Development and Validation of the Korean Diabetes Risk Score: A 10-Year National Cohort Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. djkim@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Etiology Research Center, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 5Department of Family Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- 6Policy Research Affairs, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 7Department of Family Medicine, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2422785
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0014
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
A diabetes risk score in Korean adults was developed and validated.
METHODS
This study used the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) of 359,349 people without diabetes at baseline to derive an equation for predicting the risk of developing diabetes, using Cox proportional hazards regression models. External validation was conducted using data from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Calibration and discrimination analyses were performed separately for men and women in the development and validation datasets.
RESULTS
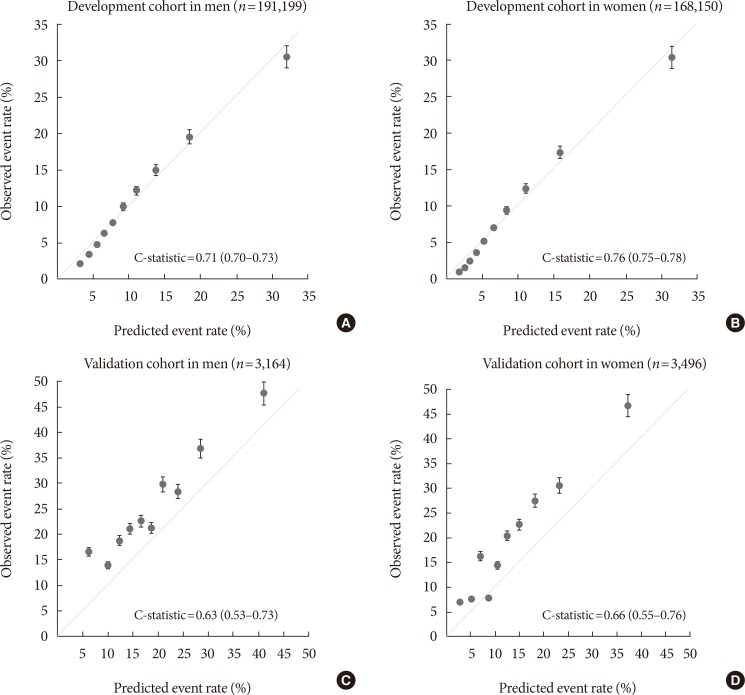
During a median follow-up of 10.8 years, 37,678 cases (event rate=10.4 per 1,000 person-years) of diabetes were identified in the development cohort. The risk score included age, family history of diabetes, alcohol intake (only in men), smoking status, physical activity, use of antihypertensive therapy, use of statin therapy, body mass index, systolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, fasting glucose, and γ glutamyl transferase (only in women). The C-statistics for the models for risk at 10 years were 0.71 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.70 to 0.73) for the men and 0.76 (95% CI, 0.75 to 0.78) for the women in the development dataset. In the validation dataset, the C-statistics were 0.63 (95% CI, 0.53 to 0.73) for men and 0.66 (95% CI, 0.55 to 0.76) for women.
CONCLUSION
The Korean Diabetes Risk Score may identify people at high risk of developing diabetes and may be an effective tool for delaying or preventing the onset of condition as risk management strategies involving modifiable risk factors can be recommended to those identified as at high risk.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Blood Pressure
Body Mass Index
Calibration
Cholesterol
Cohort Studies*
Dataset
Diabetes Mellitus
Discrimination (Psychology)
Epidemiology
Fasting
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Genome
Glucose
Humans
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
Korea
Male
Mass Screening
Motor Activity
National Health Programs
Risk Assessment
Risk Factors
Risk Management
Smoke
Smoking
Transferases
Cholesterol
Glucose
Smoke
Transferases
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Smoking as a Target for Prevention of Diabetes
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):402-404. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0126.Biomarker Score in Risk Prediction: Beyond Scientific Evidence and Statistical Performance
Heejung Bang
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):245-247. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0073.Multiple Biomarkers Improved Prediction for the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Singapore Chinese Men and Women
Yeli Wang, Woon-Puay Koh, Xueling Sim, Jian-Min Yuan, An Pan
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):295-306. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0020.Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Based Diabetes Prediction System Using a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort
Sang Youl Rhee, Ji Min Sung, Sunhee Kim, In-Jeong Cho, Sang-Eun Lee, Hyuk-Jae Chang
Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):515-525. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0081.
