRT treatment planning. Phys Med Biol. 2013. 58:301–318.
Article4.Choi KH., Kim J., Lee SW., Kang Y., Jang HS. Dosimetric comparison between modulated arc therapy and static intensity modulated radiotherapy in thoracic esophageal cancer: a single institutional experience. Radiat Oncol J. 2018. 36(1):63–70.
Article5.Liu H., Sintay B., Pearman K., Shang Q., Hayes L., Maurer J., Vanderstraeten C., Wiant D. Comparison of the progressive resolution optimizer and photon optimizer in VMAT optimization for stereotactic treatments. J App Clin Med Phys. 2018. 19(4):155–162.
Article6.Shende R., Gupta G., Patel G., Kumar S. Assessment and performance evaluation of photon optimizer vs. dose volume optimizer for IMRT and progressive resolution optimizer for RapidArc planning using a virtual phantom. Int J Cancer Ther Oncol. 2016. 4(3):437–448.7.Cozzi L., Dinshaw KA., Shrivastava SK., Mahantshetty U., Engineer R., Deshpande DD., Jamema SV., Vanetti E., Clivio A., Nicolini G., Fogliata A. A treatment planning study comparing volumetric arc modulation with RapidArc and fixed field IMRT for cervix uteri radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2008. 89(2):180–191.
Article8.Otto K. Volumetric modulated arc therapy: IMRT in a single gantry arc. Med Phys. 2008. 35:310–7.
Article9.Vanetti E., Nicolini G., Nord J., Peltola J., Clivio A., Fogliata A., Cozzi L. On the role of the optimization of RapidArc volumetric modulated arc therapy on plan quality and efficiency. Med Phys. 2011. 38:5844–5856.10.Klippel N., Schmucking M., Terribilini D., Geretschlager A., Aebersold DM., Manser P. Impoved VMAT planning for head and neck tumors with an advanced optimization algorithm. Z Med Phys. 2015. 25:333–340.11.Kim JS., Chung JB., Kim IA., Eom KY. Dosimetric effects of endorectal balloons on intensity-modulated radiation therapy plans for prostate cancer. J Korean Phys Soc. 2013. 63(8):1637–1643.
Article12.ICRU, Prescribing, Recording, and Reporting Photon-Beam Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): Contents. J ICRU. 2010. 10:NP.13.Shaw E., Kline R., Gillin M., Souhami L., Hirschfeld A., Dinapoli R., Martin L. Radiation Therapy Oncology Group: radiosurgery quality assurance guidelines. Int J Radiat Oncol, Biol, Phys. 1993. 27:1231–1239.
Article14.Gay HA., Niemierko A. A free program for calculating EUD-based NTCP and TCP in external beam radiotherapy. Phys Med. 2007. 23:115–25.
Article15.Kang SW., Suh TS., Chung JB., Eom KY., Song C., Kim IA., Kim JS., Lee JW., Cho W. Comparison of dosimetric and radiobiological parameters on plans for prostate stereotactic body radiotherapy using an endorectal balloon for different dose-calculation algorithms and delivery-beam modes. J Korean Phys Soc. 2017. 70(4):424–30.
Article16.Kang SW., Chung JB., Kim JS., Kim IA., Eom KY., Song C., Lee JW., Kim JY., Suh TS. Optimal planning strategy among various arc arrangements for prostate stereotactic body radiotherapy with volumetric modulated arc therapy technique. Radiol Oncol. 2017. 51(1):112–120.
Article17.Fogliata A., Wang PM., Belosi F., Clivio A., Nicolini G., Vanetti E., Cozzi L. Assessment of a model based optimization engine for volumetric modulated arc therapy for patients with advanced hepatocellular cancer. Radiat Oncol. 2014. 9:236.
Article18.Fogliata A., Nicolini G., Clivio A., Vanetti E., Laksar S., Tozzi A., Scorsetti M., Cozzi L. A broad scope knowledge based model for optimization of VMAT in esophageal cancer: validation and assessment of plan quality among different treatment centers. Radiat Oncol. 2015. 10:220.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Dosimetrical and Radiobiological Parameters on Three VMAT Techniques for Left-Sided Breast Cancer
- Dosimetric Evaluation of Low-Dose Spillage Volumes for Head and Neck Cancer Using Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy and Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy Treatment Techniques
- Volumetric modulated arc therapy for carotid sparing in the management of early glottic cancer
- Application of Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) in Prostate Cancer
- A Dosimetric Comparision of IMRT and VMAT in Synchronous Bilateral Breast Cancer