Clin Endosc.
2017 Jan;50(1):17-20. 10.5946/ce.2017.022.
Role of Restrictive Endoscopic Procedures in Obesity Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. alwayshang@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2383485
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.022
Abstract
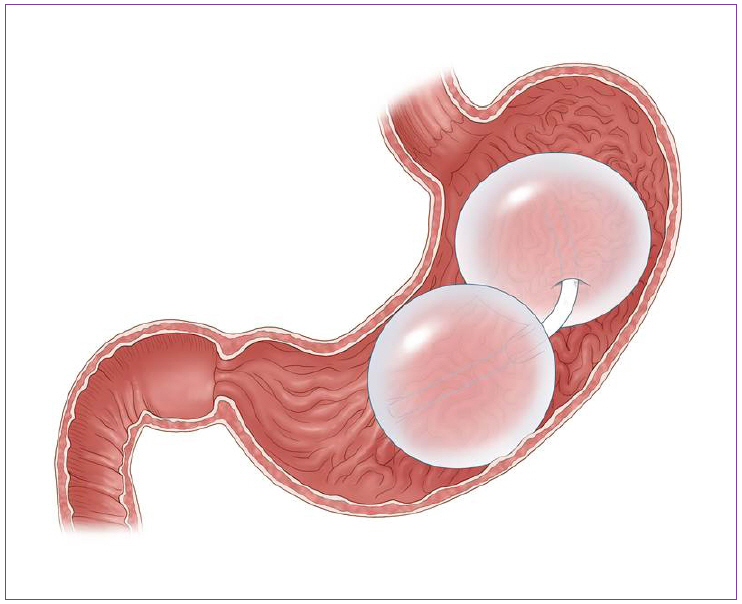
- It is well recognized that obesity is a big problem and it can induce large economic burden. Obesity affects about 40% people in the America alone and obesity also is the worldwide problem, with about 400 million obese adults. Moreover, another problem of obesity is the increasing prevalence of overweight children. Though bariatric surgery remains the gold treatment modality in the obesity treatment, endoluminal approaches may have the meaningful role for weight control. Endoscopists should have a role in the management of obesity because endoluminal therapies demonstrate their safety and efficacy over the coming years. Endoluminal therapies can be summarized by above methods: space occupying, malabsorption method, and reduction of gastric volume. In this review, we will introduce various restrictive endoscopic procedures in obesity treatment.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
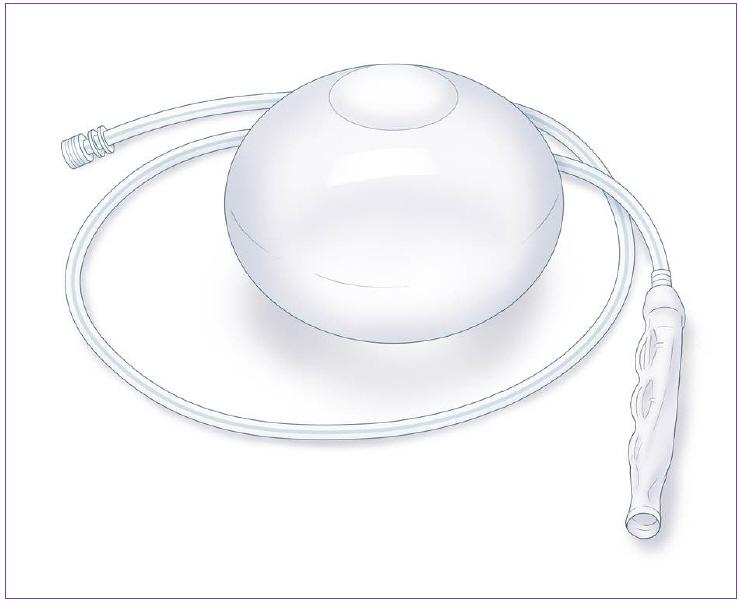
Currently Available Non-Balloon Devices
Hang Lak Lee
Clin Endosc. 2018;51(5):416-419. doi: 10.5946/ce.2018.143.