Reference
-
1. Ha KH, Kim DJ. Trends in the diabetes epidemic in Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2015; 30:142–146. PMID: 26194073.
Article2. Herman WH, Ye W, Griffin SJ, Simmons RK, Davies MJ, Khunti K, Rutten GE, Sandbaek A, Lauritzen T, Borch-Johnsen K, Brown MB, Wareham NJ. Early detection and treatment of type 2 diabetes reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality: a simulation of the results of the Anglo-Danish-Dutch Study of intensive treatment in people with screen-detected diabetes in primary care (ADDITION-Europe). Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:1449–1455. PMID: 25986661.
Article3. Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA, Nathan DM. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:393–403. PMID: 11832527.
Article4. Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hamalainen H, Ilanne-Parikka P, Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi S, Laakso M, Louheranta A, Rastas M, Salminen V, Uusitupa M. Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:1343–1350. PMID: 11333990.
Article5. Glumer C, Vistisen D, Borch-Johnsen K, Colagiuri S. DETECT-2 Collaboration. Risk scores for type 2 diabetes can be applied in some populations but not all. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:410–414. PMID: 16443896.6. Rathmann W, Martin S, Haastert B, Icks A, Holle R, Lowel H, Giani G. KORA Study Group. Performance of screening questionnaires and risk scores for undiagnosed diabetes: the KORA Survey 2000. Arch Intern Med. 2005; 165:436–441. PMID: 15738374.7. Lee YH, Bang H, Kim HC, Kim HM, Park SW, Kim DJ. A simple screening score for diabetes for the Korean population: development, validation, and comparison with other scores. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:1723–1730. PMID: 22688547.8. Lim NK, Park SH, Choi SJ, Lee KS, Park HY. A risk score for predicting the incidence of type 2 diabetes in a middle-aged Korean cohort: the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Circ J. 2012; 76:1904–1910. PMID: 22640983.9. Seong SC, Kim YY, Park SK, Khang YH, Kim HC, Park JH, Kang HJ, Do CH, Song JS, Lee EJ, Ha S, Shin SA, Jeong SL. Cohort profile: the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) in Korea. BMJ Open. 2017; 7:e016640.
Article10. World Health Organization. The Asia Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. Sydney: Health Communications;2000. p. 15–21.11. Kim Y, Han BG. KoGES group. Cohort profile: the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) consortium. Int J Epidemiol. 2017; 46:e20. PMID: 27085081.
Article12. Royston P, Altman DG. External validation of a Cox prognostic model: principles and methods. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013; 13:33. PMID: 23496923.
Article13. Harrell FE Jr, Califf RM, Pryor DB, Lee KL, Rosati RA. Evaluating the yield of medical tests. JAMA. 1982; 247:2543–2546. PMID: 7069920.
Article14. Korean Diabetes Association. Korean diabetes fact sheet 2015. cited 2018 Apr 30. Available from: http://www.diabetes.or.kr.15. Korean Diabetes Association. Korean diabetes fact sheet 2016. cited 2018 Apr 30. Available from: http://www.diabetes.or.kr.16. Noble D, Mathur R, Dent T, Meads C, Greenhalgh T. Risk models and scores for type 2 diabetes: systematic review. BMJ. 2011; 343:d7163. PMID: 22123912.
Article17. Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, Kadowaki T, Yajnik CS, Yoon KH, Hu FB. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA. 2009; 301:2129–2140. PMID: 19470990.18. Gujral UP, Pradeepa R, Weber MB, Narayan KM, Mohan V. Type 2 diabetes in South Asians: similarities and differences with white Caucasian and other populations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013; 1281:51–63. PMID: 23317344.
