Korean J Health Promot.
2016 Sep;16(3):203-213. 10.15384/kjhp.2016.16.3.203.
A Qualitative Study of Antibiotic Prescribing Decision of Physicians and Strategy of Antibiotics Prescription
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Research, Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service, Wonju, Korea. sttone@hira.or.kr
- KMID: 2354624
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15384/kjhp.2016.16.3.203
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
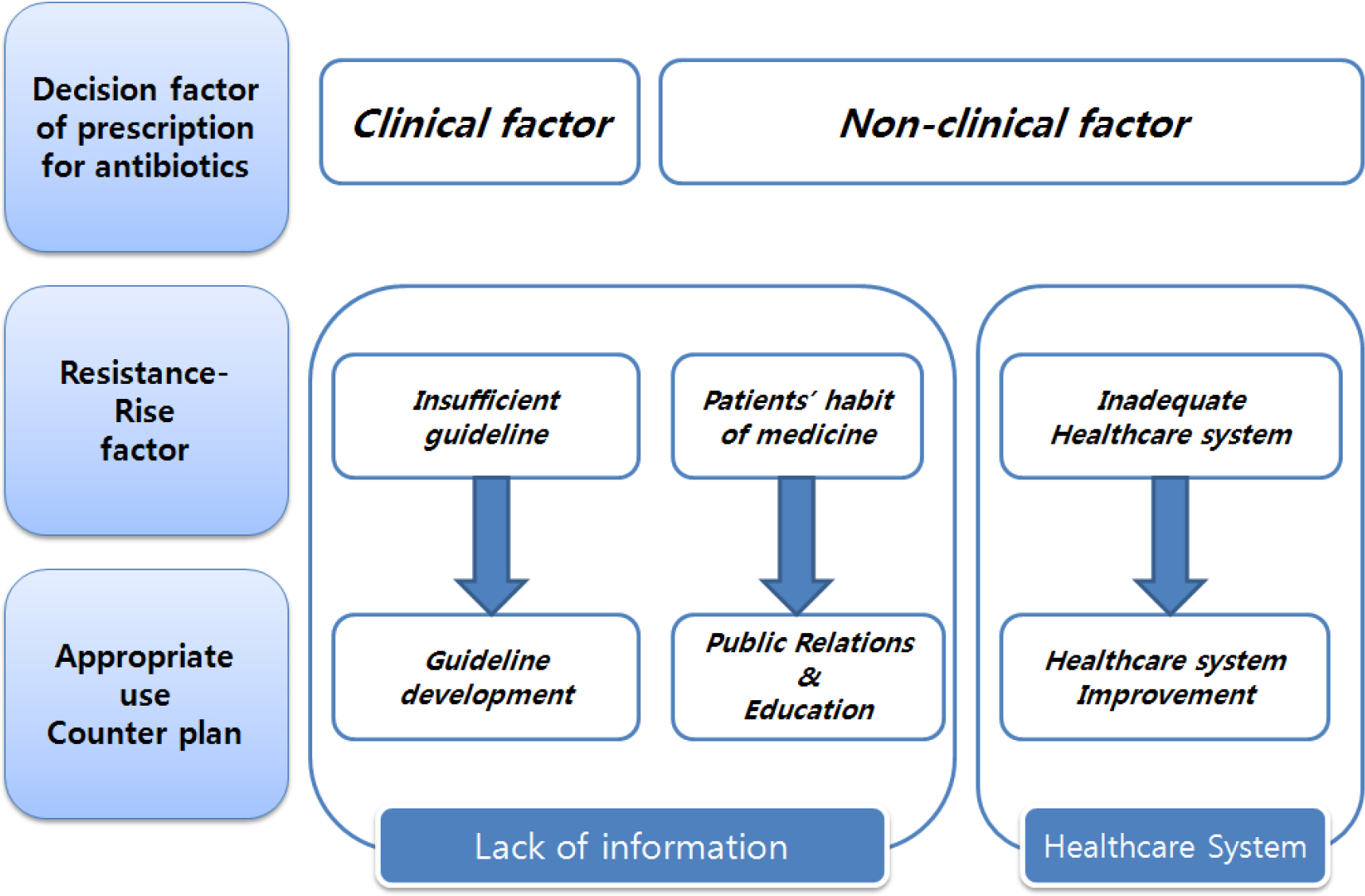
Korea has high prescribing rate and rising antibiotic resistance. This study was conducted to understand why primary physicians prescribe antibiotics for acute respiratory infections and to explore the factors that influence antibiotic resistance, and so to suggest strategy to reduce antibiotic resistance.
METHODS
A qualitative exploratory approach was used using 4 focus groups composed of physicians from different area. A semi-structured guide was applied in obtaining the physicians' opinions. Common themes were extracted by authors, which were used to gather results and draw conclusion.
RESULTS
Participants acknowledged multiple factors such as clinical factor and competitive environment are involved in physicians' decision of antibiotic prescribing. They identified that causes of rising antibiotic resistance were shortage of information, discontinuation of taking antibiotics, and other system factors.
CONCLUSION
Participants were certain that less prescribing antibiotics and selecting appropriate antibiotics might be method to reduce antibiotic resistance. To change the prescribing behavior, it should be provided periodically for community physicians with prescribing information and specific guidelines for antibiotics resistance. Patients should be also noticed about antibiotic medication information more accurately. Including prescription incentive policy, improvement of healthcare system will be carried out at the same time.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Analysis of factors affecting antibiotic use at hospitals and clinics based on the defined daily dose
Eun Jee Lee, GeunWoo Lee, Juhee Park, Dong-Sook Kim, Hyeong Sik Ahn
J Korean Med Assoc. 2018;61(11):687-698. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2018.61.11.687.
Reference
-
References
1. World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance Global Report on Surveillance 2014. Geneva: World Health Organization;2014.2. McCaig LF, Besses RE, Hughes JM. Antimicrobial drug prescription in ambulatory care settings, United States, 1992–2000. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003; 9(4):432–7.3. McCaig LF, Hughes JM. Trends in antimicrobial drug prescribing among office-based physicians in the United States. JAMA. 1995; 273(3):214–9.
Article4. Center for Disease Prevention and Control. National Diabetes Fact Sheet [Internet]. Atlanta: Center for Disease Prevention and Control;2005. [Accessed September 26, 2016]. Available from:. http://www.cdc.gov/media/pressrel/2007/r071016.htm.5. Song JH, Joo EJ. The crisis of antimicrobial resistance: current st atus and future strategies. Korean Med Assoc. 2010; 53(11):999–1005.6. Bronzwaer SL, Cars O, Buchholz U, Mölstad S, Goettsch W, Veldhuijzen IK, et al. A European study on the relationship between antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002; 8(3):278–82.7. Goossens H, Ferech M, Vander Stichele R, Elseviers M. ESAC Project Group. Outpatient antibiotic use in Europe and association with resistance: a cross-national database study. Lancet. 2005; 365(9459):579–87.
Article8. Ministry of Health and Welfare. National Antibiotics Resistance Management Counterplan 2016∼2020 [Internet]. Sejong: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2016. [Accessed August 11, 2016]. Available from:. http://www.motie.go.kr/common/download. do?fid=bbs&bbs_cd_n=81&bbs_seq_n=158481&file_seq_n=1.9. Kim DS, Bae G, Lee HS, Kim HY, Kim SK, Um JS, et al. The study on evaluation of antibiotics use in outpatients with respiratory diseases. Wonju: Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service;2010.10. Tan T, Little P, Strokes T. Guideline Development Group. Antibiotic prescribing for self limiting respiratory tract infection in primary care: summary of NICE guidance. BMJ. 2008; 337:a437.11. Kuyvenhoven MM, van Balen FA, Verheij TJ. Outpatient antibiotic prescriptions from 1992 to 2001 in the Netherlands. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003; 52(4):675–8.12. Seo OK. Inappropriate use of antimnicrobial agents in Korea and practical guidelines for its improvement. J Korean Soc Chemother. 1997; 15(2):201–3.13. Cars O, Mölstad S, Melander A. Variation in antibiotic use in the European Union. Lancet. 2001; 357(9271):1851–3.
Article14. Brookes-Howell L, Hood K, Cooper L, Little P, Verheij T, Coenen S, et al. Understanding variation in primary medical care: a nine-country qualitative study of clinicians' accounts of the nonclinical factors that shape antibiotic prescribing decisions for lower respiratory tract infection. BMJ Open. 2012; 2(4):). pii: e000796.
Article15. Barden LS, Dowell SF, Schwartz B, Lackey C. Current attitudes regarding use of antimicrobial agents: results from physician's and paren's focus groups discussions. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1998; 37(11):665–71.16. Trepka MJ, Belongia EA, Chyou PH, Davis JP, Schwartz B. The effect of a community intervention trial on parental knowledge and awareness of antibiotic resistance and appropriate antibiotic use in children. Pediatrics. 2001; 107(1):): E6.17. Mangione-Smith. R, McGlynn EA, Elliott MN, McDonald L, Franz CE, Kravitz RL. Parental expectations for antibiotic, physician-parent communication, and satisfaction. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001; 155(7):800–6.18. Kim NS, Kim DS, Jeoung HJ, Kim CK, Kim MJ, Um JS, et al. Analysis and evaluation of antibiotics use. Wonju: Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service;2006.19. Kang MA, Son JY, Kim HJ. An exploratory application of the mixed methods research: application of surveys and focus group interviews for regional public health issue decision making. J Korean Public Admin. 2007; 41(4):415–37.20. Morgan DL. Successful Focus Groups: Advancing the State of the Art. 1st ed.Thousand Oaks (CA): SAGE Publications, Inc.;1993.21. Krueger RA, Casey MA. Focus Groups: A Practical Guide for Applied Research. 4th ed.Thousand Oaks (CA): SAGE Publications, Inc.;2009.22. Lewis M. Focus group interviews in qualitative research: are-view of the literature [Internet]. NSW: The University of Sydney;2000. [Accessed September 26, 2016]. Available from:. http://www.aral.com.au/arow/rlewis.html.23. Coenen S, Van Royen P, Michiels B, Denekens J. Optimizing antibiotic prescribing for acute cough in general practice: a cluster-randomized controlled trial. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004; 54:661–72.
Article24. Jang SN, Kim NS. Understanding the culture of antibiotics prescribing of primary physicians for acute upper respiratory infection. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2004; 25(12):901–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Understanding the Culture of Antibiotics Prescribing of Primary Physicians for Acute Upper Respiratory Infection
- Factors Influencing Antibiotics Prescribing of Primary Health Physicians in Acute Upper Respiratory Infections
- Factors influencing decision making and antibiotic prescribing patterns for the treatment of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) among non-infectious physicians in Thailand: a qualitative study
- Outpatient Antibiotic Prescription Patterns for Respiratory Tract Infections of Infants
- Factors Affecting the Prescribing Patterns of Antibiotics and Injections