Ten-Year Mortality Trends for Adults with and without Diabetes Mellitus in South Korea, 2003 to 2013
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pourlife@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of International Finance, Hankuk University of Foreign Studies, Yongin, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Statistics, Korea University, Seoul, Korea. yspark@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2422784
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0088
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
To estimate and compare the trends of all-cause and cause-specific mortality rates for subjects with and without diabetes in South Korea, from 2003 to 2013.
METHODS
Using a population-based cohort (2003 to 2013), we evaluated annual mortality rates in adults (≥30 years) with and without diabetes. The number of subjects in this analysis ranged from 585,795 in 2003 to 670,020 in 2013.
RESULTS
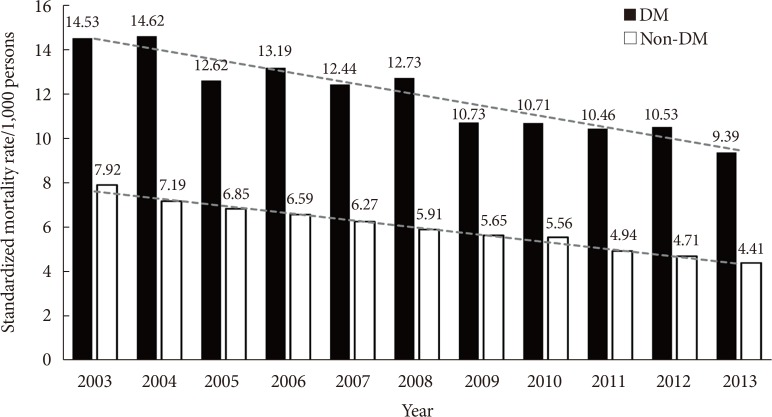
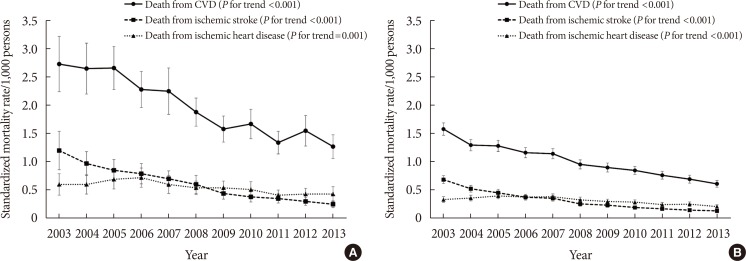
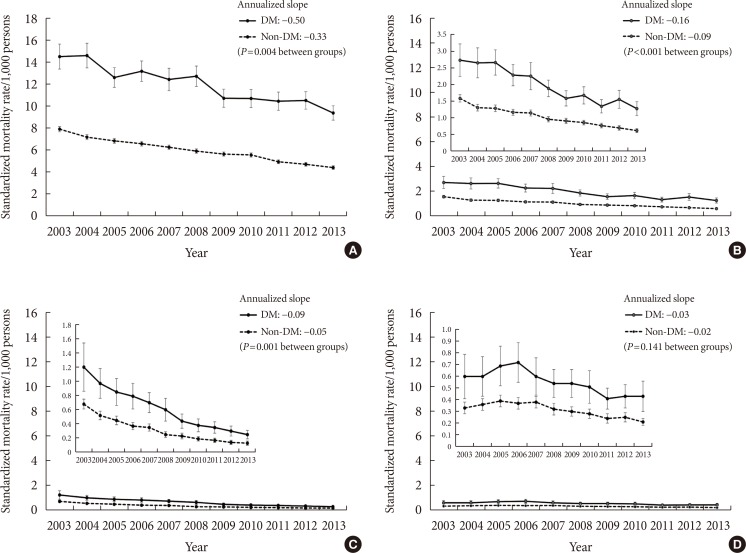
Age- and sex-adjusted all-cause mortality rates decreased consistently in both groups from 2003 to 2013 (from 14.4 to 9.3/1,000 persons in subjects with diabetes and from 7.9 to 4.4/1,000 persons in those without diabetes). The difference in mortality rates between groups also decreased (6.61 per 1,000 persons in 2003 to 4.98 per 1,000 persons in 2013). The slope associated with the mortality rate exhibited a steeper decrease in subjects with diabetes than those without diabetes (regression coefficients of time: −0.50 and −0.33, respectively; P=0.004). In subjects with diabetes, the mortality rate from cardiovascular disease decreased by 53.5% (from 2.73 to 1.27 per 1,000 persons, P for trend < 0.001). Notably, the decrease in mortality from ischemic stroke (79.2%, from 1.20 to 0.25 per 1,000 persowns) was more profound than that from ischemic heart disease (28.3%, from 0.60 to 0.43 per 1,000 persons).
CONCLUSION
All-cause and cardiovascular mortality rates decreased substantially from 2003 to 2013, and the decline in ischemic stroke mortality mainly contributed to the decreased cardiovascular mortality in Korean people with diabetes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 9 articles
-
Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports
Na-young Kim, Eunyeong Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Yong-Hoon Lee, Eun Young Choi
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):349-353. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0091.Trends of Diabetes Epidemic in Korea
Ji Cheol Bae
Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(5):377-379. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0194.Metformin Treatment for Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, ,
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):3-10. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0004.Diabetes and Cancer: Cancer Should Be Screened in Routine Diabetes Assessment
Sunghwan Suh, Kwang-Won Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):733-743. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0177.Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):464-475. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0088.Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):466-474. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2022.1440.Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):543-551. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0209.Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):1-9. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0448.The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population
Sunghwan Suh
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):522-524. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2023.502.
Reference
-
1. Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lu Y, Singh GM, Cowan MJ, Paciorek CJ, Lin JK, Farzadfar F, Khang YH, Stevens GA, Rao M, Ali MK, Riley LM, Robinson CA, Ezzati M. Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors of Chronic Diseases Collaborating Group (Blood Glucose). National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2·7 million participants. Lancet. 2011; 378:31–40. PMID: 21705069.
Article2. Gregg EW, Cheng YJ, Saydah S, Cowie C, Garfield S, Geiss L, Barker L. Trends in death rates among U.S. adults with and without diabetes between 1997 and 2006: findings from the National Health Interview Survey. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:1252–1257. PMID: 22619288.3. Lind M, Garcia-Rodriguez LA, Booth GL, Cea-Soriano L, Shah BR, Ekeroth G, Lipscombe LL. Mortality trends in patients with and without diabetes in Ontario, Canada and the UK from 1996 to 2009: a population-based study. Diabetologia. 2013; 56:2601–2608. PMID: 24114114.
Article4. Gu K, Cowie CC, Harris MI. Diabetes and decline in heart disease mortality in US adults. JAMA. 1999; 281:1291–1297. PMID: 10208144.
Article5. Preis SR, Pencina MJ, Hwang SJ, D'Agostino RB Sr, Savage PJ, Levy D, Fox CS. Trends in cardiovascular disease risk factors in individuals with and without diabetes mellitus in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2009; 120:212–220. PMID: 19581493.
Article6. Harding JL, Shaw JE, Peeters A, Guiver T, Davidson S, Magliano DJ. Mortality trends among people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in Australia: 1997–2010. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:2579–2586. PMID: 24947787.
Article7. Lipscombe LL, Hux JE. Trends in diabetes prevalence, incidence, and mortality in Ontario, Canada 1995–2005: a population-based study. Lancet. 2007; 369:750–756. PMID: 17336651.
Article8. Barquera S, Tovar-Guzman V, Campos-Nonato I, Gonzalez-Villalpando C, Rivera-Dommarco J. Geography of diabetes mellitus mortality in Mexico: an epidemiologic transition analysis. Arch Med Res. 2003; 34:407–414. PMID: 14602508.
Article9. Choi YJ, Cho YM, Park CK, Jang HC, Park KS, Kim SY, Lee HK. Rapidly increasing diabetes-related mortality with socioenvironmental changes in South Korea during the last two decades. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006; 74:295–300. PMID: 16707191.
Article10. Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J, Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, Zhu D, Ge J, Lin L, Chen L, Guo X, Zhao Z, Li Q, Zhou Z, Shan G, He J. China National Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders Study Group. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:1090–1101. PMID: 20335585.