Article19. Hu PL, Koh YL, Tan NC. The utility of diabetes risk score items as predictors of incident type 2 diabetes in Asian populations: an evidence-based review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016; 122:179–189. PMID: 27865165.
Article20. Gao WG, Dong YH, Pang ZC, Nan HR, Wang SJ, Ren J, Zhang L, Tuomilehto J, Qiao Q. A simple Chinese risk score for undiagnosed diabetes. Diabet Med. 2010; 27:274–281. PMID: 20536489.
Article21. Luo S, Han L, Zeng P, Chen F, Pan L, Wang S, Zhang T. A risk assessment model for type 2 diabetes in Chinese. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e104046. PMID: 25101994.
Article22. Sun F, Tao Q, Zhan S. An accurate risk score for estimation 5-year risk of type 2 diabetes based on a health screening population in Taiwan. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009; 85:228–234. PMID: 19500871.
Article23. Heianza Y, Arase Y, Hsieh SD, Saito K, Tsuji H, Kodama S, Tanaka S, Ohashi Y, Shimano H, Yamada N, Hara S, Sone H. Development of a new scoring system for predicting the 5 year incidence of type 2 diabetes in Japan: the Toranomon Hospital Health Management Center Study 6 (TOPICS 6). Diabetologia. 2012; 55:3213–3223. PMID: 22955996.24. Wang A, Chen G, Su Z, Liu X, Liu X, Li H, Luo Y, Tao L, Guo J, Liu L, Chen S, Wu S, Guo X. Risk scores for predicting incidence of type 2 diabetes in the Chinese population: the Kailuan prospective study. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:26548. PMID: 27221651.
Article25. Lee YH, Bang H, Kim DJ. How to establish clinical prediction models. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2016; 31:38–44. PMID: 26996421.
Article26. Aune D, Norat T, Leitzmann M, Tonstad S, Vatten LJ. Physical activity and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol. 2015; 30:529–542. PMID: 26092138.
Article27. InterAct Consortium. Spijkerman AM, van der A DL, Nilsson PM, Ardanaz E, Gavrila D, Agudo A, Arriola L, Balkau B, Beulens JW, Boeing H, de Lauzon-Guillain B, Fagherazzi G, Feskens EJ, Franks PW, Grioni S, Huerta JM, Kaaks R, Key TJ, Overvad K, Palli D, Panico S, Redondo ML, Rolandsson O, Roswall N, Sacerdote C, Sanchez MJ, Schulze MB, Slimani N, Teucher B, Tjonneland A, Tumino R, van der Schouw YT, Langenberg C, Sharp SJ, Forouhi NG, Riboli E, Wareham NJ. Smoking and long-term risk of type 2 diabetes: the EPIC-InterAct study in European populations. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:3164–3171. PMID: 25336749.28. Li XH, Yu FF, Zhou YH, He J. Association between alcohol consumption and the risk of incident type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016; 103:818–829. PMID: 26843157.
Article29. Knott C, Bell S, Britton A. Alcohol consumption and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of more than 1.9 million individuals from 38 observational studies. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:1804–1812. PMID: 26294775.
Article30. Lee DY, Yoo MG, Kim HJ, Jang HB, Kim JH, Lee HJ, Park SI. Association between alcohol consumption pattern and the incidence risk of type 2 diabetes in Korean men: a 12-years follow-up study. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:7322. PMID: 28779170.
Article31. Hong SW, Linton JA, Shim JY, Kang HT. High-risk drinking is associated with a higher risk of diabetes mellitus in Korean men, based on the 2010–2012 KNHANES. Alcohol. 2015; 49:275–281. PMID: 25920001.
Article32. Lee DH, Jacobs DR Jr. Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase: new insights about an old enzyme. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2009; 63:884–886. PMID: 19825792.33. Thayer KA, Heindel JJ, Bucher JR, Gallo MA. Role of environmental chemicals in diabetes and obesity: a National Toxicology Program workshop review. Environ Health Perspect. 2012; 120:779–789. PMID: 22296744.