Reference
-
1. Ramhamadany EM, Fowler J, Baird IM. Effect of the gastric balloon versus sham procedure on weight loss in obese subjects. Gut. 1989; 30:1054–1057.
Article2. Hogan RB, Johnston JH, Long BW, et al. A double-blind, randomized, sham-controlled trial of the gastric bubble for obesity. Gastrointest Endosc. 1989; 35:381–385.
Article3. Meshkinpour H, Hsu D, Farivar S. Effect of gastric bubble as a weight reduction device: a controlled, crossover study. Gastroenterology. 1988; 95:589–592.
Article4. Benjamin SB, Maher KA, Cattau EL Jr, et al. Double-blind controlled trial of the Garren-Edwards gastric bubble: an adjunctive treatment for exogenous obesity. Gastroenterology. 1988; 95:581–588.
Article5. McFarland RJ, Grundy A, Gazet JC, Pilkington TR. The intragastric balloon: a novel idea proved ineffective. Br J Surg. 1987; 74:137–139.
Article6. Nieben OG, Harboe H. Intragastric balloon as an artificial bezoar for treatment of obesity. Lancet. 1982; 1:198–199.7. Genco A, Bruni T, Doldi SB, et al. BioEnterics intragastric balloon: the Italian experience with 2,515 patients. Obes Surg. 2005; 15:1161–1164.
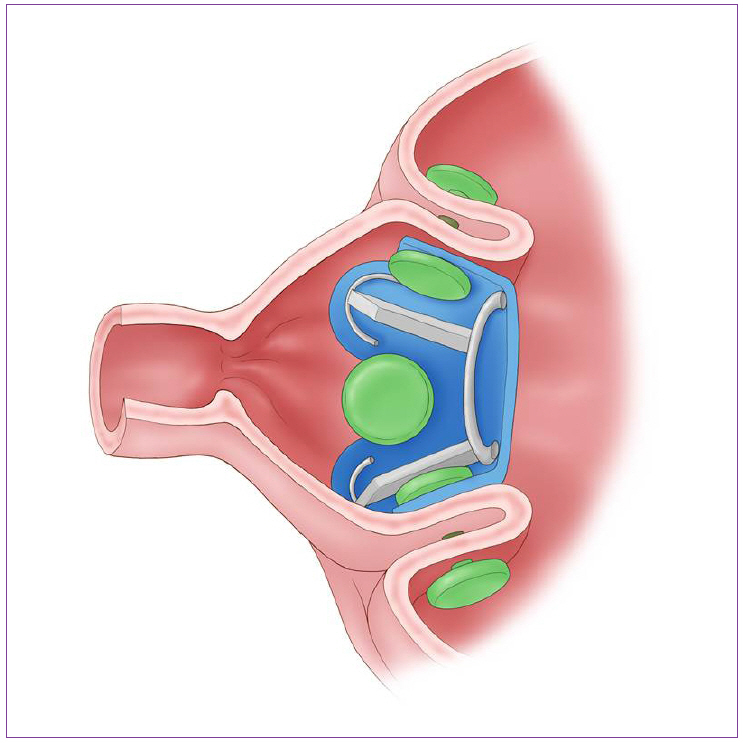
Article8. ReShape Medical Inc. Reshape intragastric balloon for the treatment of obesity (Italy III) [Internet]. Bethesda: ClinicalTrials.gov;c2009 [updated 2015 Sep 10; cited 2010 Apr 11]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01024465.9. Talarico JA, Brethauer SA, Schauer PR. Primary endoluminal techniques for weight loss. In : Thompson CC, Ryan MB, editors. Bariatric endoscopy. New York: Springer;2013. p. 195–204.10. Biertho L, Hould FS, Lebel S, Biron S. Transoral endoscopic restrictive implant system: a new endoscopic technique for the treatment of obesity. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2010; 6:203–205.
Article