Yonsei Med J.
2015 Nov;56(6):1694-1702. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1694.
Community Integration and Quality of Life in Aphasia after Stroke
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. rmpyun@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, National Rehabilitation Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2345902
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1694
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To examine community integration and contributing factors in people with aphasia (PWA) following stroke and to investigate the relationship between community integration and quality of life (QOL).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty PWA and 42 age-and education-matched control subjects were involved. Main variables were as follows: socioeconomic status, mobility, and activity of daily living (ADL) (Modified Barthel Index), language function [Frenchay Aphasia Screening Test (FAST)], depression [Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS)], Community Integration Questionnaire (CIQ) and Stroke and Aphasia Quality of Life Scale-39 (SAQOL-39). Differences between aphasia and control groups and factors affecting community integration and QOL were analyzed.
RESULTS
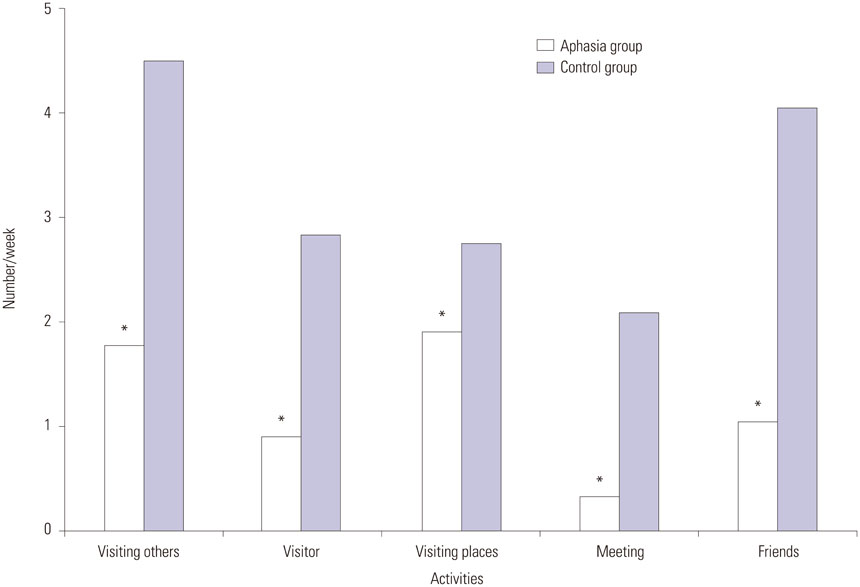
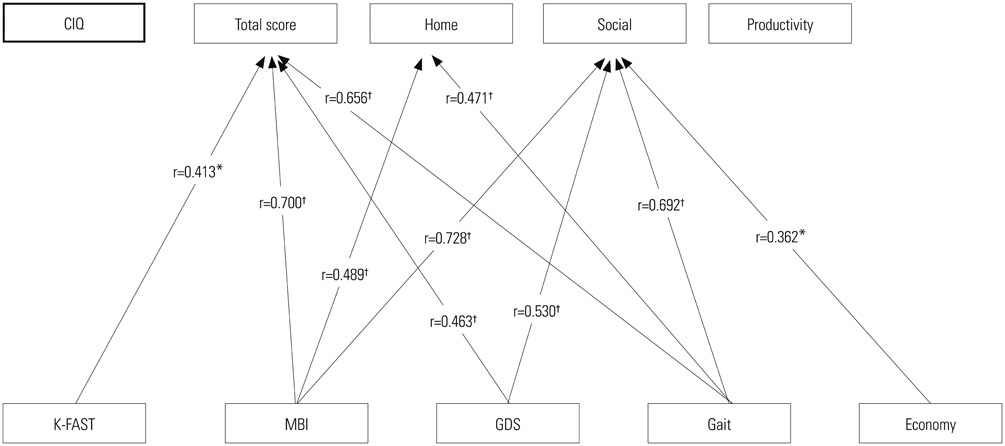
Home and social integration and productive activity were significantly decreased in the aphasia group compared to the control group; 8.5 and 18.3 points in total CIQ score, respectively. Amount of time spent outside the home and frequency of social contact were also significantly reduced in the aphasia group. Total mean score on the SAQOL-39 was 2.75+/-0.80 points and was significantly correlated with economic status, gait performance, ADL, depressive mood, and social domain score on the CIQ. Depression score measured by GDS was the single most important factor for the prediction of QOL, but the FAST score was significantly correlated only with the communication domain of the SAQOL-39.
