Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2017 Sep;20(3):160-166. 10.5223/pghn.2017.20.3.160.
Prevalence and Epidemiological Characteristics of Endoscopically Proven Reflux Esophagitis in Children in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. i101016@skku.edu
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Biostatistics and Clinical Epidemiology Center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2390547
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2017.20.3.160
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The prevalence of reflux esophagitis (RE) has increased recently in Korea. Little is known concerning the prevalence and characteristics of RE in pediatric patients. This study investigated the prevalence and influence of risk factors in endoscopically proven RE in Korea in pediatric patients over a period of 14 years.
METHODS
A retrospective chart review of all patients between the ages of 1 month and 20 years who underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy at Samsung Medical Center between 2001 and 2014 was carried out. Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted to identify independent risk factors for RE.
RESULTS
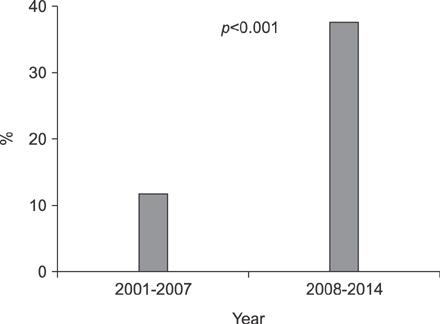
The prevalence rate of endoscopically proven RE in this study was 28.7% (978/3,413). The prevalence of RE increased from 11.8% from 2001 to 2007 to 37.7% from 2008 to 2014. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that residency in the Greater Gangnam area (odds ratio [OR], 1.21; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02-1.44) and age (OR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.11-1.15) were significant predictive factors for the presence of RE.
CONCLUSION
The prevalence rate of endoscopically proven pediatric RE has increased over the past 14 years. Residency and older age are more important independent risk factors for pediatric RE in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Is the Diagnostic Trial with Proton Pump Inhibitors Reasonable for School Age Children with Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptoms?
Jaeeun Yang, Jieon Lee, Hyunju Lee, Juyeon Lee, Young Mi Yoon, Jae Hong Choi, Yoon-Joo Kim, Hyun Sik Kang, Kyoung Hee Han, Seung Hyo Kim, Ki-Soo Kang
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2019;22(6):511-517. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.6.511.
Reference
-
1. Nelson SP, Chen EH, Syniar GM, Christoffel KK. Prevalence of symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux during childhood: a pediatric practice-based survey. Pediatric practice research group. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2000; 154:150–154.
Article2. Howard PJ, Maher L, Pryde A, Heading RC. Symptomatic gastro-oesophageal reflux, abnormal oesophageal acid exposure, and mucosal acid sensitivity are three separate, though related, aspects of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Gut. 1991; 32:128–132.
Article3. Gremse DA. GERD in the pediatric patient: management considerations. MedGenMed. 2004; 6:13.4. Waring JP, Feiler MJ, Hunter JG, Smith CD, Gold BD. Childhood gastroesophageal reflux symptoms in adult patients. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002; 35:334–338.
Article5. Rudolph CD, Mazur LJ, Liptak GS, Baker RD, Boyle JT, Colletti RB, et al. Guidelines for evaluation and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in infants and children: recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2001; 32:Suppl 2. S1–S31.6. Jung HK. Epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease in Asia: a systematic review. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011; 17:14–27.
Article7. Fock KM, Talley NJ, Fass R, Goh KL, Katelaris P, Hunt R, et al. Asia-pacific consensus on the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease: update. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:8–22.
Article8. Murao T, Sakurai K, Mihara S, Marubayashi T, Murakami Y, Sasaki Y. Lifestyle change influences on GERD in Japan: a study of participants in a health examination program. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56:2857–2864.
Article9. Matsuzaki J, Suzuki H, Kobayakawa M, Inadomi JM, Takayama M, Makino K, et al. Association of visceral fat area, smoking, and alcohol consumption with reflux esophagitis and Barrett's esophagus in Japan. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0133865.
Article10. Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, Blum AL, Armstrong D, Galmiche JP, et al. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut. 1999; 45:172–180.
Article11. Park KY, Chang SH. Gastro-esophageal reflux disease in healthy older children and adolescents. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2012; 15:220–228.
Article12. Seo JK, Chi JG, Kim EC. Gastrofibersoscopic findings and Helicobacter-pylori gastritis in children with recurrent abdominal pain. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1992; 35:1646–1656.13. Kwon HJ, Yi DY, Ryoo E, Cho KH, Son DW, Tcha H. Prevalence and risk factors associated with esophagitis in children with abdominal pain. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008; 11:103–109.
Article14. Rey E, Elola-Olaso CM, Rodríguez-Artalejo F, Locke GR 3rd, Díaz-Rubio M. Prevalence of atypical symptoms and their association with typical symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux in Spain. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 18:969–975.
Article15. Ou JL, Tu CC, Hsu PI, Pan MH, Lee CC, Tsay FW, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of erosive esophagitis in Taiwan. J Chin Med Assoc. 2012; 75:60–64.
Article16. Gilger MA, El-Serag HB, Gold BD, Dietrich CL, Tsou V, McDuffie A, et al. Prevalence of endoscopic findings of erosive esophagitis in children: a population-based study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008; 47:141–146.