Article11. World Health Organization. Global health estimates: deaths by cause, age, sex and country, 2000–2012. Geneva: World Health Organization;2014.12. Song SO, Lee YH, Kim DW, Song YD, Nam JY, Park KH, Kim DJ, Park SW, Lee HC, Lee BW. Trends in diabetes incidence in the last decade based on Korean National Health Insurance claims data. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2016; 31:292–299. PMID: 27302715.
Article13. Choi YJ, Kim HC, Kim HM, Park SW, Kim J, Kim DJ. Prevalence and management of diabetes in Korean adults: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1998–2005. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:2016–2020. PMID: 19675201.14. Korea Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2013. cited 2018 Mar 30. Available from: http://www.diabetes.or.kr/temp/diabetes_factsheet_2013111.pdf.15. Kim NH, Lee J, Kim TJ, Kim NH, Choi KM, Baik SH, Choi DS, Pop-Busui R, Park Y, Kim SG. Body mass index and mortality in the general population and in subjects with chronic disease in Korea: a nationwide cohort study (2002–2010). PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0139924. PMID: 26462235.
Article16. Indrayan A. Medical Biostatistics. 3rd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press;2012.17. Altman D, Machin D, Bryant T, Gardner M. Statistics with confidence: confidence intervals and statistical guidelines. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons;2013.18. Gregg EW, Albright AL. The public health response to diabetes: two steps forward, one step back. JAMA. 2009; 301:1596–1598. PMID: 19366782.19. Gregg EW, Li Y, Wang J, Burrows NR, Ali MK, Rolka D, Williams DE, Geiss L. Changes in diabetes-related complications in the United States, 1990–2010. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370:1514–1523. PMID: 24738668.
Article20. Gregg EW, Gu Q, Cheng YJ, Narayan KM, Cowie CC. Mortality trends in men and women with diabetes, 1971 to 2000. Ann Intern Med. 2007; 147:149–155. PMID: 17576993.
Article21. Jeon JY, Kim DJ, Ko SH, Kwon HS, Lim S, Choi SH, Kim CS, An JH, Kim NH, Won JC, Kim JH, Cha BY, Song KH. Taskforce Team of Diabetes Fact Sheet of the Korean Diabetes Association. Current status of glycemic control of patients with diabetes in Korea: the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Metab J. 2014; 38:197–203. PMID: 25003073.
Article22. Ha KH, Kim DJ. Current status of managing diabetes mellitus in Korea. Korean J Intern Med. 2016; 31:845–850. PMID: 27604796.
Article23. Shin J, Park JB, Kim KI, Kim JH, Yang DH, Pyun WB, Kim YG, Kim GH, Chae SC. Guideline Committee of the Korean Society of Hypertension. 2013 Korean Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension: part III-hypertension in special situations. Clin Hypertens. 2015; 21:3. PMID: 26893917.
Article24. Ha KH, Kwon HS, Kim DJ. Epidemiologic characteristics of dyslipidemia in Korea. J Lipid Atheroscler. 2015; 4:93–99.
Article25. Jung KH, Lee SH, Kim BJ, Yu KH, Hong KS, Lee BC, Roh JK. Korean Stroke Registry Study Group. Secular trends in ischemic stroke characteristics in a rapidly developed country: results from the Korean Stroke Registry Study (secular trends in Korean stroke). Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012; 5:327–334. PMID: 22474244.26. Hong KS, Bang OY, Kim JS, Heo JH, Yu KH, Bae HJ, Kang DW, Lee JS, Kwon SU, Oh CW, Lee BC, Yoon BW. Stroke statistics in Korea: part II. Stroke awareness and acute stroke care, a report from the Korean Stroke Society and clinical research center for stroke. J Stroke. 2013; 15:67–77. PMID: 24324942.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intervention Strategies for Older Adults with Diabetes
- Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Mortality of End-Stage Kidney Disease in South Korea
- Cause-of-Death Trends for Diabetes Mellitus over 10 Years (Korean Diabetes J 33(1):65-72, 2009)
- Cause-of-Death Trends for Diabetes Mellitus over 10 Years (Korean Diabetes J 33(1):65-72, 2009)
- Trends in Cardiovascular Complications and Mortality among Patients with Diabetes in South Korea