CONCLUSION
Community activities of PWA were very limited, and depression was highly associated with decreased community integration and QOL. Enhancing social participation and reducing emotional distress should be emphasized for rehabilitation of PWA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Activities of Daily Living
Adult
Aged
Aphasia/etiology/*psychology/rehabilitation
Case-Control Studies
Community Integration/*psychology
Depression/psychology
Female
Humans
*Interpersonal Relations
Male
Middle Aged
Psychiatric Status Rating Scales
*Quality of Life
Residence Characteristics
Sickness Impact Profile
Social Behavior
Socioeconomic Factors
Stroke/complications/psychology/*rehabilitation
Surveys and Questionnaires
Figure
Reference
-
1. Niemi ML, Laaksonen R, Kotila M, Waltimo O. Quality of life 4 years after stroke. Stroke. 1988; 19:1101–1107.2. Daniel K, Wolfe CD, Busch MA, McKevitt C. What are the social consequences of stroke for working-aged adults? A systematic review. Stroke. 2009; 40:e431–e440.3. Yoon TH, Han SJ, Yoon TS, Kim JS, Yi TI. Therapeutic effect of repetitive magnetic stimulation combined with speech and language therapy in post-stroke non-fluent aphasia. NeuroRehabilitation. 2015; 36:107–114.
Article4. Pedersen PM, Jørgensen HS, Nakayama H, Raaschou HO, Olsen TS. Aphasia in acute stroke: incidence, determinants, and recovery. Ann Neurol. 1995; 38:659–666.
Article5. Wade DT, Hewer RL, David RM, Enderby PM. Aphasia after stroke: natural history and associated deficits. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986; 49:11–16.
Article6. Hemsley G, Code C. Interactions between recovery in aphasia, emotional and psychosocial factors in subjects with aphasia, their significant others and speech pathologists. Disabil Rehabil. 1996; 18:567–584.
Article7. Cahana-Amitay D, Albert ML, Pyun SB, Westwood A, Jenkins T, Wolford S, et al. Language as a Stressor in Aphasia. Aphasiology. 2011; 25:593–614.
Article8. Pyun SB, Kim SH, Hahn MS, Kwon HK, Lee HJ. Quality of life after stroke. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1999; 23:233–239.9. Thomas SA, Lincoln NB. Predictors of emotional distress after stroke. Stroke. 2008; 39:1240–1245.
Article10. Northcott S, Hilari K. Why do people lose their friends after a stroke? Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2011; 46:524–534.
Article11. Simmons-Mackie N, Kagan A. Application of the ICF in aphasia. Semin Speech Lang. 2007; 28:244–253.
Article12. Hilari K, Byng S, Lamping DL, Smith SC. Stroke and Aphasia Quality of Life Scale-39 (SAQOL-39): evaluation of acceptability, reliability, and validity. Stroke. 2003; 34:1944–1950.13. Worrall LE, Holland AL. Editorial: Quality of life in aphasia. Aphasiology. 2003; 17:329–332.
Article14. Cruice M, Worrall L, Hickson L, Murison R. Finding a focus for quality of life with aphasia: social and emotional health, and psychological well-being. Aphasiology. 2003; 17:333–353.
Article15. Code C. The quantity of life for people with chronic aphasia. Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2003; 13:379–390.
Article16. Dalemans RJ, De Witte LP, Beurskens AJ, Van Den Heuvel WJ, Wade DT. An investigation into the social participation of stroke survivors with aphasia. Disabil Rehabil. 2010; 32:1678–1685.
Article17. Ignatiou M, Christaki V, Chelas EN, Efstratiadou EA, Hilari K. Agreement between people with aphasia and their proxies on health-related quality of life after stroke, using the Greek SAQOL-39g. Psychology. 2012; 3:686–690.
Article18. Pyun SB, Hwang YM, Ha JW, Yi H, Park KW, Nam K. Standardization of Korean Version of Frenchay Aphasia Screening Test in normal adults. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2009; 33:436–440.19. Salter K, Jutai J, Foley N, Hellings C, Teasell R. Identification of aphasia post stroke: a review of screening assessment tools. Brain Inj. 2006; 20:559–568.
Article20. Gillen R, Tennen H, McKee TE, Gernert-Dott P, Affleck G. Depressive symptoms and history of depression predict rehabilitation efficiency in stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001; 82:1645–1649.
Article21. Carod-Artal FJ, Ferreira Coral L, Trizotto DS, Menezes Moreira C. Poststroke depression: prevalence and determinants in Brazilian stroke patients. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009; 28:157–165.
Article22. Hosomi A, Nagakane Y, Yamada K, Kuriyama N, Mizuno T, Nishimura T, et al. Assessment of arcuate fasciculus with diffusion-tensor tractography may predict the prognosis of aphasia in patients with left middle cerebral artery infarcts. Neuroradiology. 2009; 51:549–555.
Article23. Dalemans RJ, de Witte LP, Beurskens AJ, van den Heuvel WJ, Wade DT. Psychometric properties of the community integration questionnaire adjusted for people with aphasia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010; 91:395–399.
Article24. Hinckley JJ, Packard ME. Family education seminars and social functioning of adults with chronic aphasia. J Commun Disord. 2001; 34:241–254.
Article25. Dalemans R, de Witte LP, Lemmens J, van den Heuvel WJ, Wade DT. Measures for rating social participation in people with aphasia: a systematic review. Clin Rehabil. 2008; 22:542–555.
Article26. Dalemans RJ, de Witte L, Wade D, van den Heuvel W. Social participation through the eyes of people with aphasia. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2010; 45:537–550.
Article27. Labi ML, Phillips TF, Greshman GE. Psychosocial disability in physically restored long-term stroke survivors. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1980; 61:561–565.28. Treger I, Shames J, Giaquinto S, Ring H. Return to work in stroke patients. Disabil Rehabil. 2007; 29:1397–1403.
Article29. Wozniak MA, Kittner SJ. Return to work after ischemic stroke: a methodological review. Neuroepidemiology. 2002; 21:159–166.
Article30. Hinckley JJ. Investigating the predictors of lifestyle satisfaction among younger adults with chronic aphasia. Aphasiology. 1998; 12:509–518.
Article31. van Velzen JM, van Bennekom CA, Edelaar MJ, Sluiter JK, Frings-Dresen MH. How many people return to work after acquired brain injury?: a systematic review. Brain Inj. 2009; 23:473–488.
Article32. Hilari K, Needle JJ, Harrison KL. What are the important factors in health-related quality of life for people with aphasia? A systematic review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012; 93:1 Suppl. S86–S95.
Article33. Code C, Hemsley G, Herrmann M. The emotional impact of aphasia. Semin Speech Lang. 1999; 20:19–31.
Article34. Tateno A, Kimura M, Robinson RG. Phenomenological characteristics of poststroke depression: early-versus late-onset. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2002; 10:575–582.
Article35. Cruice M, Worrall L, Hickson L. Reporting on psychological well-being of older adults with chronic aphasia in the context of unaffected peers. Disabil Rehabil. 2011; 33:219–228.
Article36. Code C, Herrmann M. The relevance of emotional and psychosocial factors in aphasia to rehabilitation. Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2003; 13:109–132.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Evidence for Post Stroke Aphasia Treatment
- Why Is It Difficult to Predict Language Impairment and Outcome in Patients with Aphasia after Stroke?
- Subcortical Aphasia in Stroke Patients
- Prolonged Ictal Aphasia Presenting as Clinical-Diffusion Mismatch in a Patient with Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Characteristics of Cognitive Impairment in Patients With Post-stroke Aphasia