Article17. Amano K, Adachi K, Katsube T, Watanabe M, Kinoshita Y. Role of hiatus hernia and gastric mucosal atrophy in the development of reflux esophagitis in the elderly. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001; 16:132–136.
Article18. Shimazu T, Matsui T, Furukawa K, Oshige K, Mitsuyasu T, Kiyomizu A, et al. A prospective study of the prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease and confounding factors. J Gastroenterol. 2005; 40:866–872.
Article19. Mishima I, Adachi K, Arima N, Amano K, Takashima T, Moritani M, et al. Prevalence of endoscopically negative and positive gastroesophageal reflux disease in the Japanese. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2005; 40:1005–1009.
Article20. Kinoshita Y, Kawanami C, Kishi K, Nakata H, Seino Y, Chiba T. Helicobacter pylori independent chronological change in gastric acid secretion in the Japanese. Gut. 1997; 41:452–458.
Article21. Matsuura B, Nunoi H, Miyake T, Hiasa Y, Onji M. Obesity and gastrointestinal liver disorders in Japan. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 28:Suppl 4. 48–53.
Article22. Marcon MA. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Curr Opin Pediatr. 1997; 9:490–493.
Article23. Krug E, Bergmeijer JH, Dees J, de Krijger R, Mooi WJ, Hazebroek FW. Gastroesophageal reflux and Barrett's esophagus in adults born with esophageal atresia. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999; 94:2825–2828.
Article24. Taylor LA, Weiner T, Lacey SR, Azizkhan RG. Chronic lung disease is the leading risk factor correlating with the failure (wrap disruption) of antireflux procedures in children. J Pediatr Surg. 1994; 29:161–164. discussion 164-6.
Article25. Gilger MA. Pediatric otolaryngologic manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2003; 5:247–252.
Article26. El-Serag HB, Graham DY, Satia JA, Rabeneck L. Obesity is an independent risk factor for GERD symptoms and erosive esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:1243–1250.
Article27. Fujiwara Y, Higuchi K, Shiba M, Yamamori K, Watanabe Y, Sasaki E, et al. Differences in clinical characteristics between patients with endoscopy-negative reflux disease and erosive esophagitis in Japan. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:754–758.
Article28. Du J, Liu J, Zhang H, Yu CH, Li YM. Risk factors for gastroesophageal reflux disease, reflux esophagitis and non-erosive reflux disease among Chinese patients undergoing upper gastrointestinal endoscopic examination. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13:6009–6015.
Article29. Elitsur Y, Dementieva Y, Elitsur R, Rewalt M. Obesity is not a risk factor in children with reflux esophagitis: a retrospective analysis of 738 children. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2009; 7:211–214.
Article30. Maekawa T, Kinoshita Y, Okada A, Fukui H, Waki S, Hassan S, et al. Relationship between severity and symptoms of reflux oesophagitis in elderly patients in Japan. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998; 13:927–930.
Article31. Grande L, Lacima G, Ros E, Pera M, Ascaso C, Visa J, et al. Deterioration of esophageal motility with age: a manometric study of 79 healthy subjects. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999; 94:1795–1801.
Article32. Deprez P, Fiasse R. Healing of severe esophagitis improves esophageal peristaltic dysfunction. Dig Dis Sci. 1999; 44:125–133.33. Ma XQ, Cao Y, Wang R, Yan X, Zhao Y, Zou D, et al. Prevalence of, and factors associated with, gastroesophageal reflux disease: a population-based study in Shanghai, China. Dis Esophagus. 2009; 22:317–322.
Article34. Ford AC, Forman D, Reynolds PD, Cooper BT, Moayyedi P. Ethnicity, gender, and socioeconomic status as risk factors for esophagitis and Barrett's esophagus. Am J Epidemiol. 2005; 162:454–460.
Article35. de Belmont Hollingshead A. Four factor index of social status. New Haven, CT: Yale University;1975.36. Yim SH. Geographical features of social polarization in Seoul, South Korea. In : Mizuuchi T, editor. Representing local places and raising voices from below. Osaka: Osaka City University;2003. p. 31–40.37. Kim KH. Housing and the Korean economy. J Hous Econ. 2004; 13:321–341.
Article38. Song EM, Jung HK, Jung JM. The association between reflux esophagitis and psychosocial stress. Dig Dis Sci. 2013; 58:471–477.
Article39. Lee SP, Sung IK, Kim JH, Lee SY, Park HS, Shim CS. The effect of emotional stress and depression on the prevalence of digestive diseases. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015; 21:273–282.
Article40. Treem WR, Davis PM, Hyams JS. Gastroesophageal reflux in the older child: presentation, response to treatment and long-term follow-up. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1991; 30:435–440.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence and clinical characteristics of gastroesophageal reflux disease and reflux esophagitis in chuncheon city-Health care examination study
- The prevalence and associated factors of reflux esophagitis in routine check-up subjects
- Gastroesophageal Reflux in Peptic Ulcer Patients
- Prevalence Alteration of Reflux Esophagitis in Recent Years
- Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Noncardiac Chest Pain with Reflux Esophagitis in Korea