Article34. Lee DH, Jacobs DR Jr, Gross M, Kiefe CI, Roseman J, Lewis CE, Steffes M. Gamma-glutamyltransferase is a predictor of incident diabetes and hypertension: the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Clin Chem. 2003; 49:1358–1366. PMID: 12881453.35. Nguyen NT, Nguyen XM, Lane J, Wang P. Relationship between obesity and diabetes in a US adult population: findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2006. Obes Surg. 2011; 21:351–355. PMID: 21128002.
Article36. Sairenchi T, Iso H, Irie F, Fukasawa N, Ota H, Muto T. Underweight as a predictor of diabetes in older adults: a large cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:583–584. PMID: 18071003.37. Wei GS, Coady SA, Goff DC Jr, Brancati FL, Levy D, Selvin E, Vasan RS, Fox CS. Blood pressure and the risk of developing diabetes in African Americans and Whites: ARIC, CARDIA, and the Framingham Heart Study. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:873–879. PMID: 21346180.38. Cho NH, Kim KM, Choi SH, Park KS, Jang HC, Kim SS, Sattar N, Lim S. High blood pressure and its association with incident diabetes over 10 years in the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES). Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:1333–1338. PMID: 25986660.
Article39. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, DePalma SM, Gidding S, Jamerson KA, Jones DW, MacLaughlin EJ, Muntner P, Ovbiagele B, Smith SC Jr, Spencer CC, Stafford RS, Taler SJ, Thomas RJ, Williams KA Sr, Williamson JD, Wright JT Jr. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018; 71:e127–e248. PMID: 29146535.
Article40. Han SJ, Kim HJ, Kim DJ, Lee KW, Cho NH. Incidence and predictors of type 2 diabetes among Koreans: a 12-year follow up of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017; 123:173–180. PMID: 28043048.
Article41. Jeon JY, Ko SH, Kwon HS, Kim NH, Kim JH, Kim CS, Song KH, Won JC, Lim S, Choi SH, Jang MJ, Kim Y, Oh K, Kim DJ, Cha BY. Taskforce Team of Diabetes Fact Sheet of the Korean Diabetes Association. Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes according to fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c. Diabetes Metab J. 2013; 37:349–357. PMID: 24199164.
Article42. Song SO, Song YD, Nam JY, Park KH, Yoon JH, Son KM, Ko Y, Lim DH. Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes mellitus in Korea through an investigation of the National Registration Project of type 1 diabetes for the reimbursement of glucometer strips with additional analyses using claims data. Diabetes Metab J. 2016; 40:35–45. PMID: 26912154.
Article43. Kahn HS, Cheng YJ, Thompson TJ, Imperatore G, Gregg EW. Two risk-scoring systems for predicting incident diabetes mellitus in U.S. adults age 45 to 64 years. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 150:741–751. PMID: 19487709.
Article44. Mooradian AD. Dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 5:150–159. PMID: 19229235.
Article45. Esposito K, Chiodini P, Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, Panagiotakos D, Giugliano D. Which diet for prevention of type 2 diabetes? A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Endocrine. 2014; 47:107–116. PMID: 24744219.
Article46. Imamura F, O'Connor L, Ye Z, Mursu J, Hayashino Y, Bhupathiraju SN, Forouhi NG. Consumption of sugar sweetened beverages, artificially sweetened beverages, and fruit juice and incidence of type 2 diabetes: systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimation of population attributable fraction. BMJ. 2015; 351:h3576. PMID: 26199070.
Article47. Micha R, Wallace SK, Mozaffarian D. Red and processed meat consumption and risk of incident coronary heart disease, stroke, and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2010; 121:2271–2283. PMID: 20479151.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development and validation of a clinical score to predict 1-year survival of arteriovenous fistula access: a diagnostic study
- Development and validation of risk score for predicting spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Prediction of the 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in the Korean population
- Development and validation of a comorbidity index for predicting survival outcomes after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in adult patients with acute leukemia: a Korean nationwide cohort study
- Predicting the Development of Myocardial Infarction in Middle-Aged Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Risk Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea